FIGURE 12.1 The purely competitive seller's demand for a resource. The MRP curve is the resource demand curve; each of its points relates a particular resource price (= MRP when profit is maximized) with a corresponding quantity of the resource demanded. Under pure competition, product price is constant; therefore, the downward slope of the D = MRP curve is due solely to the decline in the resource's marginal product (law of diminishing marginal returns). P $14 12 10 8 4 2 D = MRP 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 Quantity of resource demanded Resource price (wage rate) 6. TABLE 12.1 The Demand for Labor: Pure Competition in the Sale of the Product (6) Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) (1) (2) Total Product (3) Marginal Product (MP) (4) Product (5) Total Revenue, Units of Resource (Output) Price (2) x (4) $2 $ 0 -7 $14 2 6 12 13- 18 2 26 -5 10 3 36 -4 4 22 2 44 3 5 25 2 50 -2 4 2 54 2 28 56 2. 67
FIGURE 12.1 The purely competitive seller's demand for a resource. The MRP curve is the resource demand curve; each of its points relates a particular resource price (= MRP when profit is maximized) with a corresponding quantity of the resource demanded. Under pure competition, product price is constant; therefore, the downward slope of the D = MRP curve is due solely to the decline in the resource's marginal product (law of diminishing marginal returns). P $14 12 10 8 4 2 D = MRP 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 Quantity of resource demanded Resource price (wage rate) 6. TABLE 12.1 The Demand for Labor: Pure Competition in the Sale of the Product (6) Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) (1) (2) Total Product (3) Marginal Product (MP) (4) Product (5) Total Revenue, Units of Resource (Output) Price (2) x (4) $2 $ 0 -7 $14 2 6 12 13- 18 2 26 -5 10 3 36 -4 4 22 2 44 3 5 25 2 50 -2 4 2 54 2 28 56 2. 67
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter8: Perfect Competition
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6SCQ: A firms marginal cost curve above the average variable cost curve is equal to the films individual...
Related questions
Question
Suppose that marginal product tripled while product
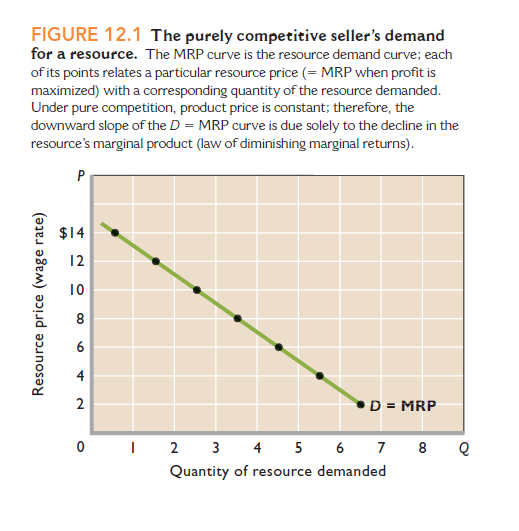
Transcribed Image Text:FIGURE 12.1 The purely competitive seller's demand
for a resource. The MRP curve is the resource demand curve; each
of its points relates a particular resource price (= MRP when profit is
maximized) with a corresponding quantity of the resource demanded.
Under pure competition, product price is constant; therefore, the
downward slope of the D = MRP curve is due solely to the decline in the
resource's marginal product (law of diminishing marginal returns).
P
$14
12
10
8
4
2
D = MRP
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2
Quantity of resource demanded
Resource price (wage rate)
6.
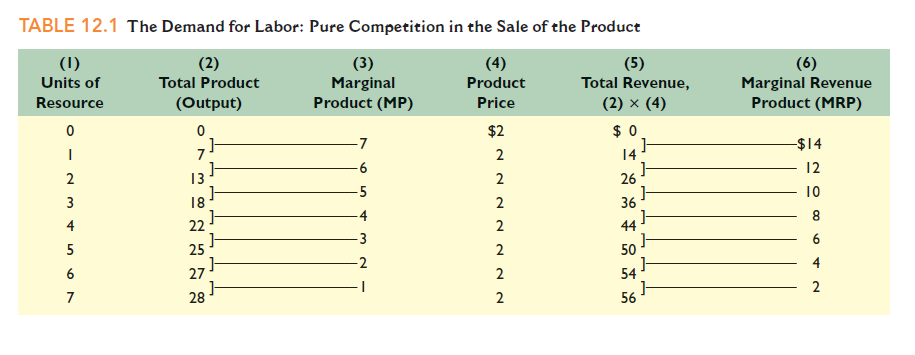
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 12.1 The Demand for Labor: Pure Competition in the Sale of the Product
(6)
Marginal Revenue
Product (MRP)
(1)
(2)
Total Product
(3)
Marginal
Product (MP)
(4)
Product
(5)
Total Revenue,
Units of
Resource
(Output)
Price
(2) x (4)
$2
$ 0
-7
$14
2
6
12
13-
18
2
26
-5
10
3
36
-4
4
22
2
44
3
5
25
2
50
-2
4
2
54
2
28
56
2.
67
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax
