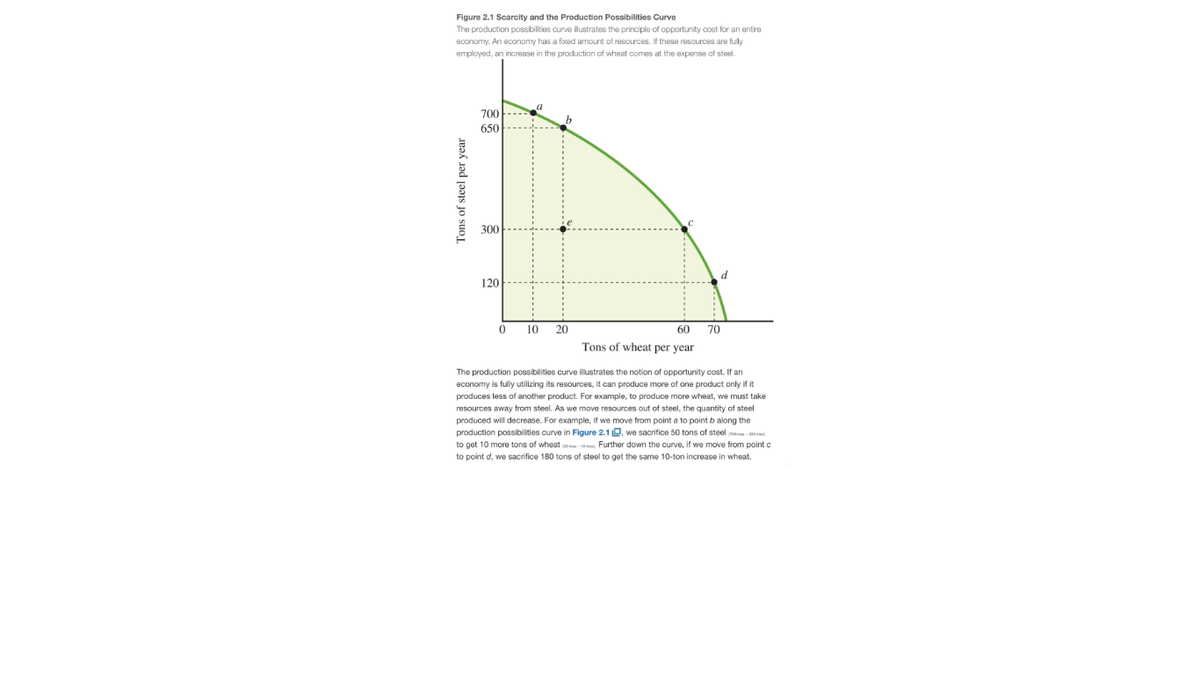
Figure 2.1 Scarcity and the Production Possibilities Curve The production possibilities curve illustrates the principle of opportunity cost for an entire economy. An economy has a fixed amount of resources. If these resources are fully employed, an increase in the production of wheat comes at the expense of steel. 700 650 300 120 10 20 60 70 Tons of wheat per year The production possibilities curve illustrates the notion of opportunity cost. If an economy is fully utilizing its resources, it can produce more of one product only if it produces less of another product. For example, to produce more wheat, we must take resources away from steel. we move resources out of steel, the quantity of steel produced will decrease. For example, if we move from point a to point b along the production possibilities curve in Figure 2.1 O, we sacrifice 50 tons of steel o- to get 10 more tons of wheat - Further down the curve, if we move from point c to point d, we sacrifice 180 tons of steel to get the same 10-ton increase in wheat. Tons of steel per year
Figure 2.1 Scarcity and the Production Possibilities Curve The production possibilities curve illustrates the principle of opportunity cost for an entire economy. An economy has a fixed amount of resources. If these resources are fully employed, an increase in the production of wheat comes at the expense of steel. 700 650 300 120 10 20 60 70 Tons of wheat per year The production possibilities curve illustrates the notion of opportunity cost. If an economy is fully utilizing its resources, it can produce more of one product only if it produces less of another product. For example, to produce more wheat, we must take resources away from steel. we move resources out of steel, the quantity of steel produced will decrease. For example, if we move from point a to point b along the production possibilities curve in Figure 2.1 O, we sacrifice 50 tons of steel o- to get 10 more tons of wheat - Further down the curve, if we move from point c to point d, we sacrifice 180 tons of steel to get the same 10-ton increase in wheat. Tons of steel per year
Chapter2: Productions Possibilities, Opportunity Costs, And Economic Growth
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6SQP
Related questions
Question
The Principle of
- Apply the principle of opportunity cost.
- 1.1 Consider Figure 2.1 on page 30. Between points c and d, the opportunity cost of...............tons of wheat is.................tons of steel.
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 2.1 Scarcity and the Production Possibilities Curve
The production possibilities curve illustrates the principle of opportunity cost for an entire
economy. An economy has a fixed amount of resources. If these resources are fully
employed, an increase in the production of wheat comes at the expense of steel.
700
650
300
120
10
20
60
70
Tons of wheat per year
The production possibilities curve illustrates the notion of opportunity cost. If an
economy is fully utilizing its resources, it can produce more of one product only if it
produces less of another product. For example, to produce more wheat, we must take
resources away from steel.
we move resources out of steel, the quantity of steel
produced will decrease. For example, if we move from point a to point b along the
production possibilities curve in Figure 2.1 O, we sacrifice 50 tons of steel o-
to get 10 more tons of wheat - Further down the curve, if we move from point c
to point d, we sacrifice 180 tons of steel to get the same 10-ton increase in wheat.
Tons of steel per year
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you







Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
