FIGURE 28.7 Recessionary and inflationary expenditure gaps. The equilibrium and full-employment GDPS may not coincide. (a) A recessionary expenditure gap is the amount by which aggregate expenditures at the full-employment GDP fall short of those needed to achieve the full-employment GDP Here, the $5 billion recessionary expenditure gap causes a $20 billion negative GDP gap. (b) An iflationary expenditure gap is the amount by which aggregate expenditures at the full-employment GDP exceed those just sufficient to achieve the full-employment GDP. Here, the inflationary expenditure gap is $5 billion; this overspending produces demand-pull inflation. AE2 AE, AEo 530 AET 530 510 510 Recessionary expenditure gap = $5 billion Inflationary expenditure gap = $5 billion 490 490 Full Full 45° employment 45° employment 490 510 530 490 510 530 Real GDP Real GDP (а) Recessionary expenditure gap (b) Inflationary expenditure gap Aggregate expenditures (billio ns of dollars) Aggregate expenditures (billions of dollars)
FIGURE 28.7 Recessionary and inflationary expenditure gaps. The equilibrium and full-employment GDPS may not coincide. (a) A recessionary expenditure gap is the amount by which aggregate expenditures at the full-employment GDP fall short of those needed to achieve the full-employment GDP Here, the $5 billion recessionary expenditure gap causes a $20 billion negative GDP gap. (b) An iflationary expenditure gap is the amount by which aggregate expenditures at the full-employment GDP exceed those just sufficient to achieve the full-employment GDP. Here, the inflationary expenditure gap is $5 billion; this overspending produces demand-pull inflation. AE2 AE, AEo 530 AET 530 510 510 Recessionary expenditure gap = $5 billion Inflationary expenditure gap = $5 billion 490 490 Full Full 45° employment 45° employment 490 510 530 490 510 530 Real GDP Real GDP (а) Recessionary expenditure gap (b) Inflationary expenditure gap Aggregate expenditures (billio ns of dollars) Aggregate expenditures (billions of dollars)
Chapter9: Aggregate Demand
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.13P
Related questions
Question
(For students who were assigned Chapter 28) Use the aggregate expenditures model to show how government fiscal policy could eliminate either a recessionary expenditure gap or an inflationary expenditure gap (Figure 28.7). Explain how equal-size increases in G and T could eliminate a recessionary gap and how equal-size decreases in G and T could eliminate an inflationary gap.
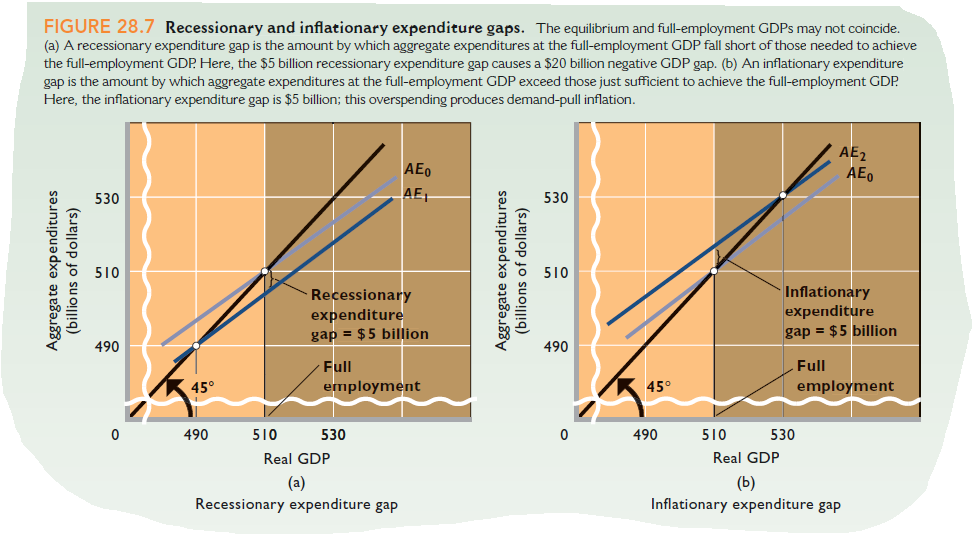
Transcribed Image Text:FIGURE 28.7 Recessionary and inflationary expenditure gaps. The equilibrium and full-employment GDPS may not coincide.
(a) A recessionary expenditure gap is the amount by which aggregate expenditures at the full-employment GDP fall short of those needed to achieve
the full-employment GDP Here, the $5 billion recessionary expenditure gap causes a $20 billion negative GDP gap. (b) An iflationary expenditure
gap is the amount by which aggregate expenditures at the full-employment GDP exceed those just sufficient to achieve the full-employment GDP.
Here, the inflationary expenditure gap is $5 billion; this overspending produces demand-pull inflation.
AE2
AE,
AEo
530
AET
530
510
510
Recessionary
expenditure
gap = $5 billion
Inflationary
expenditure
gap = $5 billion
490
490
Full
Full
45°
employment
45°
employment
490
510
530
490
510
530
Real GDP
Real GDP
(а)
Recessionary expenditure gap
(b)
Inflationary expenditure gap
Aggregate expenditures
(billio ns of dollars)
Aggregate expenditures
(billions of dollars)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



