3. Short Run Costs: List all of the costs associated with your firm. Separate them into fixed and -variable costs. Add them up and get your total costs. Calculate your average costs and your marginal costs. You will need a minimum of two graphs here. One for your total costs (TC, TVC & TFC), and one for your average/marginal costs (ATC, AVC, AFC & MC). 4. How much are you selling your product for at the profit maximizing price? How many units? What is your total revenue? What are your explicit & implicit costs? What are your accounting and economic profits at the end of the first year (these might be negative, and that's ok). How long will it take you to break even, or turn a profit? 5. Do the same for the long run. What are your returns to scale? firm project. Firm Name: TechGadget Innovations Product: Our company could produce modern clever wearable devices, inclusive of smartwatches and fitness trackers, with superior fitness tracking and connectivity features. Inputs and Capital Needed: To manufacture our clever wearable gadgets, we'd require raw substances together with circuit boards, sensors, batteries, and durable casing substances. Additionally, we'd want specialized device and equipment for meeting and trying out strategies. Furthermore, we would need professional labor for product design, engineering, production, and fine control. Fixed Costs: Fixed charges would consist of prices which includes hire for production centers, salaries for permanent group of workers, utilities, equipment protection, and administrative overhead. Variable Costs for a hundred Units: Variable expenses would encompass the cost of raw materials, labor for manufacturing, packaging materials, and any variable overhead costs. Let's say the variable fee in keeping with unit is $50 for our clever wearable gadgets. Variable Cost in step with Unit Number of Units = $50 x100 = $5000 Total Costs for the First 100 Units: Total Costs = Fixed Costs Variable Costs Let's assume constant fees are $10,000. Total Costs = $10,000 (Fixed Costs) $5,000 (Variable Costs) = $15,000 Selling Price: We could sell our clever wearable devices for $150 in line with unit. Years to Turn a Positive Profit: Estimating the time it takes to turn a advantageous income depends pn various factors consisting of marketplace call for, competition, manufacturing efficiency, pricing strategy, and preliminary investment. Assuming steady growth and a success market penetration, it can take 2-3 years to achieve superb accounting or economic earnings. However, this timeline should range based on market conditions and the effectiveness of our business strategies.create a firm, explain, chart and graph all of the necessary information in the production function. This can be anything that you like. It works best if you pick something you are interested in, or model it after your place of employment, or what you want to do in the future. In the past I've see everything from tattoo parlors to magical brooms, and pretty much everything in between. The only requirement for the output is that it has to be measurable. Since everything has to be measured in terms of costs and labor per unit, it is easiest to have the product be a tangible good (not a service). In the case of the tattoo parlor, the student was able to break down exactly how much ink, paper, cleaning solution, pens, plastic wrap, electricity, etc. would be used per artist on a 15 min interval. you can put in as much as you would like, and your grade is based accordingly. Here is the minimum that you have to do: 1. Tell the story of your firm. What is the name of the firm? What do you produce? Where is your market? You must have a minimum of 10 employees and output of at least 100 units per month. What are your inputs (capital, labor and materials) and your output? 2. Short Run Production Function and Total Product curve. You will need words, a chart and a graph here. Next, be sure to do the same for average and marginal product of labor. Explain what is going on in your graphs.
3. Short Run Costs: List all of the costs associated with your firm. Separate them into fixed and -variable costs. Add them up and get your total costs. Calculate your average costs and your marginal costs. You will need a minimum of two graphs here. One for your total costs (TC, TVC & TFC), and one for your average/marginal costs (ATC, AVC, AFC & MC). 4. How much are you selling your product for at the profit maximizing price? How many units? What is your total revenue? What are your explicit & implicit costs? What are your accounting and economic profits at the end of the first year (these might be negative, and that's ok). How long will it take you to break even, or turn a profit? 5. Do the same for the long run. What are your returns to scale? firm project. Firm Name: TechGadget Innovations Product: Our company could produce modern clever wearable devices, inclusive of smartwatches and fitness trackers, with superior fitness tracking and connectivity features. Inputs and Capital Needed: To manufacture our clever wearable gadgets, we'd require raw substances together with circuit boards, sensors, batteries, and durable casing substances. Additionally, we'd want specialized device and equipment for meeting and trying out strategies. Furthermore, we would need professional labor for product design, engineering, production, and fine control. Fixed Costs: Fixed charges would consist of prices which includes hire for production centers, salaries for permanent group of workers, utilities, equipment protection, and administrative overhead. Variable Costs for a hundred Units: Variable expenses would encompass the cost of raw materials, labor for manufacturing, packaging materials, and any variable overhead costs. Let's say the variable fee in keeping with unit is $50 for our clever wearable gadgets. Variable Cost in step with Unit Number of Units = $50 x100 = $5000 Total Costs for the First 100 Units: Total Costs = Fixed Costs Variable Costs Let's assume constant fees are $10,000. Total Costs = $10,000 (Fixed Costs) $5,000 (Variable Costs) = $15,000 Selling Price: We could sell our clever wearable devices for $150 in line with unit. Years to Turn a Positive Profit: Estimating the time it takes to turn a advantageous income depends pn various factors consisting of marketplace call for, competition, manufacturing efficiency, pricing strategy, and preliminary investment. Assuming steady growth and a success market penetration, it can take 2-3 years to achieve superb accounting or economic earnings. However, this timeline should range based on market conditions and the effectiveness of our business strategies.create a firm, explain, chart and graph all of the necessary information in the production function. This can be anything that you like. It works best if you pick something you are interested in, or model it after your place of employment, or what you want to do in the future. In the past I've see everything from tattoo parlors to magical brooms, and pretty much everything in between. The only requirement for the output is that it has to be measurable. Since everything has to be measured in terms of costs and labor per unit, it is easiest to have the product be a tangible good (not a service). In the case of the tattoo parlor, the student was able to break down exactly how much ink, paper, cleaning solution, pens, plastic wrap, electricity, etc. would be used per artist on a 15 min interval. you can put in as much as you would like, and your grade is based accordingly. Here is the minimum that you have to do: 1. Tell the story of your firm. What is the name of the firm? What do you produce? Where is your market? You must have a minimum of 10 employees and output of at least 100 units per month. What are your inputs (capital, labor and materials) and your output? 2. Short Run Production Function and Total Product curve. You will need words, a chart and a graph here. Next, be sure to do the same for average and marginal product of labor. Explain what is going on in your graphs.
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter1: Introduction: What This Book Is About
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1IP
Related questions
Question
Can you just answer the question from the firm project I create in the first picture
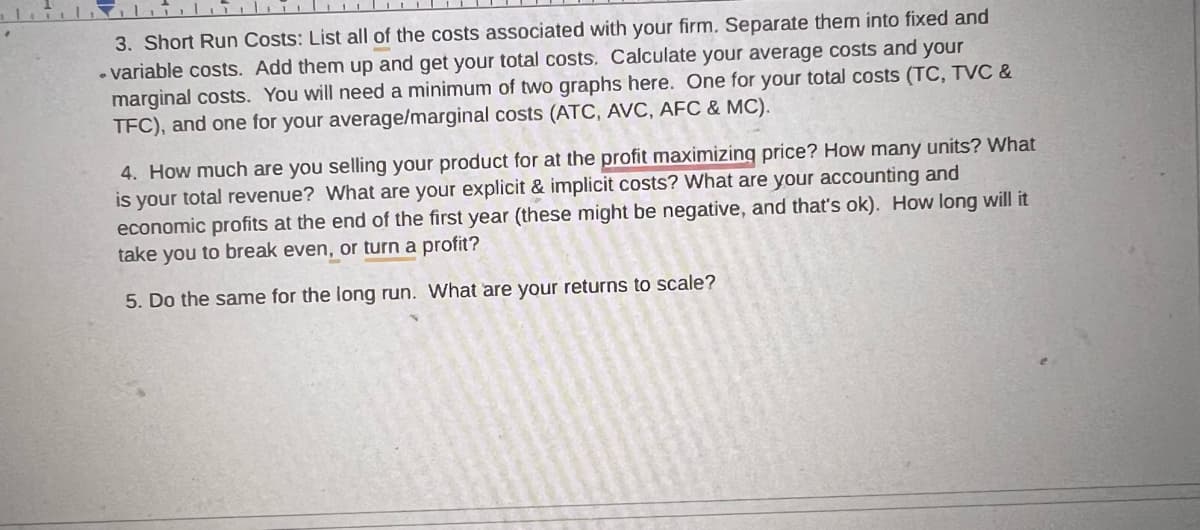
Transcribed Image Text:3. Short Run Costs: List all of the costs associated with your firm. Separate them into fixed and
-variable costs. Add them up and get your total costs. Calculate your average costs and your
marginal costs. You will need a minimum of two graphs here. One for your total costs (TC, TVC &
TFC), and one for your average/marginal costs (ATC, AVC, AFC & MC).
4. How much are you selling your product for at the profit maximizing price? How many units? What
is your total revenue? What are your explicit & implicit costs? What are your accounting and
economic profits at the end of the first year (these might be negative, and that's ok). How long will it
take you to break even, or turn a profit?
5. Do the same for the long run. What are your returns to scale?

Transcribed Image Text:firm project. Firm Name: TechGadget Innovations
Product: Our company could produce modern clever wearable devices, inclusive of smartwatches
and fitness trackers, with superior fitness tracking and connectivity features.
Inputs and Capital Needed: To manufacture our clever wearable gadgets, we'd require raw
substances together with circuit boards, sensors, batteries, and durable casing substances.
Additionally, we'd want specialized device and equipment for meeting and trying out strategies.
Furthermore, we would need professional labor for product design, engineering, production, and fine
control.
Fixed Costs: Fixed charges would consist of prices which includes hire for production centers,
salaries for permanent group of workers, utilities, equipment protection, and administrative overhead.
Variable Costs for a hundred Units: Variable expenses would encompass the cost of raw materials,
labor for manufacturing, packaging materials, and any variable overhead costs. Let's say the variable
fee in keeping with unit is $50 for our clever wearable gadgets. Variable Cost in step with Unit
Number of Units = $50 x100 = $5000
Total Costs for the First 100 Units: Total Costs = Fixed Costs Variable Costs Let's assume constant
fees are $10,000. Total Costs = $10,000 (Fixed Costs) $5,000 (Variable Costs) = $15,000
Selling Price: We could sell our clever wearable devices for $150 in line with unit.
Years to Turn a Positive Profit: Estimating the time it takes to turn a advantageous income depends
pn various factors consisting of marketplace call for, competition, manufacturing efficiency, pricing
strategy, and preliminary investment. Assuming steady growth and a success market penetration, it
can take 2-3 years to achieve superb accounting or economic earnings. However, this timeline should
range based on market conditions and the effectiveness of our business strategies.create a firm,
explain, chart and graph all of the necessary information in the production function. This can be
anything that you like. It works best if you pick something you are interested in, or model it after your
place of employment, or what you want to do in the future. In the past I've see everything from tattoo
parlors to magical brooms, and pretty much everything in between. The only requirement for the
output is that it has to be measurable. Since everything has to be measured in terms of costs and
labor per unit, it is easiest to have the product be a tangible good (not a service). In the case of the
tattoo parlor, the student was able to break down exactly how much ink, paper, cleaning solution,
pens, plastic wrap, electricity, etc. would be used per artist on a 15 min interval. you can put in as
much as you would like, and your grade is based accordingly. Here is the minimum that you have to
do: 1. Tell the story of your firm. What is the name of the firm? What do you produce? Where is your
market? You must have a minimum of 10 employees and output of at least 100 units per month.
What are your inputs (capital, labor and materials) and your output?
2. Short Run Production Function and Total Product curve. You will need words, a chart and a graph
here. Next, be sure to do the same for average and marginal product of labor. Explain what is going
on in your graphs.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning