For a population that is left skewed with a mean of 23 and a standard deviation equal to 14, determine the probability of observing a sample mean of 21 or more from a sample of size 32. Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table What is the probability of observing a sample mean of 21 or more from a sample of size 32? P(X≥21) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (...
For a population that is left skewed with a mean of 23 and a standard deviation equal to 14, determine the probability of observing a sample mean of 21 or more from a sample of size 32. Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table What is the probability of observing a sample mean of 21 or more from a sample of size 32? P(X≥21) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (...
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
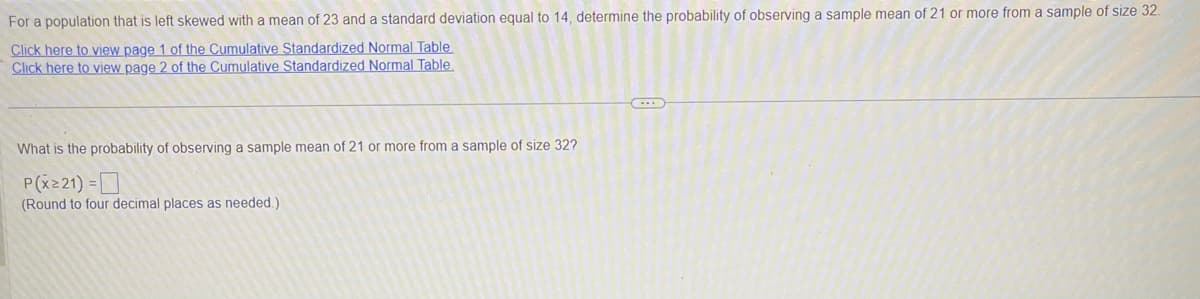
Transcribed Image Text:For a population that is left skewed with a mean of 23 and a standard deviation equal to 14, determine the probability of observing a sample mean of 21 or more from a sample of size 32.
Click here to view page 1 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table
Click here to view page 2 of the Cumulative Standardized Normal Table
What is the probability of observing a sample mean of 21 or more from a sample of size 32?
P(x221) =
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill