Listed in the data table are amounts of strontium-90 (in millibecquerels, or mBq, per gram of calcium) in a simple random sample of baby teeth obtained from residents in two cities. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean amount of strontium-90 from city #1 residents is greater than the mean amount from city #2 residents. Click the icon to view the data table of strontium-90 amounts. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Assume that population 1 consists of amounts from city #1 levels and population 2 consists of amounts from city #2. A. Ho: ₁ = ₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ C. Ho: ₁ = ₂ H₁: M₁ M₂ The test statistic is B. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ D. Ho: H₁ H₁: H₁ (Round to two decimal places as needed.) H₂ H₂
Listed in the data table are amounts of strontium-90 (in millibecquerels, or mBq, per gram of calcium) in a simple random sample of baby teeth obtained from residents in two cities. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean amount of strontium-90 from city #1 residents is greater than the mean amount from city #2 residents. Click the icon to view the data table of strontium-90 amounts. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Assume that population 1 consists of amounts from city #1 levels and population 2 consists of amounts from city #2. A. Ho: ₁ = ₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ C. Ho: ₁ = ₂ H₁: M₁ M₂ The test statistic is B. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ D. Ho: H₁ H₁: H₁ (Round to two decimal places as needed.) H₂ H₂
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 41RE
Related questions
Question
I need help with this one please thank you

Transcribed Image Text:Listed in the data table are amounts of strontium-90 (in millibecquerels, or mBq, per gram of calcium) in a simple random
sample of baby teeth obtained from residents in two cities. Assume that the two samples are independent simple
random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviations
are equal. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean amount of strontium-90 from city #1 residents is
greater than the mean amount from city #2 residents.
Click the icon to view the data table of strontium-90 amounts.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Assume that population 1 consists of amounts from city #1 levels and
population 2 consists of amounts from city #2.
A. Ho: M₁ = ₂
H₁: H₁ H₂
C. Ho: ₁ = ₂
H₁: µ₁ µ₂
The test statistic is
B. Ho: ₁ μ₂
H₁: H₁ H₂
D. Ho: ₁ ≤₂
H₁: H₁ H₂
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
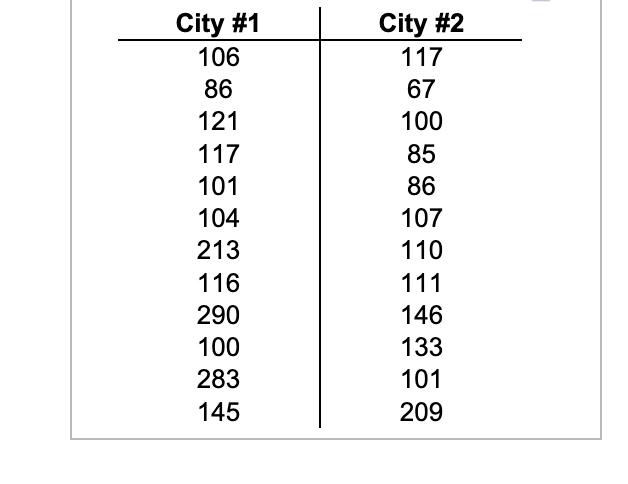
Transcribed Image Text:City #1
106
86
121
117
101
104
213
116
290
100
283
145
City #2
117
67
100
85
86
107
110
111
146
133
101
209
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
