Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter2: The First Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.52E: Use the data in Table 2.2 to determine Hp T for Ar at 0C and 1atm. Make any reasonable assumptions...
Related questions
Question
100%
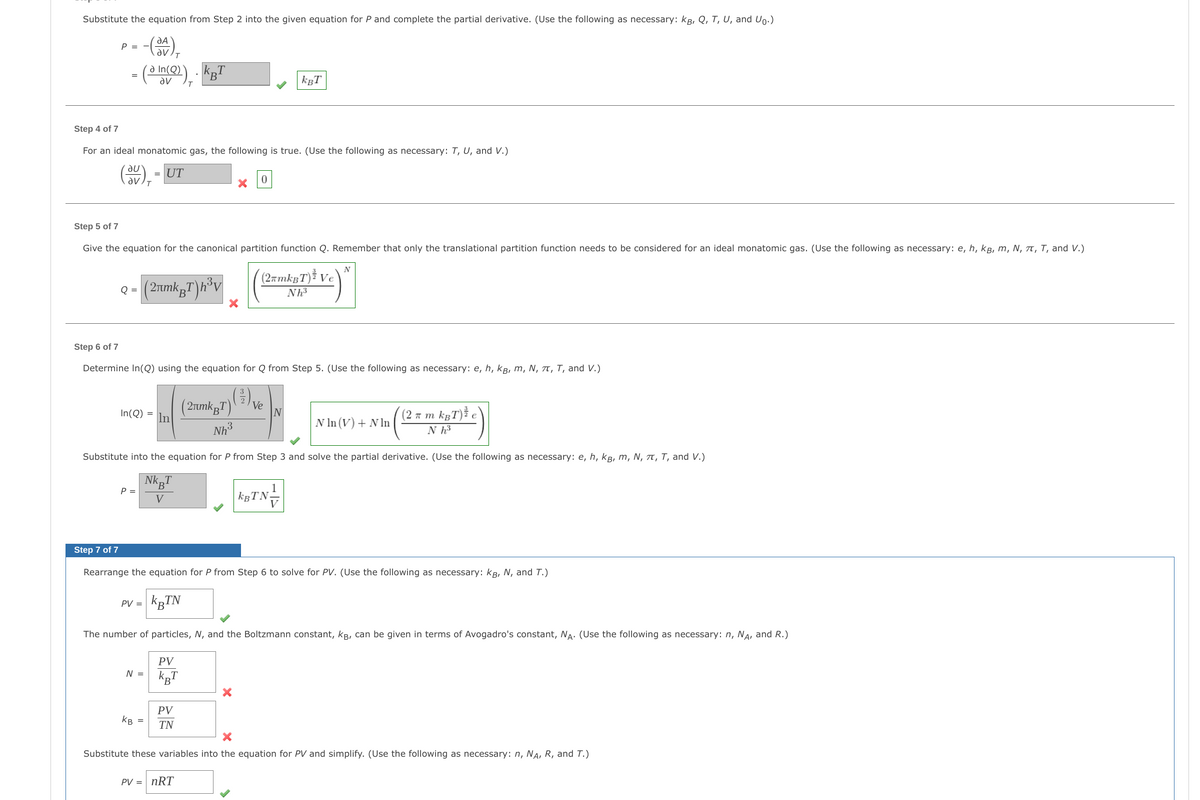
Transcribed Image Text:Substitute the equation from Step 2 into the given equation for P and complete the partial derivative. (Use the following as necessary: kg, Q, T, U, and Up.)
P = -
-(3+),
T
- (ain(@)),
КВТ
=
KBT
Step 4 of 7
For an ideal monatomic gas, the following is true. (Use the following as necessary: T, U, and V.)
(3V)₁ = 1 UT
0
Step 5 of 7
Give the equation for the canonical partition function Q. Remember that only the translational partition function needs to be considered for an ideal monatomic gas. (Use the following as necessary: e, h, kg, m, N, T, T, and V.)
N
(2πmkBT) Ve
Nh³
Q =
(2µmkµT)h³v
X
Step 6 of 7
Determine In(Q) using the equation for Q from Step 5. (Use the following as necessary: e, h, kB, M, N, π, T, and V.)
Ve
In(Q)
N
In
(2μmkBT)
Nh³
(2π m kBT) e
N ln (V) + Nln
Nh³
Substitute into the equation for P from Step 3 and solve the partial derivative. (Use the following as necessary: e, h, kg, m, N, π, T, and V.)
NKB
T
P =
V
|KBTN-
V
Step 7 of 7
Rearrange the equation for P from Step 6 to solve for PV. (Use the following as necessary: KB, N, and T.)
PV =
KBTN
The number of particles, N, and the Boltzmann constant, kB, can be given in terms of Avogadro's constant, NA. (Use the following as necessary: n, NA, and R.)
PV
N =
КВТ
X
PV
KB
TN
X
Substitute these variables into the equation for PV and simplify. (Use the following as necessary: n, NA, R, and T.)
PV = nRT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,