For each term in the first column below, identify its definition (or partial definition). Each definition may be used once or not at all. # Definition (or Partial Definition) 1 A defined rate of departure from prescribed controls. Also referred to as occurrence rate or exception rate. 2 A sampling plan for locating at least 1 deviation, providing that the deviation occurs in the population with a specified frequency. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Also referred to as precision, a measure of the difference between a sample estimate (projection) and the tolerable rate of deviation or tolerable misstatement at a specified sampling risk. An estimate of the most likely amount of monetary misstatement in a population. The complement of the risk of incorrect acceptance. The maximum population rate of deviations from a prescribed control that the auditors will accept without modifying the planned assessment of control risk. The possibility that the assessed level of control risk based on the sample is less than the true operating effectiveness of the controls. The risk that sample results will indicate that a population is not materially misstated when, in fact, it is materially misstated. The risk that the auditors' conclusion based on a sample might be different from the conclusion they would reach if the test were applied to the entire population. Term
For each term in the first column below, identify its definition (or partial definition). Each definition may be used once or not at all. # Definition (or Partial Definition) 1 A defined rate of departure from prescribed controls. Also referred to as occurrence rate or exception rate. 2 A sampling plan for locating at least 1 deviation, providing that the deviation occurs in the population with a specified frequency. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Also referred to as precision, a measure of the difference between a sample estimate (projection) and the tolerable rate of deviation or tolerable misstatement at a specified sampling risk. An estimate of the most likely amount of monetary misstatement in a population. The complement of the risk of incorrect acceptance. The maximum population rate of deviations from a prescribed control that the auditors will accept without modifying the planned assessment of control risk. The possibility that the assessed level of control risk based on the sample is less than the true operating effectiveness of the controls. The risk that sample results will indicate that a population is not materially misstated when, in fact, it is materially misstated. The risk that the auditors' conclusion based on a sample might be different from the conclusion they would reach if the test were applied to the entire population. Term
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337619455
Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Chapter8: Specialized Audit Tools: Attributes Sampling, Monetary Unit Sampling, And Data Analytics Tools
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 35CYBK
Related questions
Question
100%
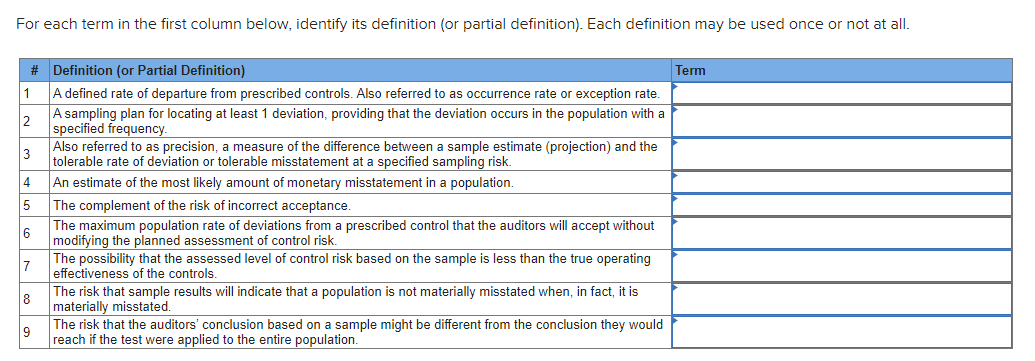
Transcribed Image Text:For each term in the first column below, identify its definition (or partial definition). Each definition may be used once or not at all.
#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Definition (or Partial Definition)
A defined rate of departure from prescribed controls. Also referred to as occurrence rate or exception rate.
A sampling plan for locating at least 1 deviation, providing that the deviation occurs in the population with a
specified frequency.
Also referred to as precision, a measure of the difference between a sample estimate (projection) and the
tolerable rate of deviation or tolerable misstatement at a specified sampling risk.
An estimate of the most likely amount of monetary misstatement in a population.
The complement of the risk of incorrect acceptance.
The maximum population rate of deviations from a prescribed control that the auditors will accept without
modifying the planned assessment of control risk.
The possibility that the assessed level of control risk based on the sample is less than the true operating
effectiveness of the controls.
The risk that sample results will indicate that a population is not materially misstated when, in fact, it is
materially misstated.
The risk that the auditors' conclusion based on a sample might be different from the conclusion they would
reach if the test were applied to the entire population.
Term
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337619455
Author:
Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305080577
Author:
Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337619455
Author:
Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305080577
Author:
Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning