For the following double-replacement reaction: (NH4)2SO4(aq) + CaBr2(aq) a) Predict the products (and their phases!) b) Write a complete ionic equation for the reaction. c) Write the net ionic equation for the reaction. d) What are the spectator ions in this reaction?
For the following double-replacement reaction: (NH4)2SO4(aq) + CaBr2(aq) a) Predict the products (and their phases!) b) Write a complete ionic equation for the reaction. c) Write the net ionic equation for the reaction. d) What are the spectator ions in this reaction?
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter4: Reactions In Aqueous Solution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 78QAP: When 85.0 mL of 0.250 M Ba(OH)2 solution is added to 85.00 mL of 0.250 M Al (NO3)3 solution, a white...
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:1) For the following double-replacement reaction:
(NH4)2SO4(aq) + CaBr2(aq)
a) Predict the products (and their phases!)
b) Write a complete ionic equation for the reaction.
c) Write the net ionic equation for the reaction.
d) What are the spectator ions in this reaction?
2) A sample from a mine's tailings pond contains Pb2+, Ag+, Mg2+, and Na+ cations. What
ionic compounds can be added to this solution, and in what order, to separate these
cations from one another?
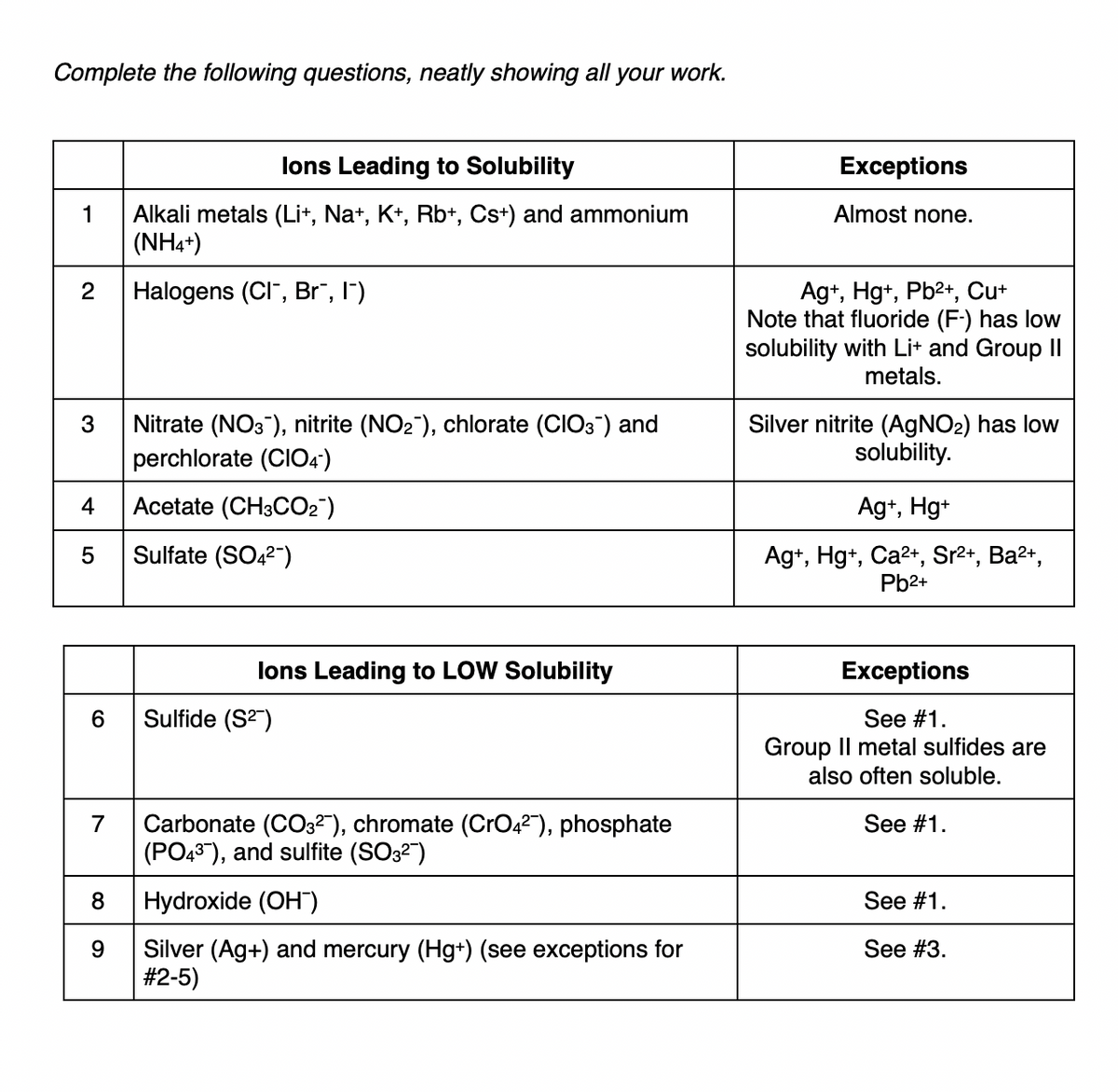
Transcribed Image Text:Complete the following questions, neatly showing all your work.
lons Leading to Solubility
Exceptions
Alkali metals (Lit, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) and ammonium
(NH4+)
1
Almost none.
Halogens (CI", Br", l")
Ag+, Hg+, Pb2+, Cut
Note that fluoride (F-) has low
solubility with Lit and Group II
metals.
2
Nitrate (NO3), nitrite (NO2), chlorate (CIO3) and
perchlorate (CIO4')
Silver nitrite (AGNO2) has low
solubility.
3
4
Acetate (CH3CO2")
Ag+, Hg+
Sulfate (SO42")
Ag+, Hg+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+,
Pb2+
lons Leading to LOW Solubility
Exceptions
Sulfide (S2)
See #1.
Group Il metal sulfides are
also often soluble.
Carbonate (CO3²"), chromate (CrO42"), phosphate
(PO43), and sulfite (SO32")
7
See #1.
8
Hydroxide (OH")
See #1.
Silver (Ag+) and mercury (Hg+) (see exceptions for
#2-5)
9
See #3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning