FORMULA: Substance SOLUTION: AH of Some Common Substances C (graphite) CO (g) CO₂(g) C₂H₂OH (1) CaCO3 (s) CaO (s) Fe2O3 (s) H₂O(g) Specific Heat A Hof (kJ/mol) 5. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide. Determine the heat of reaction. CaCO3(s) à CO2(g) + CaO(s) 0 -110.5 -393.5 -277.7 -1206.9 -635.6 -824.2 -241.8 Substance H₂O (1) N₂(g) NaCl (s) NH:(g) NO (g) NO₂ (g) N₂O (g) O₂ (g) Specific Heat AH% (kJ/mol) -285.8 0 -411.2 FORMULA: 6. When potassium chloride reacts with oxygen under the right conditions, potassium chloride is formed. Given the heat formation of KCl(s) (-435.9) and KCIO3(s) (-391.4). Calculate the standard molar enthalpy of reaction for 2KC1)+302(g) à 2KCIO3(s) -46.3 90.29 33.85 81.56 0 SOLUTION:
FORMULA: Substance SOLUTION: AH of Some Common Substances C (graphite) CO (g) CO₂(g) C₂H₂OH (1) CaCO3 (s) CaO (s) Fe2O3 (s) H₂O(g) Specific Heat A Hof (kJ/mol) 5. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide. Determine the heat of reaction. CaCO3(s) à CO2(g) + CaO(s) 0 -110.5 -393.5 -277.7 -1206.9 -635.6 -824.2 -241.8 Substance H₂O (1) N₂(g) NaCl (s) NH:(g) NO (g) NO₂ (g) N₂O (g) O₂ (g) Specific Heat AH% (kJ/mol) -285.8 0 -411.2 FORMULA: 6. When potassium chloride reacts with oxygen under the right conditions, potassium chloride is formed. Given the heat formation of KCl(s) (-435.9) and KCIO3(s) (-391.4). Calculate the standard molar enthalpy of reaction for 2KC1)+302(g) à 2KCIO3(s) -46.3 90.29 33.85 81.56 0 SOLUTION:
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter4: Energy And Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 116QRT
Related questions
Question
5 only
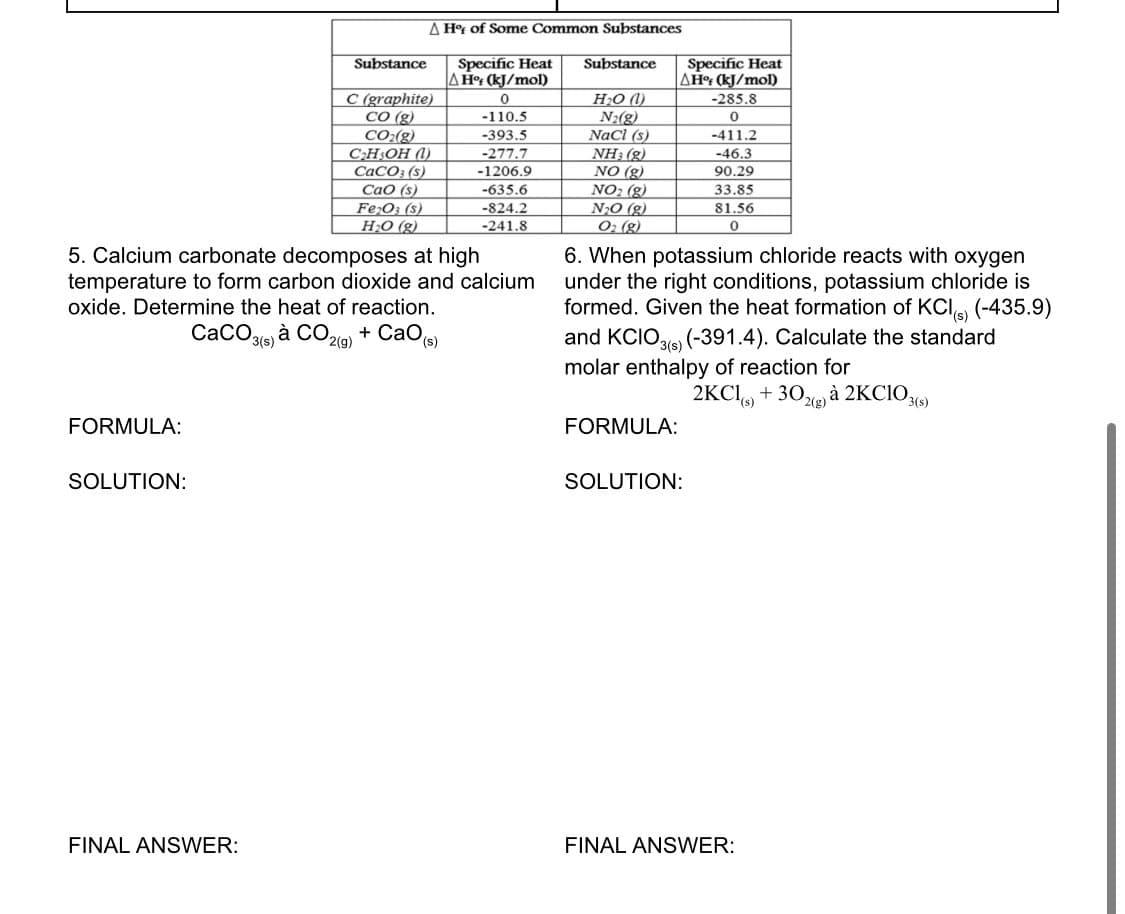
Transcribed Image Text:FORMULA:
SOLUTION:
Substance
FINAL ANSWER:
A Hof of Some Common Substances
C (graphite)
CO (g)
CO₂(g)
C₂H5OH (1)
CaCO3 (s)
CaO (s)
Fe₂O3 (s)
H₂O(g)
5. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high
temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium
oxide. Determine the heat of reaction.
CaCO3(s) à CO2(g) + CaO (s)
Specific Heat
A Hof (kJ/mol)
0
-110.5
-393.5
-277.7
-1206.9
-635.6
-824.2
-241.8
Substance
H₂O (
N₂(g)
NaCl (s)
NH3(g)
NO (g)
NO₂ (g)
N₂O(g)
O₂ (g)
Specific Heat
AH% (kJ/mol)
-285.8
0
FORMULA:
6. When potassium chloride reacts with oxygen
under the right conditions, potassium chloride is
formed. Given the heat formation of KCl) (-435.9)
and KCIO3(s) (-391.4). Calculate the standard
molar enthalpy of reaction for
2KCl(s) + 302(g) à 2KCIO3(s)
-411.2
-46.3
90.29
33.85
81.56
0
SOLUTION:
FINAL ANSWER:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning