fusion began. The fusion of hydrogen atoms in the core of this proto- sun emitted large amount of energy, which is the continued source of light and heat that now reaches our planet. Why does our sun generate energy? SELECT ONE OF THE FOLLOWING OPTIONS: A. It emits residual energy from the formation of the solar system B. Atoms within the sun are so densely packed that nuclear fusion occurs, generating large quantities of energy C. Friction created by motion of particles within the sun generates heat Submit answer
fusion began. The fusion of hydrogen atoms in the core of this proto- sun emitted large amount of energy, which is the continued source of light and heat that now reaches our planet. Why does our sun generate energy? SELECT ONE OF THE FOLLOWING OPTIONS: A. It emits residual energy from the formation of the solar system B. Atoms within the sun are so densely packed that nuclear fusion occurs, generating large quantities of energy C. Friction created by motion of particles within the sun generates heat Submit answer
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter20: Nuclear Chemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20.117QP
Related questions
Question
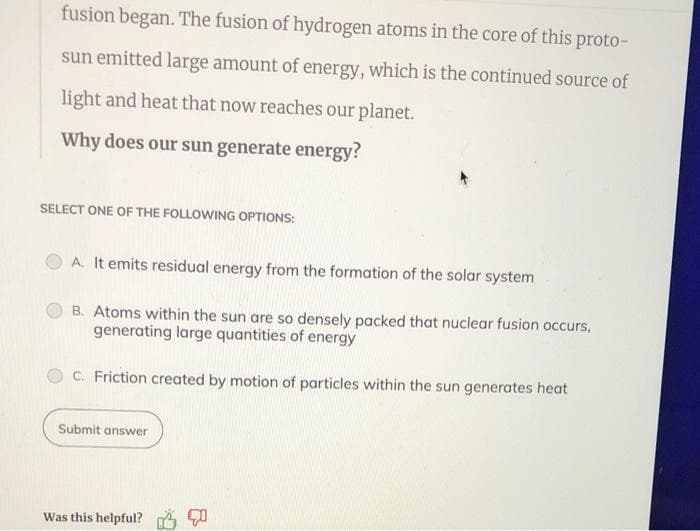
Transcribed Image Text:fusion began. The fusion of hydrogen atoms in the core of this proto-
sun emitted large amount of energy, which is the continued source of
light and heat that now reaches our planet.
Why does our sun generate energy?
SELECT ONE OF THE FOLLOWING OPTIONS:
A. It emits residual energy from the formation of the solar system
B. Atoms within the sun are so densely packed that nuclear fusion occurs,
generating large quantities of energy
C. Friction created by motion of particles within the sun generates heat
Submit answer
Was this helpful?
4

Transcribed Image Text:Gravity caused the dust and gases (mostly hydrogen, H, and helium,
He) in the nebula to begin to accumulate in the center of the newly
condensing protoplanetary disk. The origin of the solar system from
a condensing nebula is called the "nebular hypothesis." When gas
and dust at the center of this rotating disk became packed very
tightly together, the atoms became so tightly packed that nuclear
fusion began. The fusion of hydrogen atoms in the core of this proto-
sun emitted large amount of energy, which is the continued source of
light and heat that now reaches our planet.
Why does our sun generate energy?
SELECT ONE OF THE FOLLOWING OPTIONS:
A. It emits residual energy from the formation of the solar system
B. Atoms within the sun are so densely packed that nuclear fusion occurs,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning