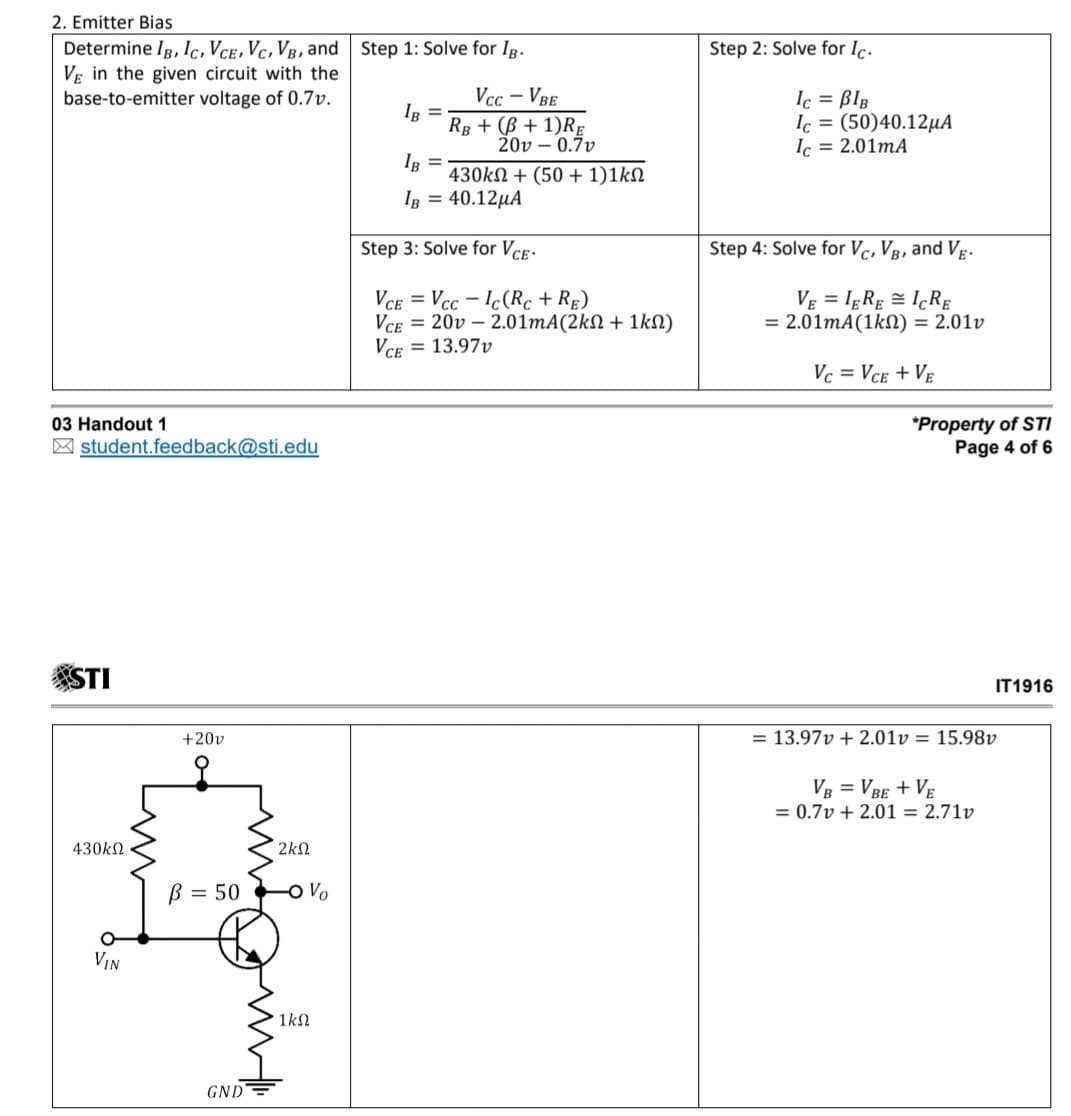
Given a Fixed-Biased transistor circuit with Beta DC is 200 , voltage at common collector is +22v ,base supply voltage is +11V, Base resistor is 47kOhms , collector resistor is 390 ohms ,Voltage at Base-emitter junction is 0.7v. Determine the Q-point of collector current and Voltage at collector-emitter junction. These might be help as a guide to solve the problem.
Instructions and Operation
Nowadays, electrical engineers are required to evolve their practices by incorporating embedded processes, microcontrollers, digital signal processors, and so on. These processors are beneficial in many ways and have changed the perspective of electronic design.
Subroutine Instruction
Subroutine instruction is defined as the instructions used in the programming language in a sequence form saved in memory. They are used to doing a specific task. Subroutine instruction is called a unit that instructs to perform some needed task. There are many programming languages in which subroutine instructions are used but have a different identity or name, such as method, function, subprogram, routine, etc. Subroutine or sub-program is designed or coded as they can be called multiple times while executing the program.
Classification of Buses
A bus inside a microprocessor is a collection of wirelines that contain related information. A group of wires required for communication among the microprocessor and peripherals is known as a system bus. A bus is an electrical or digital passage across which bits are transferred between a variety of computer elements. It mainly links all the internal parts to the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and main memory. The width or size of any bus is crucial since it affects the amount of data that is transferred at a certain time period. Buses always transmit data parallelly, in a 32-bit bus, the information is supplied over 32 wirelines simultaneously and each bus comprises a clock speed measurable in MHz. The various types of buses inside a microprocessor are address bus, data bus, and control bus.
Execution of Instruction
A sequence of instructions makes up a program stored in a computer's memory unit. The CPU executes these instructions by going through a cycle for each instruction. The instruction cycle in a simple computer includes the steps listed below:
Draw, Illustrate and label your schematic diagram before solving the problem.
1) Given a Fixed-Biased transistor circuit with Beta DC is 200 , voltage at common collector is +22v ,base supply voltage is +11V, Base resistor is 47kOhms , collector resistor is 390 ohms ,Voltage at Base-emitter junction is 0.7v. Determine the Q-point of collector current and Voltage at collector-emitter junction.
These might be help as a guide to solve the problem.
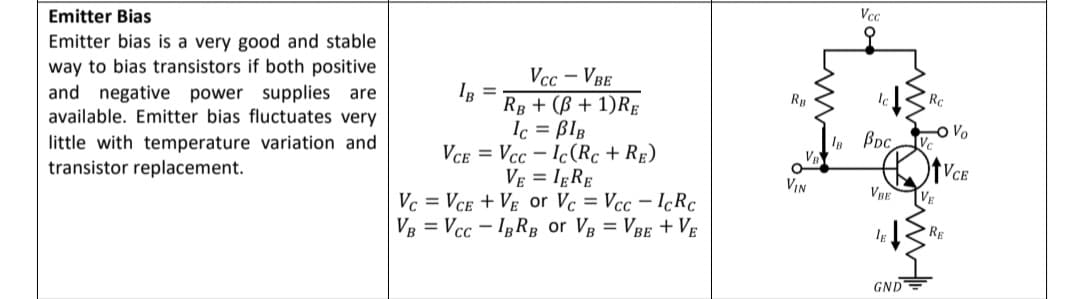
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images


