Greetings thank you for your help...i appreciate you please write legibly thank you A truck with 0.420-m-radius tires travels at 32.0 m/s. What is the angular velocity of the rotating tires in radians per second? What is this in rev/min?
Greetings thank you for your help...i appreciate you please write legibly thank you A truck with 0.420-m-radius tires travels at 32.0 m/s. What is the angular velocity of the rotating tires in radians per second? What is this in rev/min?
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter7: Gravitation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 89A
Related questions
Question
Greetings thank you for your help...i appreciate you
please write legibly thank you
A truck with 0.420-m-radius tires travels at 32.0 m/s. What
is the
second? What is this in rev/min?
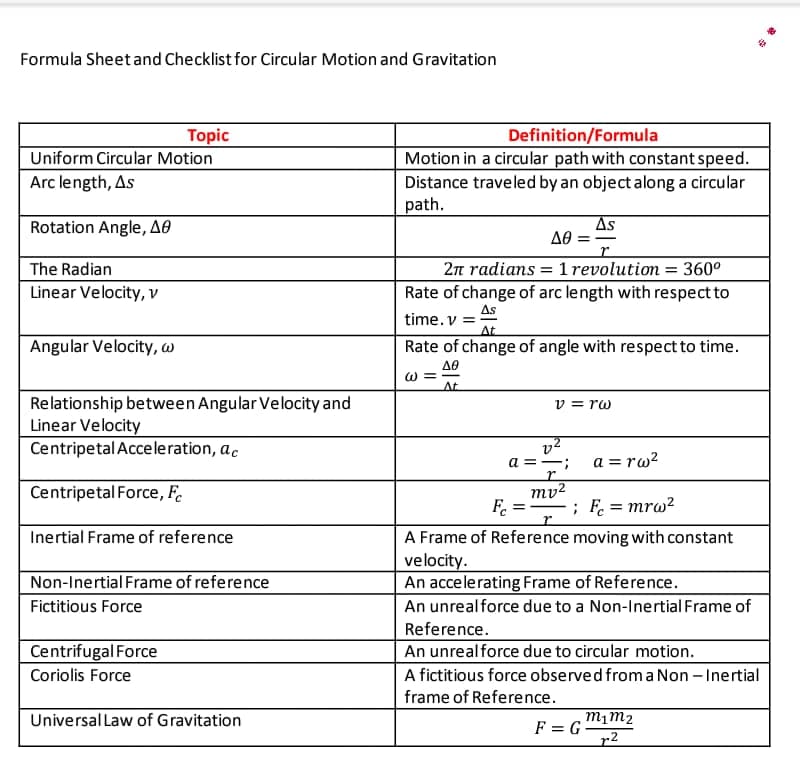
Transcribed Image Text:Formula Sheet and Checklist for Circular Motion and Gravitation
Topic
Uniform Circular Motion
Definition/Formula
Motion in a circular path with constant speed.
Distance traveled by an object along a circular
path.
Arc length, As
Rotation Angle, AO
As
The Radian
Linear Velocity, v
2n radians = 1 revolution = 360°
Rate of change of arc length with respect to
As
time. v =
At
Angular Velocity, w
Rate of change of angle with respectto time.
W =
At
Relationship between Angular Velocity and
Linear Velocity
Centripetal Acceleration, ac
v = rw
v2
a =
a = rw?
Centripetal Force, F.
mv2
F =
; F = mrw?
%3D
Inertial Frame of reference
A Frame of Reference moving with constant
velocity.
Non-Inertial Frame of reference
An accelerating Frame of Reference.
Fictitious Force
An unrealforce due to a Non-Inertial Frame of
Reference.
Centrifugal Force
An unrealforce due to circular motion.
Coriolis Force
A fictitious force observed froma Non - Inertial
frame of Reference.
Universal Law of Gravitation
F = G
r2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill