H. NH2 Bond cleavage (R145) n-1 NH, .(H69) Zn² (E72) (H196) (E270) H NH, (R145) 'n-1 NH, (H69) (E72) (H196) (E270) NH, (R145) H I., NH, Rn-1 Но (H69) Zn2 (E72) (H196) (E270) Release products and blnd water A FIGURE 8.19 The mechanism of the protease carboxypeptidase A. The zinc ion (orange circle) binds a water molecule (blue) and serves as an electrostatic catalyst to promote hydrolysis of the C-terminal amino acid from a peptide substrate (green). It does so by stabilizing the nega- tive charge on the oxygen in the tetrahedral transition state. Enzyme active site residues are indicated by black coloring. The bond cleaved is indicated by the dashed red arrow.
H. NH2 Bond cleavage (R145) n-1 NH, .(H69) Zn² (E72) (H196) (E270) H NH, (R145) 'n-1 NH, (H69) (E72) (H196) (E270) NH, (R145) H I., NH, Rn-1 Но (H69) Zn2 (E72) (H196) (E270) Release products and blnd water A FIGURE 8.19 The mechanism of the protease carboxypeptidase A. The zinc ion (orange circle) binds a water molecule (blue) and serves as an electrostatic catalyst to promote hydrolysis of the C-terminal amino acid from a peptide substrate (green). It does so by stabilizing the nega- tive charge on the oxygen in the tetrahedral transition state. Enzyme active site residues are indicated by black coloring. The bond cleaved is indicated by the dashed red arrow.
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter20: Dienes, Conjugated Systems, And Pericyclic Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20.48P
Related questions
Question
As shown a proposed mechanism for carboxypeptidase A.
(a) What is the role of Glu 270 in catalysis?
(b) What is the role of Arg 145 in catalysis?
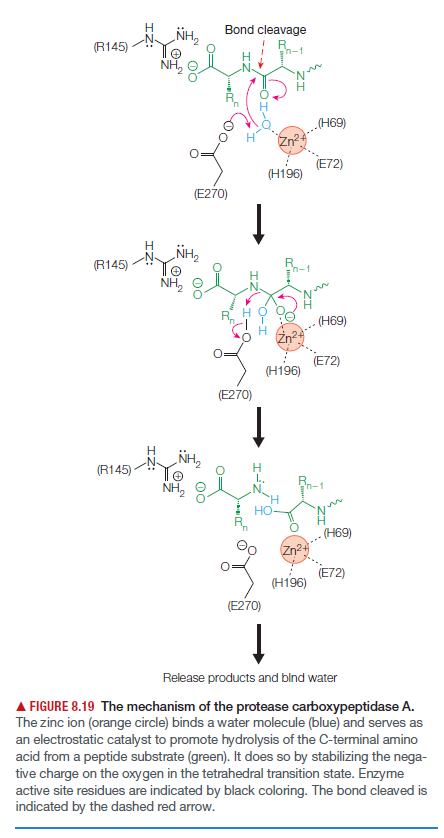
Transcribed Image Text:H.
NH2
Bond cleavage
(R145)
n-1
NH,
.(H69)
Zn²
(E72)
(H196)
(E270)
H
NH,
(R145)
'n-1
NH,
(H69)
(E72)
(H196)
(E270)
NH,
(R145)
H
I.,
NH,
Rn-1
Но
(H69)
Zn2
(E72)
(H196)
(E270)
Release products and blnd water
A FIGURE 8.19 The mechanism of the protease carboxypeptidase A.
The zinc ion (orange circle) binds a water molecule (blue) and serves as
an electrostatic catalyst to promote hydrolysis of the C-terminal amino
acid from a peptide substrate (green). It does so by stabilizing the nega-
tive charge on the oxygen in the tetrahedral transition state. Enzyme
active site residues are indicated by black coloring. The bond cleaved is
indicated by the dashed red arrow.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577190
Author:
Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577190
Author:
Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning