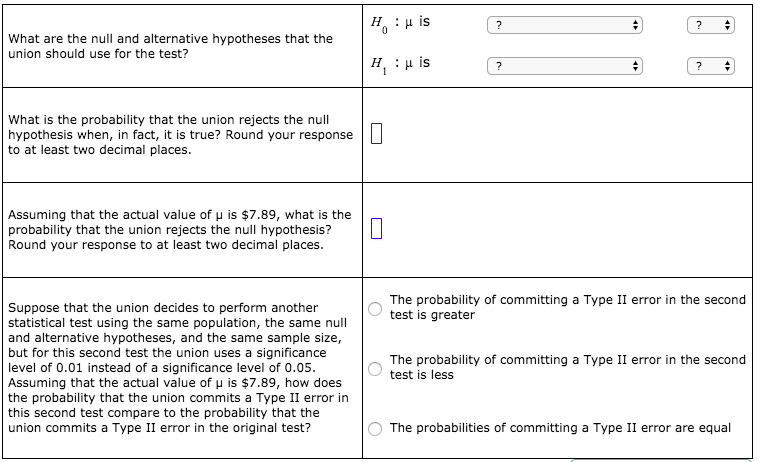
H :µ is What are the null and alternative hypotheses that the union should use for the test? H :H is What is the probability that the union rejects the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is true? Round your response ||| to at least two decimal places. Assuming that the actual value of u is $7.89, what is the probability that the union rejects the null hypothesis? Round your response to at least two decimal places. The probability of committing a Type II error in the second test is greater Suppose that the union decides to perform another statistical test using the same population, the same null and alternative hypotheses, and the same sample size, but for this second test the union uses a significance level of 0.01 instead of a significance level of 0.05. Assuming that the actual value of u is $7.89, how does the probability that the union commits a Type II error in this second test compare to the probability that the union commits a Type II error in the original test? The probability of committing a Type II error in the second test is less The probabilities of committing a Type II error are equal
A union of restaurant and foodservice workers would like to estimate this year's mean hourly wage
for foodservice workers in the U.S. Last year's mean hourly wage was
, and there is reason to believe that this year's value is less than last year's.
The union decides to do a statistical test to see if it can be concluded that the mean has decreased. The union chooses a random sample of
wages from this year.
Suppose that the population of hourly wages of foodservice workers in the U.S. has a standard deviation of
and that the union performs its hypothesis test using the
level of significance.
- Hi, on a pervious question that I submitted for help I was told that there is a limit to the number of subsection questions that you guys are allowed to answer and according to the response it was a max of 3. IF this is so, could you please then answer subquestions #1 #3 & #4. I am fairly positive that the answer to subquestion #2 is 0.05. Thank you
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images








