(h) or greater is achieved. (Fill in the A baseline separation is seen if a resolution of blank). Calculate the number of plates needed to increase resolution of the two peaks so this value for resolution is obtained, if k' and a remain constant.
(h) or greater is achieved. (Fill in the A baseline separation is seen if a resolution of blank). Calculate the number of plates needed to increase resolution of the two peaks so this value for resolution is obtained, if k' and a remain constant.
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Chapter27: Gas Chromatography
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 27.22QAP
Related questions
Question
question h only only
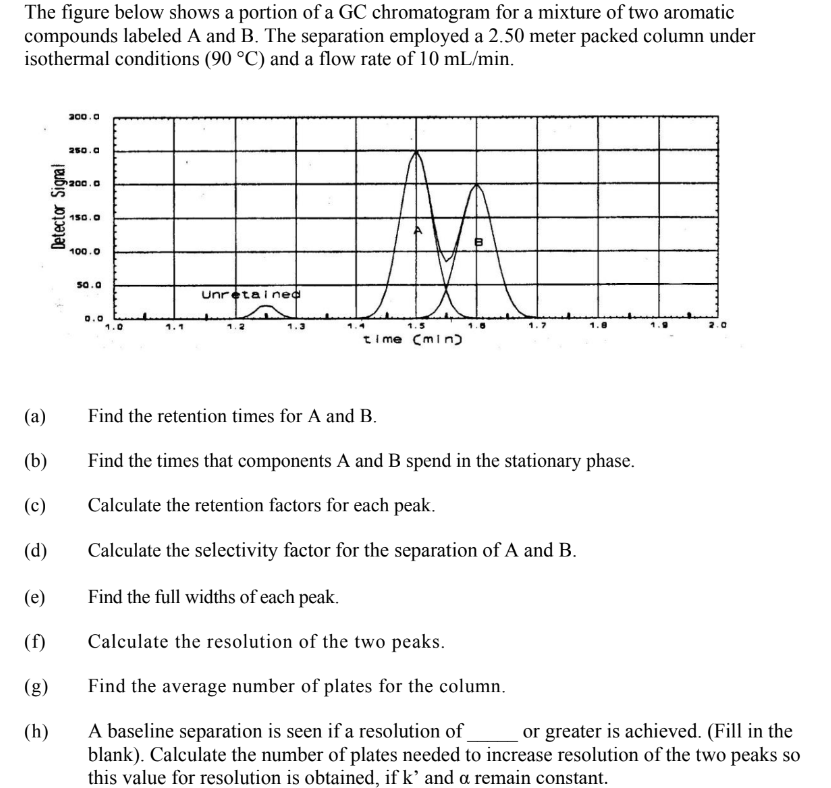
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows a portion of a GC chromatogram for a mixture of two aromatic
compounds labeled A and B. The separation employed a 2.50 meter packed column under
isothermal conditions (90 °C) and a flow rate of 10 mL/min.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
Detector Signal
300.0
250.0
200.0
150.0
100.0
50.0
0.0
1.0
1.1
Unretained
1.2
1.5
time (min)
1.7
O
Find the retention times for A and B.
Find the times that components A and B spend in the stationary phase.
Calculate the retention factors for each peak.
Calculate the selectivity factor for the separation of A and B.
Find the full widths of each peak.
Calculate the resolution of the two peaks.
Find the average number of plates for the column.
A baseline separation is seen if a resolution of or greater is achieved. (Fill in the
blank). Calculate the number of plates needed to increase resolution of the two peaks so
this value for resolution is obtained, if k' and a remain constant.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT