(h) Write down the Lagrange's polynomial through (xo, fo). (x1,fi), (X2, f2). Hence express 3x² +x+1 (x – 1)(x– 2)(x– 3) as sum of partial fractions.
(h) Write down the Lagrange's polynomial through (xo, fo). (x1,fi), (X2, f2). Hence express 3x² +x+1 (x – 1)(x– 2)(x– 3) as sum of partial fractions.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section9.10: Partial Fractions
Problem 17E
Related questions
Question
100%
Work out (h) and (j)
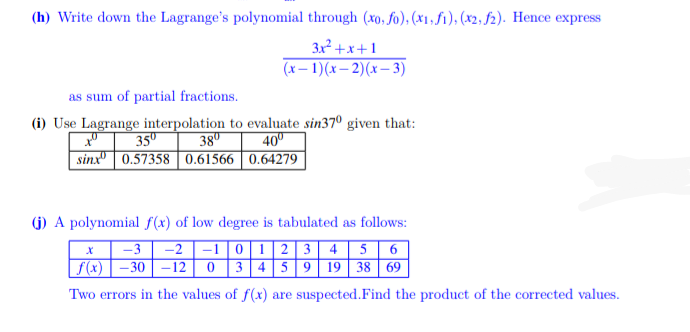
Transcribed Image Text:(h) Write down the Lagrange's polynomial through (xo, fo), (x1, f1), (x2, f2). Hence express
3x² +x+1
(x– 1)(x– 2)(x– 3)
as sum of partial fractions.
(i) Use Lagrange interpolation to evaluate sin37º given that:
38"
35º
40º
sinx" | 0.57358 | 0.61566 | 0.64279
(G) A polynomial f(x) of low degree is tabulated as follows:
-3
-2 |-1|0|1 | 2 3 4 5 6
|f(x) | – 30 | –12 0 3 45 | 9 19 38 69
Two errors in the values of f(x) are suspected.Find the product of the corrected values.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage