H₂C CH3 CH₂ Br₂ CH₂C₂ Br- H₂C CH3 CH3 Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂Cl₂. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
H₂C CH3 CH₂ Br₂ CH₂C₂ Br- H₂C CH3 CH3 Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂Cl₂. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
Chapter19: Aldehydes And Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
Section19.SE: Something Extra
Problem 28VC
Related questions
Question
196.
Subject : - Chemistry
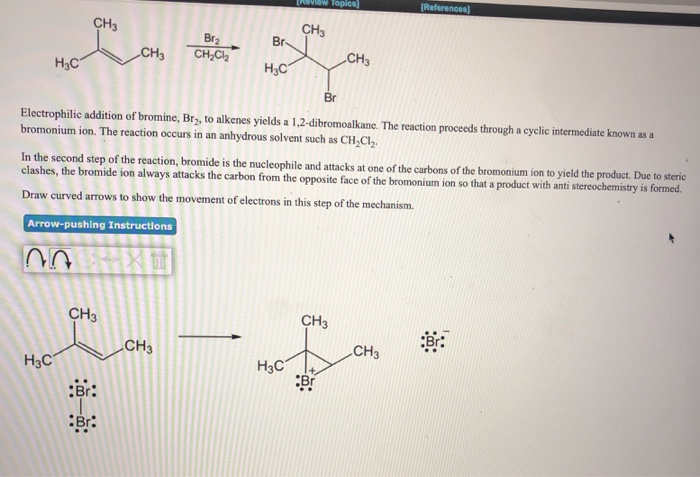
Transcribed Image Text:H₂C
CH3
H3C
CH3
CH3
:Br:
Br:
Br₂
CH₂Cl₂2
Br-
H3C
Br
Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br₂, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a
bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂Cl₂.
CH3
In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric
clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed.
Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
Arrow-pushing Instructions
27
[Review Topica
CH3
H3C
CH3
CH3
Br
[References)
CH3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

