Homework (Ch 33) Attempts Average / 3 6. Why the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run In the short run, the quantity of output supplied by firms can deviate from the natural level of output if the actual price level deviates from the expected price level in the economy. A number of theories explain reasons why this might happen. For example, the sticky-price theory asserts that the output prices of some goods and services adjust slowly to changes in the price level. Suppose firms announce the prices for their products in advance, based on an expected price level of 100 for the coming year. Many of the firms sell their goods through catalogs and face high costs of reprinting if they change prices. The actual price level turns out to be 90. Faced with high menu costs, the firms that rely on catalog sales choose not to adjust their prices. Sales from catalogs will ▼ , and firms that rely on catalogs will respond by the quantity of output they supply. If enough firms face high costs of adjusting prices, the unexpected decrease in the price level causes the quantity of output supplied to the natural level of output in the short run. Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate su exceed fall short of ve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = Natural Level of Output + ax (Price Level Actual - Price Level Expected) The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. In this case, assume 0 US
Homework (Ch 33) Attempts Average / 3 6. Why the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run In the short run, the quantity of output supplied by firms can deviate from the natural level of output if the actual price level deviates from the expected price level in the economy. A number of theories explain reasons why this might happen. For example, the sticky-price theory asserts that the output prices of some goods and services adjust slowly to changes in the price level. Suppose firms announce the prices for their products in advance, based on an expected price level of 100 for the coming year. Many of the firms sell their goods through catalogs and face high costs of reprinting if they change prices. The actual price level turns out to be 90. Faced with high menu costs, the firms that rely on catalog sales choose not to adjust their prices. Sales from catalogs will ▼ , and firms that rely on catalogs will respond by the quantity of output they supply. If enough firms face high costs of adjusting prices, the unexpected decrease in the price level causes the quantity of output supplied to the natural level of output in the short run. Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate su exceed fall short of ve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = Natural Level of Output + ax (Price Level Actual - Price Level Expected) The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. In this case, assume 0 US
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter15: Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PA
Related questions
Question
100%
The short-run quantity of output supplied by firms will exceed the natural level of output when the actual price level ———-that people expected.
Transcribed Image Text:Homework (Ch 33)
Attempts
Average / 3
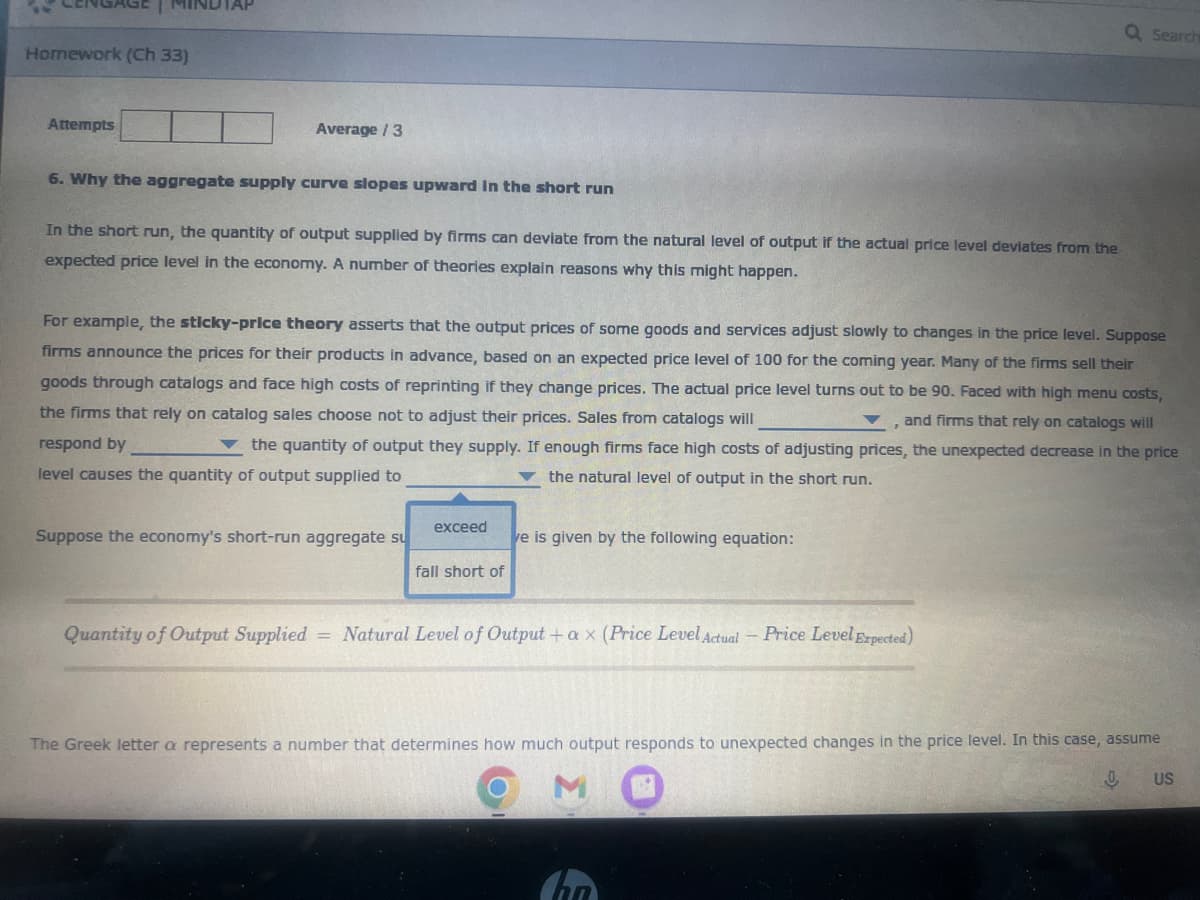
6. Why the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run
In the short run, the quantity of output supplied by firms can deviate from the natural level of output if the actual price level deviates from the
expected price level in the economy. A number of theories explain reasons why this might happen.
For example, the sticky-price theory asserts that the output prices of some goods and services adjust slowly to changes in the price level. Suppose
firms announce the prices for their products in advance, based on an expected price level of 100 for the coming year. Many of the firms sell their
goods through catalogs and face high costs of reprinting if they change prices. The actual price level turns out to be 90. Faced with high menu costs,
the firms that rely on catalog sales choose not to adjust their prices. Sales from catalogs will
▼ and firms that rely on catalogs will
respond by
the quantity of output they supply. If enough firms face high costs of adjusting prices, the unexpected decrease in the price
level causes the quantity of output supplied to
the natural level of output in the short run.
Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate su
exceed
fall short of
ve is given by the following equation:
Q Search
Quantity of Output Supplied = Natural Level of Output + ax (Price Level Actual - Price Level Expected)
The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. In this case, assume
0
US
Transcribed Image Text:CENGAGE MINDTAP
Homework (Ch 33)
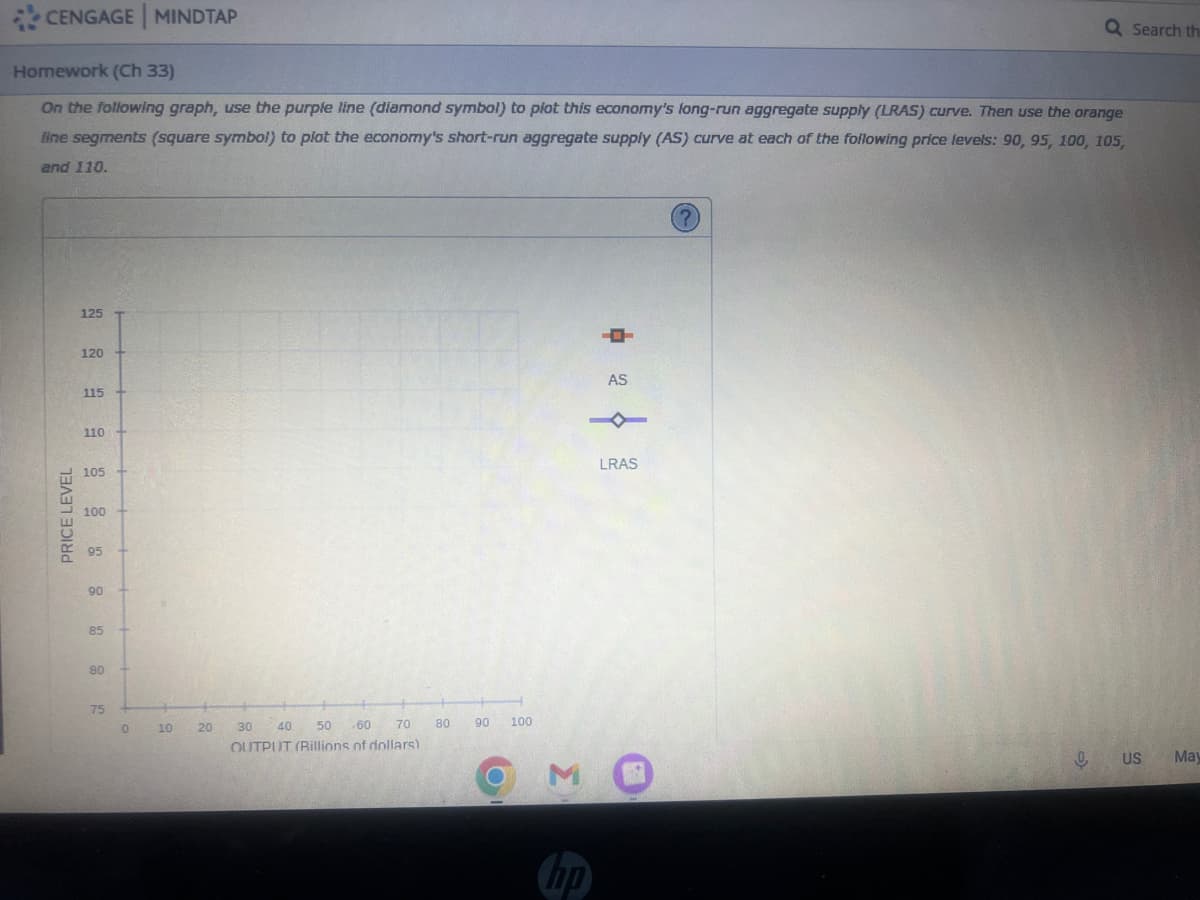
On the following graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to plot this economy's long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve. Then use the orange
line segments (square symbol) to plot the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve at each of the following price levels: 90, 95, 100, 105,
and 110.
PRICE LEVEL
125
120
115 +
110 +
105
100
95
90
85
80
75
0
10
20
30
50
60
70
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
40
80
90
100
3
AS
LRAS
Q Search th
(?)
0 US
May
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506756
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
