How do the fares for airlines that directly compete compare? The accompanying table contains roundtrip fares for nonstop travel from a particular city to 10 different destinations in the same country on two airlines that a frequent flyer collected. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Click the icon to view the data on roundtrip airline fares. a. At the 0.10 level of significance, is there evidence of a difference in mean roundtrip fare between Airline A and Airline B? Let μ₁ be the mean roundtrip fares for Airline A, and let µ₂ be the mean roundtrip fares for Airline B. What are the correct null and alternative hypotheses? A. Ho: HD 0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD #0 B. Ho: HD >0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD ≤0 C. Ho: HD 20 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD <0 D. Ho: HD <0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD 20 E. Ho: HD #0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) - F. Ho: HD ≤0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD > 0 H₁: HD = 0 What is the test statistic? tSTAT = (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
How do the fares for airlines that directly compete compare? The accompanying table contains roundtrip fares for nonstop travel from a particular city to 10 different destinations in the same country on two airlines that a frequent flyer collected. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Click the icon to view the data on roundtrip airline fares. a. At the 0.10 level of significance, is there evidence of a difference in mean roundtrip fare between Airline A and Airline B? Let μ₁ be the mean roundtrip fares for Airline A, and let µ₂ be the mean roundtrip fares for Airline B. What are the correct null and alternative hypotheses? A. Ho: HD 0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD #0 B. Ho: HD >0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD ≤0 C. Ho: HD 20 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD <0 D. Ho: HD <0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD 20 E. Ho: HD #0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) - F. Ho: HD ≤0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂) H₁: HD > 0 H₁: HD = 0 What is the test statistic? tSTAT = (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
What is the 1.test statistic and 2. p-value for this test statistics?
The test is a two-tailed test.

Transcribed Image Text:How do the fares for airlines that directly compete compare? The accompanying table contains roundtrip fares for
nonstop travel from a particular city to 10 different destinations in the same country on two airlines that a frequent flyer
collected. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
Click the icon to view the data on roundtrip airline fares.
...
a. At the 0.10 level of significance, is there evidence of a difference in mean roundtrip fare between Airline A and Airline
B?
Let μ₁ be the mean roundtrip fares for Airline A, and let μ₂ be the mean roundtrip fares for Airline B. What are the correct
null and alternative hypotheses?
A. Ho: HD 0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂)
B. Ho: HD >0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂)
H₁: HD ≤0
H₁: HD #0
≥0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂)
Ho: HD
H₁ HD <0
Ho: HD <0 (where μ = μ₁ −μ₂)
H₁: HD 20
E. Ho: HD #0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂)
F. Ho: HD ≤0 (where μD = μ₁ −μ₂)
H₁: HD
= 0
H₁: HD > 0
What is the test statistic?
=
tSTAT (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
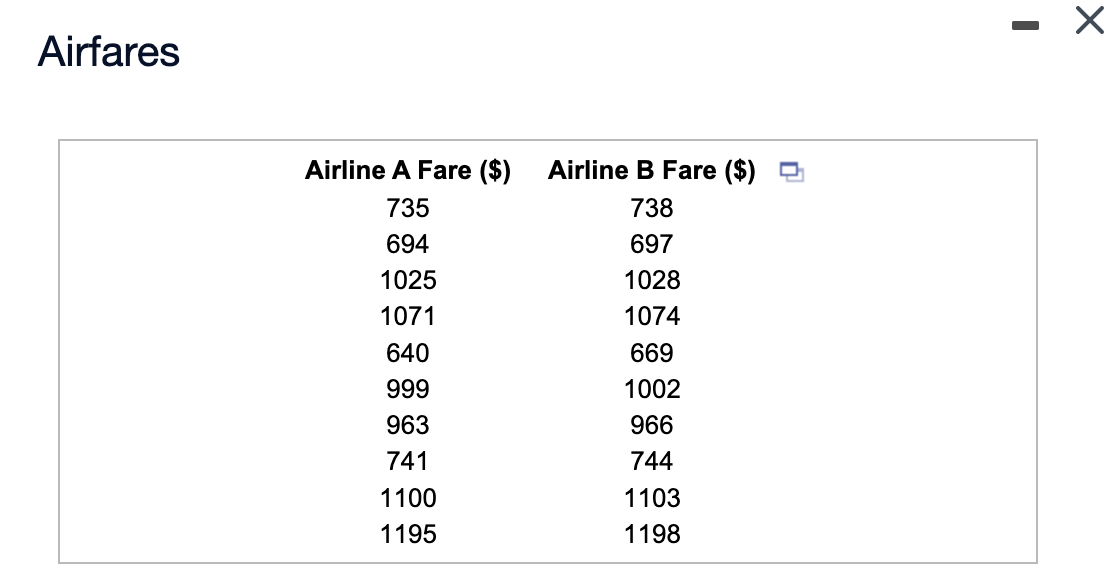
Transcribed Image Text:Airfares
Airline A Fare ($)
735
694
1025
1071
640
999
963
741
1100
1195
Airline B Fare ($)
738
697
1028
1074
669
1002
966
744
1103
1198
I
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill