I Review I Constants I Periodic Table In addition to mass balance, oxidation-reduction reactions must be balanced such that the number Acidic solution of electrons lost in the oxidation equals the number of electrons gained in the reduction. This balancing can be done by two methods: the half-reaction In acidic solution, the iodate ion can be used to react with a number of metal ions. One such reaction is IO3 (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)→I¯(aq)+ Sn*+ (aq) method or the oxidation number method. The half- reaction method balances the electrons lost in the Since this reaction takes place in acidic solution, H2O(1) and H (aq) will be involved in the reaction. Places oxidation half-reaction with the electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction. In either method for these species are indicated by the blanks in the following restatement of the equation: H2O(1), OH-(aq), and H+ (aq) may be added IO3 (aq) + Sn2+(aq) +_→I-(aq) + Snt+ (aq) + to complete the mass balance. Which substances are used depends on the reaction conditions. Part A What are the coefficients of the reactants and products in the balanced equation above? Remember to include H2O(1) and H* (aq) in the appropriate blanks. Your answer should have six terms. Enter the equation coefficients in order separated by commas (e.g., 2,2,1,4,4,3). Include coefficients of 1, as required, for grading purposes. • View Available Hint(s) Submit Basic solution Potassium permanganate, KMNO4, is a powerful oxidizing agent. The products of a given redox reaction with the permanganate ion depend on the reaction conditions used. In basic solution, the following equation represents the reaction of this ion with a solution containing sodium fluoride: MnO4 (aq) + F (aq)→MnO2 (s)+F2 (aq)
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table In addition to mass balance, oxidation-reduction reactions must be balanced such that the number Acidic solution of electrons lost in the oxidation equals the number of electrons gained in the reduction. This balancing can be done by two methods: the half-reaction In acidic solution, the iodate ion can be used to react with a number of metal ions. One such reaction is IO3 (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)→I¯(aq)+ Sn*+ (aq) method or the oxidation number method. The half- reaction method balances the electrons lost in the Since this reaction takes place in acidic solution, H2O(1) and H (aq) will be involved in the reaction. Places oxidation half-reaction with the electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction. In either method for these species are indicated by the blanks in the following restatement of the equation: H2O(1), OH-(aq), and H+ (aq) may be added IO3 (aq) + Sn2+(aq) +_→I-(aq) + Snt+ (aq) + to complete the mass balance. Which substances are used depends on the reaction conditions. Part A What are the coefficients of the reactants and products in the balanced equation above? Remember to include H2O(1) and H* (aq) in the appropriate blanks. Your answer should have six terms. Enter the equation coefficients in order separated by commas (e.g., 2,2,1,4,4,3). Include coefficients of 1, as required, for grading purposes. • View Available Hint(s) Submit Basic solution Potassium permanganate, KMNO4, is a powerful oxidizing agent. The products of a given redox reaction with the permanganate ion depend on the reaction conditions used. In basic solution, the following equation represents the reaction of this ion with a solution containing sodium fluoride: MnO4 (aq) + F (aq)→MnO2 (s)+F2 (aq)
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Chapter5: Gases, Liquids, And Solids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.21P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:11:23 Mon May 3
Done <
AA
A session.masteringchemistry.com
<Problem Set #9 (Ch 19) Adaptive Follow-Up
Balancing Redox Equations: Half-reaction Method
Item 4
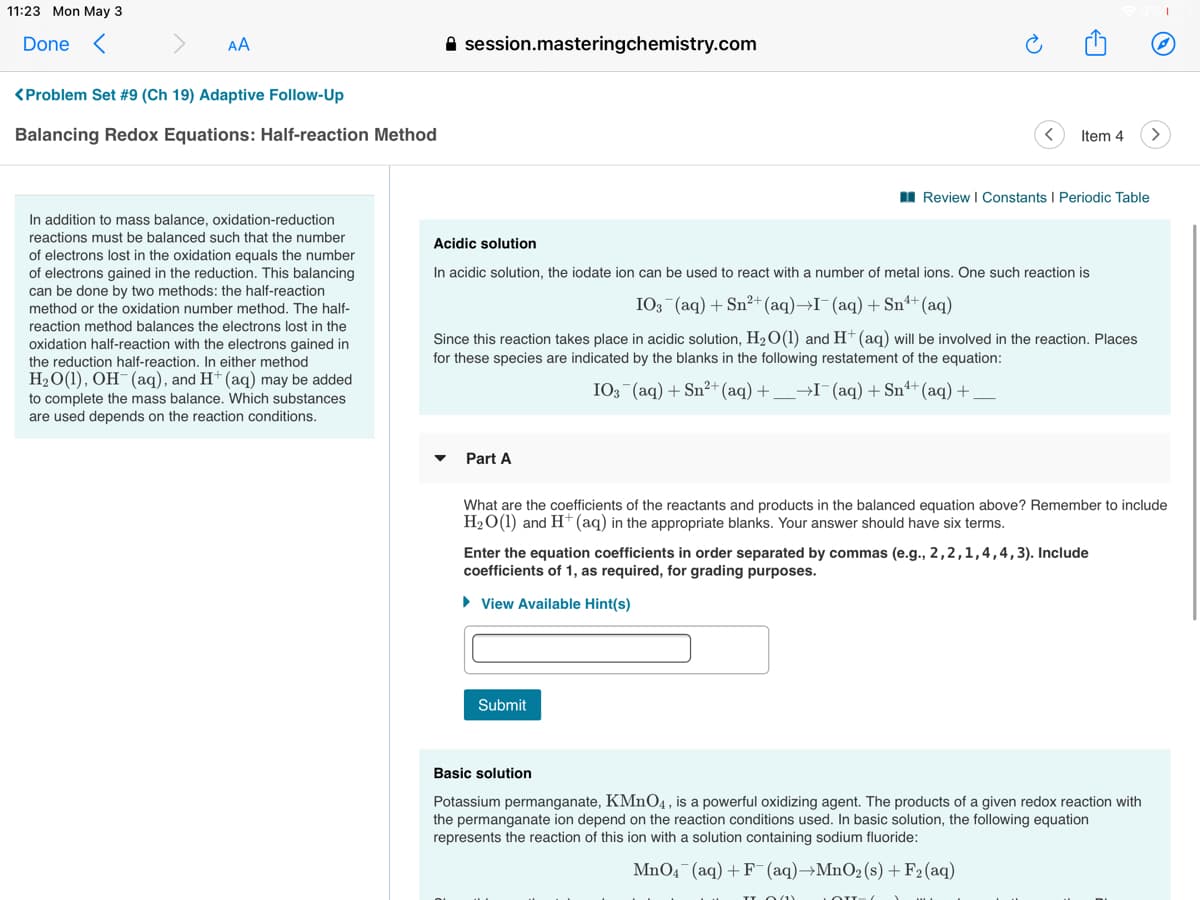
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table
In addition to mass balance, oxidation-reduction
reactions must be balanced such that the number
Acidic solution
of electrons lost in the oxidation equals the number
of electrons gained in the reduction. This balancing
can be done by two methods: the half-reaction
In acidic solution, the iodate ion can be used to react with a number of metal ions. One such reaction is
method or the oxidation number method. The half-
IO3 (aq) + Sn²+(aq)→I¯(aq)+Snª+(aq)
reaction method balances the electrons lost in the
oxidation half-reaction with the electrons gained in
the reduction half-reaction. In either method
H2O(1), OH-(aq), and H+ (aq) may be added
Since this reaction takes place in acidic solution, H2O(1) and H (aq) will be involved in the reaction. Places
for these species are indicated by the blanks in the following restatement of the equation:
I03 (aq) + Sn²+ (aq) +_→I¯(aq) + Snª+ (aq) +
to complete the mass balance. Which substances
are used depends on the reaction conditions.
Part A
What are the coefficients of the reactants and products in the balanced equation above? Remember to include
H2O(1) and H* (aq) in the appropriate blanks. Your answer should have six terms.
Enter the equation coefficients in order separated by commas (e.g., 2,2,1,4,4,3). Include
coefficients of 1, as required, for grading purposes.
• View Available Hint(s)
Submit
Basic solution
Potassium permanganate, KMNO4, is a powerful oxidizing agent. The products of a given redox reaction with
the permanganate ion depend on the reaction conditions used. In basic solution, the following equation
represents the reaction of this ion with a solution containing sodium fluoride:
MnO4 (aq) + F (aq)→MnO2(s)+F2(aq)
Transcribed Image Text:11:23 Mon May 3
Done <
AA
A session.masteringchemistry.com
<Problem Set #9 (Ch 19) Adaptive Follow-Up
Balancing Redox Equations: Half-reaction Method
Item 4
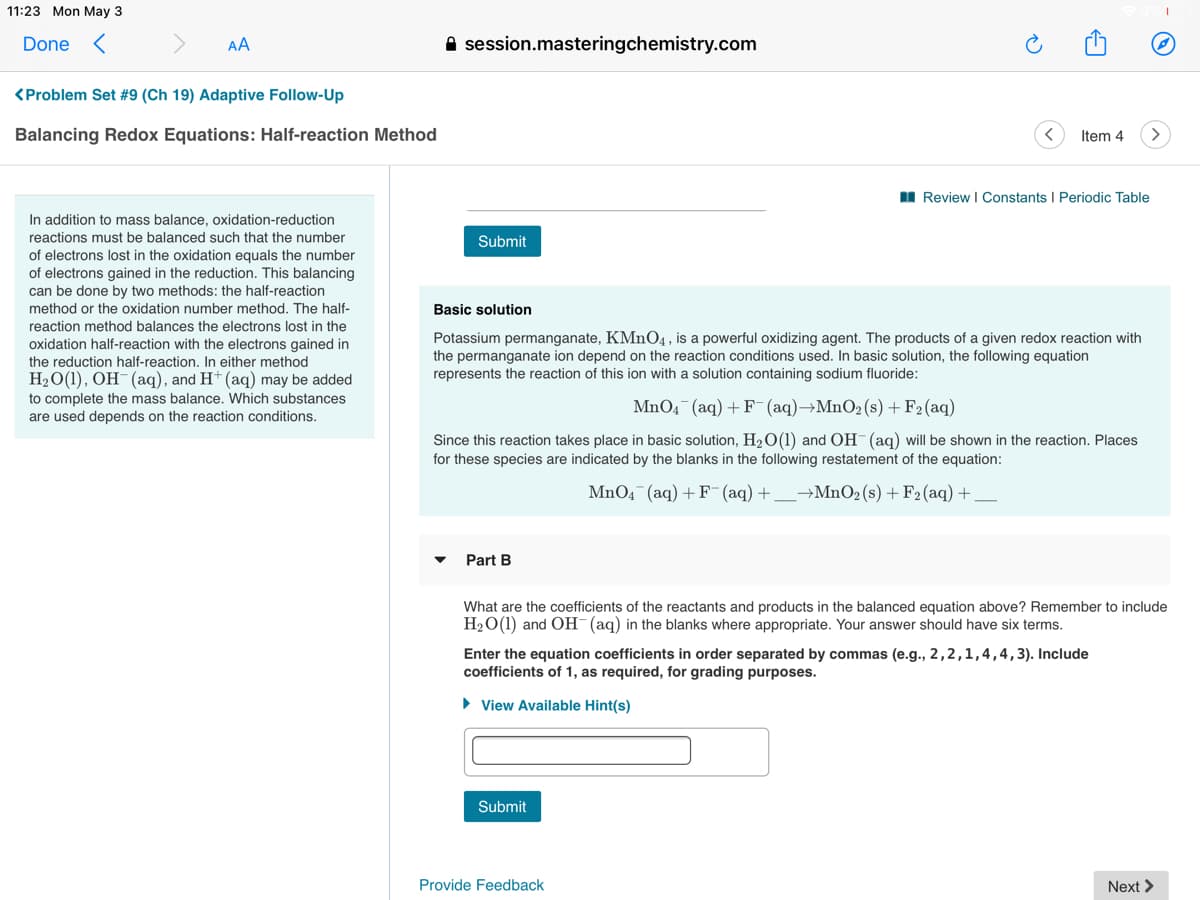
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table
In addition to mass balance, oxidation-reduction
reactions must be balanced such that the number
Submit
of electrons lost in the oxidation equals the number
of electrons gained in the reduction. This balancing
can be done by two methods: the half-reaction
method or the oxidation number method. The half-
Basic solution
reaction method balances the electrons lost in the
oxidation half-reaction with the electrons gained in
the reduction half-reaction. In either method
H2O(1), OH-(aq), and H+ (aq) may be added
Potassium permanganate, KMN04, is a powerful oxidizing agent. The products of a given redox reaction with
the permanganate ion depend on the reaction conditions used. In basic solution, the following equation
represents the reaction of this ion with a solution containing sodium fluoride:
to complete the mass balance. Which substances
MnO4¯(aq) + F¯ (aq)→MnO2(s) + F2(aq)
are used depends on the reaction conditions.
Since this reaction takes place in basic solution, H2O(1) and OH (aq) will be shown in the reaction. Places
for these species are indicated by the blanks in the following restatement of the equation:
MnO4 (aq) + F (aq) +
→MnO2 (s) + F2 (aq) +
Part B
What are the coefficients of the reactants and products in the balanced equation above? Remember to include
H2O(1) and OH (aq) in the blanks where appropriate. Your answer should have six terms.
Enter the equation coefficients in order separated by commas (e.g., 2,2,1,4,4,3). Include
coefficients of 1, as required, for grading purposes.
• View Available Hint(s)
Submit
Provide Feedback
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning