I1. A force parallel to the x-axis acts on a particle moving along the x-axis. This force produces potential energy given by U(x) = ax where a = 1.20]/m*. What is the force (magnitude and direction) when the particle is at x = -0.80m?
I1. A force parallel to the x-axis acts on a particle moving along the x-axis. This force produces potential energy given by U(x) = ax where a = 1.20]/m*. What is the force (magnitude and direction) when the particle is at x = -0.80m?
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter7: Conservation Of Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 55P: A horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant of k = 850 N/m. A block of mass m = 1.00...
Related questions
Question
How can I solve this question?
![11. A force parallel to the x-axis acts on a particle moving along the x-axis. This force produces
potential energy given by U(x) = ax* where a = 1.20]/m*. What is the force (magnitude and
direction) when the particle is at x = -0.80m?
12. A marble moves along the x-axis. The potential-energy function is
shown in Figure. (a) at which of the labeled x-coordinates is the force
on the marble zero? (b) Which of the labeled x-coordinates is a
position of stable equilibrium? (c) Which of the labeled x-
coordinates is a position of unstable equilibrium?
U0)
4.0
2.0
ds
(m)
150 2.5
-2.0
13. Figure below showing potential energy function of a particle. Rank the magnitude of force in the
region AB, CD, EF and GH. What value must the total mechanical energy Ene of the particle not
exceed if the particle is to be trapped between A and D?
AB
GH
Power
14. In three situations a single force acts on a moving particle. Here are the velocities and forces:
(i)
i = (-4) m/s and F = (61 – 205) N;
(ii) i = (2i – 3) m/s and F = (-2j + 7k) N;
(iii) i = (-31 + ) m/s and F = (21 + 6) N:
Rank the situations according to the rate at which energy is being transferred, highest to lowest.
15. What is the resistive force on a cyclist who has leg muscles of power 200
W each and who reaches a top speed of 10 ms' on a level road?](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F6d9decaf-6300-435c-b1de-335061c858b3%2F6af37cd9-e8fb-4a09-889a-6b18a80c5ab8%2F0s6zo3_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:11. A force parallel to the x-axis acts on a particle moving along the x-axis. This force produces
potential energy given by U(x) = ax* where a = 1.20]/m*. What is the force (magnitude and
direction) when the particle is at x = -0.80m?
12. A marble moves along the x-axis. The potential-energy function is
shown in Figure. (a) at which of the labeled x-coordinates is the force
on the marble zero? (b) Which of the labeled x-coordinates is a
position of stable equilibrium? (c) Which of the labeled x-
coordinates is a position of unstable equilibrium?
U0)
4.0
2.0
ds
(m)
150 2.5
-2.0
13. Figure below showing potential energy function of a particle. Rank the magnitude of force in the
region AB, CD, EF and GH. What value must the total mechanical energy Ene of the particle not
exceed if the particle is to be trapped between A and D?
AB
GH
Power
14. In three situations a single force acts on a moving particle. Here are the velocities and forces:
(i)
i = (-4) m/s and F = (61 – 205) N;
(ii) i = (2i – 3) m/s and F = (-2j + 7k) N;
(iii) i = (-31 + ) m/s and F = (21 + 6) N:
Rank the situations according to the rate at which energy is being transferred, highest to lowest.
15. What is the resistive force on a cyclist who has leg muscles of power 200
W each and who reaches a top speed of 10 ms' on a level road?
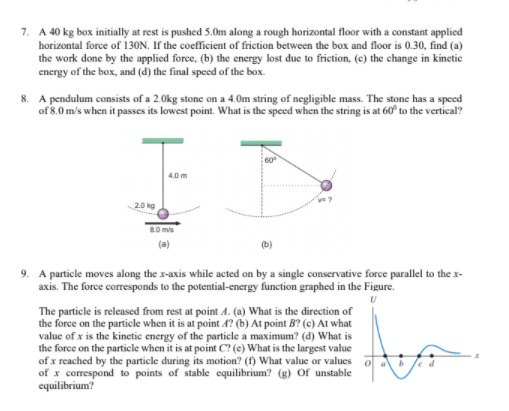
Transcribed Image Text:7. A 40 kg box initially at rest is pushed 5.0m along a rough horizontal floor with a constant applied
horizontal force of 130N. If the coefficient of friction between the box and floor is 0.30, find (a)
the work done by the applied force, (b) the energy lost due to friction, (e) the change in kinetic
energy of the box, and (d) the final speed of the box.
8. A pendulum consists of a 2.0kg stone on a 4.0m string of negligible mass. The stone has a speed
of 8.0 m/s when it passes its lowest point. What is the speed when the string is at 60° to the vertical?
60
4.0 m
20 kg
80 mis
(a)
(b)
9. A particle moves along the x-axis while acted on by a single conservative force parallel to the x-
axis. The force coresponds to the potential-energy function graphed in the Figure.
The particle is released from rest at point A. (a) What is the direction of
the force on the particle when it is at point A? (b) At point B? (c) At what
value of x is the kinetic energy of the particle a maximum? (d) What is
the force on the particle when it is at point C? (e) What is the largest value
of x reached by the particle during its motion? (f) What value or values
of x correspond to points of stable equilibrium? (g) Of unstable
equilibrium?
ed
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning