If she can visit only one of the stores, which one would she go and what would be her optimal bundle there? Could she afford this very bundle at the other store? (b) If she can freely visit both stores, (buying each commodity from the store where it is cheaper !!) what would be her optimal bundle? What would she buy from each store? (c) Back to (a), how much money would she willing to give up (out of her $720 budget) for the ability to visit both stores rather than only one store? (HINT: After giving up that money, she is left with less money with which optimizing utility with the option of visiting both stores -buying each commodity from the cheaper store- she is able to achieve the same level of utility in the scenario with the original uncut budget but having to choose only one of the stores to shop at)
question as image
a. If she can visit only one of the stores, which one would she go and what would be her optimal bundle there? Could she afford this very bundle at the other store?
(b) If she can freely visit both stores, (buying each commodity from the store where it is cheaper !!) what would be her optimal bundle? What would she buy from each store?
(c) Back to (a), how much money would she willing to give up (out of her $720 budget) for the ability to visit both stores rather than only one store? (HINT: After giving up that money, she is left with less money with which optimizing utility with the option of visiting both stores -buying each commodity from the cheaper store- she is able to achieve the same level of utility in the scenario with the original uncut budget but having to choose only one of the stores to shop at)
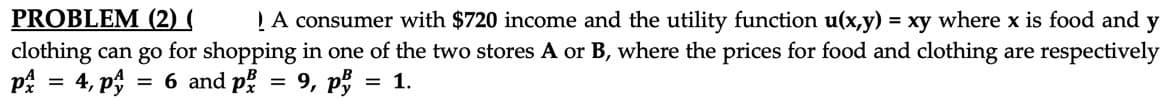
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









