If young children have an illness that causes diarrhea and vomiting, they can quickly become seriously ill from dehydration and the loss of sodium and other vital chemicals. Rehydration solutions contain sodium along with chemicals to help the intestine absorb the sodium. The table below lists the solutes in a rehydration solution that is designed for children. Calculate the mass/volume percent concentration of the potassium citrate in the rehydration solution? Calculate the concentration of sodium citrate in parts per million? Calculate the molar concentration of dextrose? Calculate the molar concentration of sodium ions from the sodium citrate? Calculate the total molar concentration of sodium ions in the entire solution?
If young children have an illness that causes diarrhea and vomiting, they can quickly become seriously ill from dehydration and the loss of sodium and other vital chemicals. Rehydration solutions contain sodium along with chemicals to help the intestine absorb the sodium. The table below lists the solutes in a rehydration solution that is designed for children. Calculate the mass/volume percent concentration of the potassium citrate in the rehydration solution? Calculate the concentration of sodium citrate in parts per million? Calculate the molar concentration of dextrose? Calculate the molar concentration of sodium ions from the sodium citrate? Calculate the total molar concentration of sodium ions in the entire solution?
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter17: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 80AP
Related questions
Question
If young children have an illness that causes diarrhea and vomiting, they can quickly become seriously ill from dehydration and the loss of sodium and other vital chemicals. Rehydration solutions contain sodium along with chemicals to help the intestine absorb the sodium. The table below lists the solutes in a rehydration solution that is designed for children.
Calculate the mass/volume percent concentration of the potassium citrate in the rehydration solution?
Calculate the concentration of sodium citrate in parts per million?
Calculate the molar concentration of dextrose?
Calculate the molar concentration of sodium ions from the sodium citrate?
Calculate the total molar concentration of sodium ions in the entire solution?
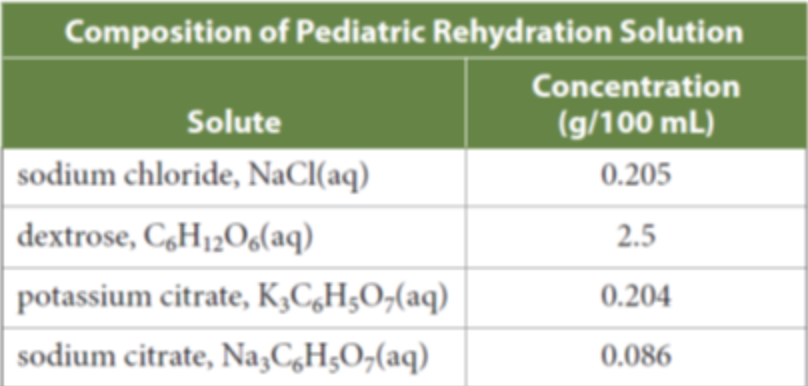
Transcribed Image Text:Composition of Pediatric Rehydration Solution
Concentration
Solute
(g/100 mL)
sodium chloride, NaCl(aq)
0.205
|dextrose, C,H12O6(aq)
2.5
potassium citrate, K,C,H;O,(aq)
0.204
sodium citrate, Na,C,H;O,(aq)
0.086
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning