Imagine that a different researcher looks at these results and disagrees with them, arguing that happy people tend to listen to more prosocial music than unhappy people, and they also tend to be more cooperative. How might Greitemeyer respond to this criticism? O a. You're right, I hadn't considered this alternative explanation. O b. You're right, correlation is not causation. O c. Because I manipulated the IV, I ruled out this alternative explanation. O d. Because I randomized participants to condition, I ruled out this alternative explanation.
Imagine that a different researcher looks at these results and disagrees with them, arguing that happy people tend to listen to more prosocial music than unhappy people, and they also tend to be more cooperative. How might Greitemeyer respond to this criticism? O a. You're right, I hadn't considered this alternative explanation. O b. You're right, correlation is not causation. O c. Because I manipulated the IV, I ruled out this alternative explanation. O d. Because I randomized participants to condition, I ruled out this alternative explanation.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13PT
Related questions
Question
A1
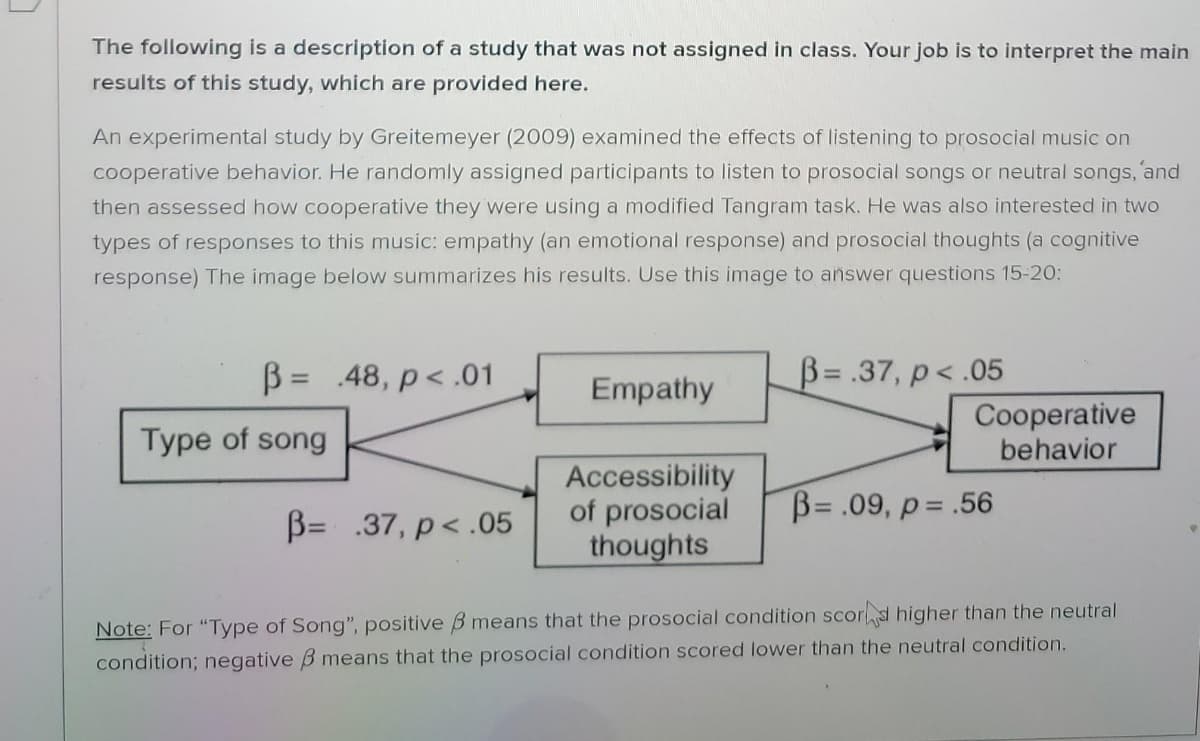
Transcribed Image Text:The following is a description of a study that was not assigned in class. Your job is to interpret the main
results of this study, which are provided here.
An experimental study by Greitemeyer (2009) examined the effects of listening to prosocial music on
cooperative behavior. He randomly assigned participants to listen to prosocial songs or neutral songs, and
then assessed how cooperative they were using a modified Tangram task. He was also interested in two
types of responses to this music: empathy (an emotional response) and prosocial thoughts (a cognitive
response) The image below summarizes his results. Use this image to answer questions 15-20:
B = .48, p< .01
B= .37, p< .05
%D
Empathy
Type of song
Cooperative
behavior
Accessibility
of prosocial
thoughts
B= .09, p= .56
B= .37, p< .05
Note: For "Type of Song", positive B means that the prosocial condition scor d higher than the neutral
condition; negative B means that the prosocial condition scored lower than the neutral condition.
Transcribed Image Text:Question 19
Imagine that a different researcher looks at these results and disagrees with them, arguing that happy
people tend to listen to more prosocial music than unhappy people, and they also tend to be more
cooperative. How might Greitemeyer respond to this criticism?
O a. You're right, I hadn't considered this alternative explanation.
b. You're right, correlation is not causation.
O c. Because I manipulated the IV, I ruled out this alternative explanation.
O d. Because I randomized participants to condition, I ruled out this alternative explanation.
Question 2O
Imagine that a different researcher looks at these results and remains unconinced by the measure of
cooperative behavior. She does not think that a "modified Tangram task" approximates any form of real
cooperative behavior that people care about in everyday life. This researcher is questioning the
of this study.
O a. internal validity
O b. external validity
O c. IV manipulation
O d. statistical significance
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL