In radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine atoms at different rates. At 35 C, prim These are conditions of kinetic control where product ratios are determined by relative rates of formation. For example, Consider chlorination of the alkane below at 35 °C. 1. Specify the most reactive C-H bonist), a. Two non-equivalent C-H bonds of comparable reactivity ahould be separated by commas, ie a.c. 2. Specify the site of chlorination in the major monochloro substitution product, a-c. Two products that form in comparable quantities should be separated by commas, 1e. a,c
In radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine atoms at different rates. At 35 C, prim These are conditions of kinetic control where product ratios are determined by relative rates of formation. For example, Consider chlorination of the alkane below at 35 °C. 1. Specify the most reactive C-H bonist), a. Two non-equivalent C-H bonds of comparable reactivity ahould be separated by commas, ie a.c. 2. Specify the site of chlorination in the major monochloro substitution product, a-c. Two products that form in comparable quantities should be separated by commas, 1e. a,c
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter8: Haloalkanes, Halogenation, And Radical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.18P
Related questions
Question
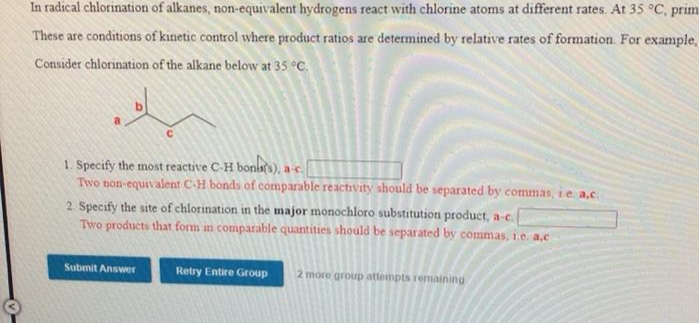
Transcribed Image Text:In radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine atoms at different rates. At 35 °C, prim
These are conditions of kinetic control where product ratios are determined by relative rates of formation. For example,
Consider chlorination of the alkane below at 35 °C.
1. Specify the most reactive C-H bonas), a-c.
Two non-equivalent C-H bonds of comparable reactivity should be separated by commas, i.e a.c.
2. Specify the site of chlorination in the major monochloro substitution product, a-c.
Two products that form in comparable quantities should be separated by commas, 1.e. a.c
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
2 more group attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577190
Author:
Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:
Brooks Cole


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577190
Author:
Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:
Brooks Cole
