In the short-run, we assume that capital is a fixed input and labor is a variable input, so the firm can increase output only by increasing the amount of labor it uses. In the short-run, the firm's production function is q = f(L, K), where q is output, L is workers, and K is the fixed number of units of capital. Given a specific equation for production: or, when K = 29, Calculate the q = 8LK+ 5L² (3) ²³ q= (8L x 29) + 5L² · 52² - (37) ₁³. Average Product = q and enter the values in the table to the right. (Round your answers to the nearest integer.) Labor 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Production Output or Marginal Product Product 0 481 987 1,500 2,005 2487 2,928 241 253 257 253 241 221 Average Product 241 247 251 249
In the short-run, we assume that capital is a fixed input and labor is a variable input, so the firm can increase output only by increasing the amount of labor it uses. In the short-run, the firm's production function is q = f(L, K), where q is output, L is workers, and K is the fixed number of units of capital. Given a specific equation for production: or, when K = 29, Calculate the q = 8LK+ 5L² (3) ²³ q= (8L x 29) + 5L² · 52² - (37) ₁³. Average Product = q and enter the values in the table to the right. (Round your answers to the nearest integer.) Labor 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Production Output or Marginal Product Product 0 481 987 1,500 2,005 2487 2,928 241 253 257 253 241 221 Average Product 241 247 251 249
Chapter9: Production Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.8P
Related questions
Question
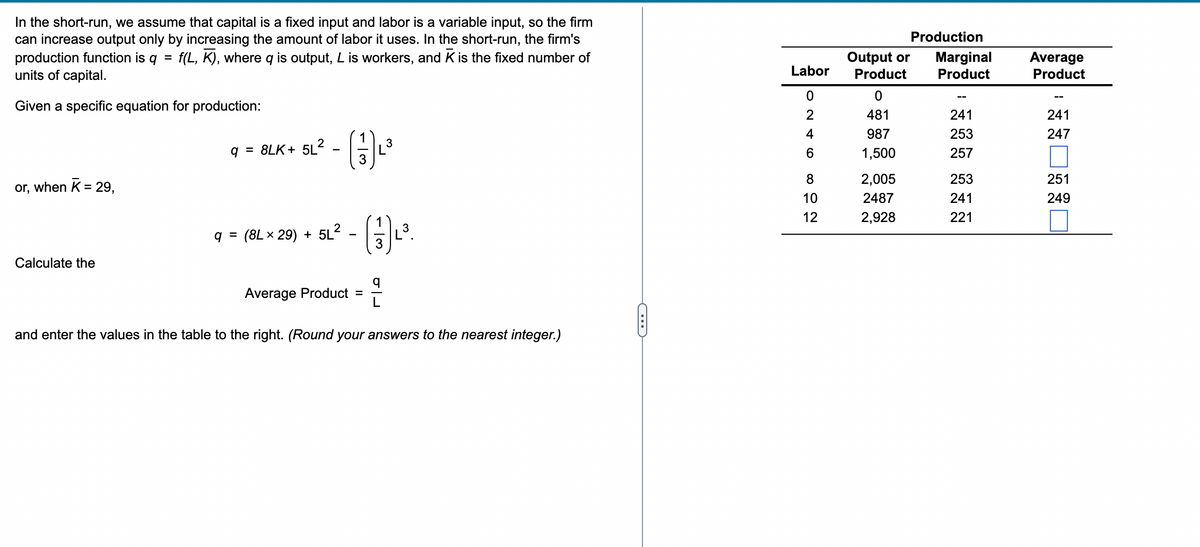
Transcribed Image Text:In the short-run, we assume that capital is a fixed input and labor is a variable input, so the firm
can increase output only by increasing the amount of labor it uses. In the short-run, the firm's
production function is q = f(L, K), where is output, L is workers, and K is the fixed number of
units of capital.
Given a specific equation for production:
or, when K = 29,
Calculate the
q = 8LK+ 5L²
q =
(8L × 29) + 5L²
X
-
Average Product =
3
(13) ₁³.
102
and enter the values in the table to the right. (Round your answers to the nearest integer.)
E
Labor
624
0
6
8
10
12
Output or
Product
0
481
987
1,500
2,005
2487
2,928
Production
Marginal
Product
--
241
253
257
253
241
221
Average
Product
--
241
247
251
249
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
