In triathlons, it is common for racers to be placed into age and gender groups. Friends Leo and Mary both completed the Hermosa Beach Triathlon: • Leo competed in the Men, Ages 30 - 34 group and completed the race 1:22:28 (4948 seconds), while the finishing times of his group had a mean of 4313 seconds and standard deviation of 583 seconds. • Mary completed in the Women, Ages 25 - 29 group and completed the race in 1:31:53 (5513 seconds), while the finishing times of her group had a mean of 5261 seconds and standard deviation of 807 seconds. Obviously Leo finished faster, but they are curious about how they did within their respective groups. Can you help them? You may assume the distributions of finishing times for both groups are approximately Normal. (Remember: a better performance corresponds to a faster finish.) a) What is the Z score for Leo's finishing time? 1.089 b) What is the Z score for Mary's finishing time? .312 c) Did Leo or Mary rank better in their respective groups? O Leo ranked better than Mary since his Z score was smaller. O Mary ranked better than Leo since her Z score was larger. O Mary ranked better than Leo since her Z score was smaller. O Leo ranked better than Mary since his Z score was larger. d) What proportion of the triathletes did Leo finish faster than in his group? e) What proportion of the triathletes did Mary finish faster than in her group? f) If the distributions of finishing times are not nearly normal, would your answers to parts (d) and (e) change? O Yes, the Z scores would not change, but we could not answer parts (d) and (e) since we cannot use the normalcdf command to calculate probabilities and percentiles without a normal model. O Yes, the Z scores would be different, so the answers from parts (d) and (e) would be different. O No, the Z scores would not change so the answers from parts (d) and (e) would stay the same.
In triathlons, it is common for racers to be placed into age and gender groups. Friends Leo and Mary both completed the Hermosa Beach Triathlon: • Leo competed in the Men, Ages 30 - 34 group and completed the race 1:22:28 (4948 seconds), while the finishing times of his group had a mean of 4313 seconds and standard deviation of 583 seconds. • Mary completed in the Women, Ages 25 - 29 group and completed the race in 1:31:53 (5513 seconds), while the finishing times of her group had a mean of 5261 seconds and standard deviation of 807 seconds. Obviously Leo finished faster, but they are curious about how they did within their respective groups. Can you help them? You may assume the distributions of finishing times for both groups are approximately Normal. (Remember: a better performance corresponds to a faster finish.) a) What is the Z score for Leo's finishing time? 1.089 b) What is the Z score for Mary's finishing time? .312 c) Did Leo or Mary rank better in their respective groups? O Leo ranked better than Mary since his Z score was smaller. O Mary ranked better than Leo since her Z score was larger. O Mary ranked better than Leo since her Z score was smaller. O Leo ranked better than Mary since his Z score was larger. d) What proportion of the triathletes did Leo finish faster than in his group? e) What proportion of the triathletes did Mary finish faster than in her group? f) If the distributions of finishing times are not nearly normal, would your answers to parts (d) and (e) change? O Yes, the Z scores would not change, but we could not answer parts (d) and (e) since we cannot use the normalcdf command to calculate probabilities and percentiles without a normal model. O Yes, the Z scores would be different, so the answers from parts (d) and (e) would be different. O No, the Z scores would not change so the answers from parts (d) and (e) would stay the same.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
I just need help with how to find the proportion part D and E please.
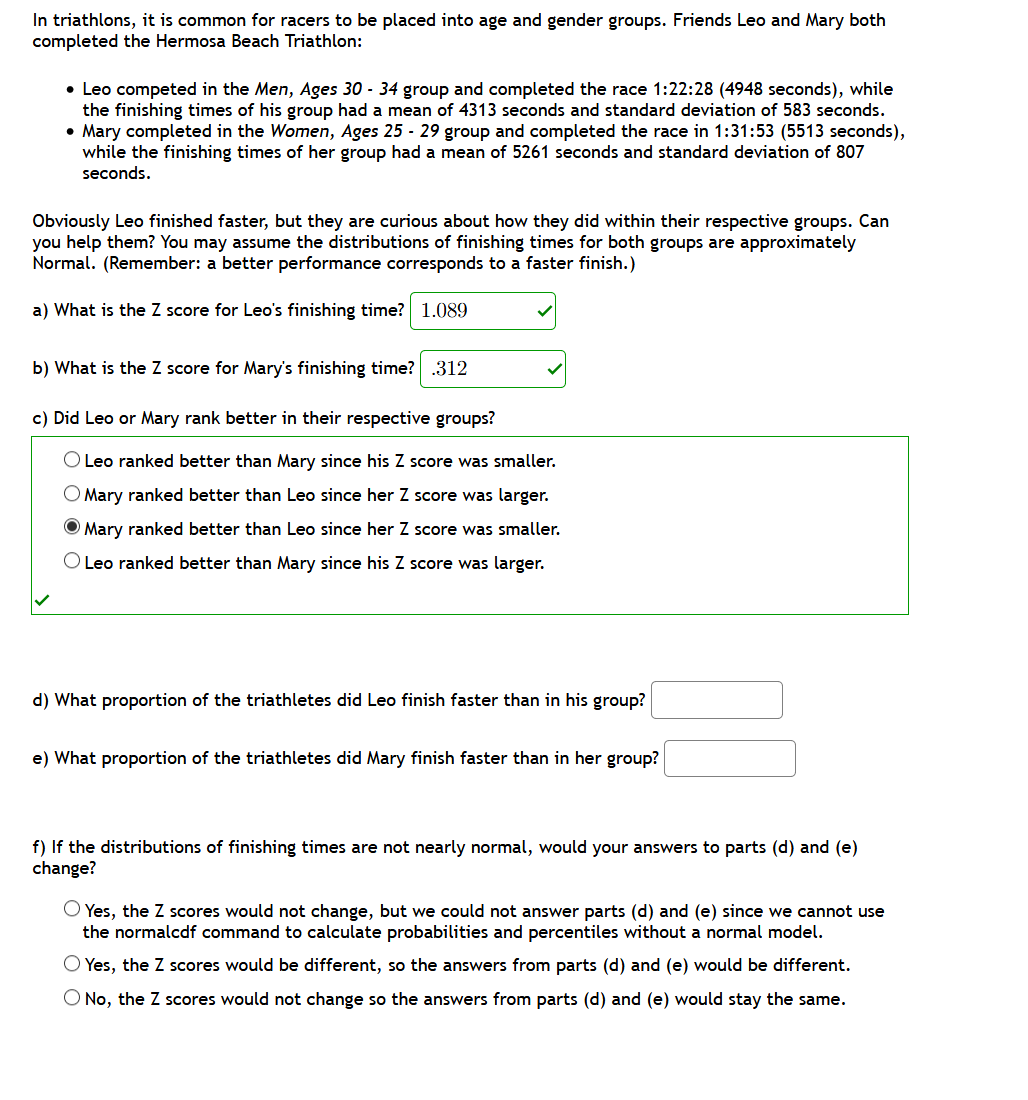
Transcribed Image Text:In triathlons, it is common for racers to be placed into age and gender groups. Friends Leo and Mary both
completed the Hermosa Beach Triathlon:
• Leo competed in the Men, Ages 30 - 34 group and completed the race 1:22:28 (4948 seconds), while
the finishing times of his group had a mean of 4313 seconds and standard deviation of 583 seconds.
• Mary completed in the Women, Ages 25 - 29 group and completed the race in 1:31:53 (5513 seconds),
while the finishing times of her group had a mean of 5261 seconds and standard deviation of 807
seconds.
Obviously Leo finished faster, but they are curious about how they did within their respective groups. Can
you help them? You may assume the distributions of finishing times for both groups are approximately
Normal. (Remember: a better performance corresponds to a faster finish.)
a) What is the Z score for Leo's finishing time? 1.089
b) What is the Z score for Mary's finishing time? .312
c) Did Leo or Mary rank better in their respective groups?
O Leo ranked better than
ary since his Z score
smaller.
Mary ranked better than Leo since her Z score was larger.
O Mary ranked better than Leo since her Z score was smaller.
O Leo ranked better than Mary since his Z score was larger.
d) What proportion of the triathletes did Leo finish faster than in his group?
e) What proportion of the triathletes did Mary finish faster than in her group?
f) If the distributions of finishing times are not nearly normal, would your answers to parts (d) and (e)
change?
O Yes, the Z scores would not change, but we could not answer parts (d) and (e) since we cannot use
the normalcdf command to calculate probabilities and percentiles without a normal model.
O Yes, the Z cores would be different, so the answers from parts (d) and (e) would be different.
O No, the Z scores would not change so the answers from parts (d) and (e) would stay the same.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill