In Version 4 of the Internet Protocol (IPV4), an IP address is a string of 32 bits. It begins with a network number (netid followed by a host number (hostid), which identifies a computer as a member of a particular network. Class A net id (7 bit) host id (24 bit) Class B 10 net id (14 bit) host id (16 bit) ClassC 110 net id (21 bit) host id (8 bit) Three forms of addresses are used, with different numbers of bits used for netids and hostids. Class A addresses, used for the largest networks, consist of 0, followed by a 7-bit netid and a 24-bit hostid. Class B addresses, used for medium-sized networks, consist of 10, followed by a 14-bit netid and a 16-bit hostid. Class C addresses, used for the smallest networks, consist of 110, followed by a 21-bit netid and an 8-bit hostid. There are several restrictions on addresses because of special uses: 1111111 is not available as the netid of a Class A network, and the hostids consisting of all Os and all 1s are not available for use in any network. A computer on the Internet has either a Class A, a Class B, or a Class C address. How many different IPV4 addresses are available for computers on the Internet?
In Version 4 of the Internet Protocol (IPV4), an IP address is a string of 32 bits. It begins with a network number (netid followed by a host number (hostid), which identifies a computer as a member of a particular network. Class A net id (7 bit) host id (24 bit) Class B 10 net id (14 bit) host id (16 bit) ClassC 110 net id (21 bit) host id (8 bit) Three forms of addresses are used, with different numbers of bits used for netids and hostids. Class A addresses, used for the largest networks, consist of 0, followed by a 7-bit netid and a 24-bit hostid. Class B addresses, used for medium-sized networks, consist of 10, followed by a 14-bit netid and a 16-bit hostid. Class C addresses, used for the smallest networks, consist of 110, followed by a 21-bit netid and an 8-bit hostid. There are several restrictions on addresses because of special uses: 1111111 is not available as the netid of a Class A network, and the hostids consisting of all Os and all 1s are not available for use in any network. A computer on the Internet has either a Class A, a Class B, or a Class C address. How many different IPV4 addresses are available for computers on the Internet?
Chapter12: Network Configuration
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13RQ
Related questions
Question
Discrete Structures or Discrete Mathematics
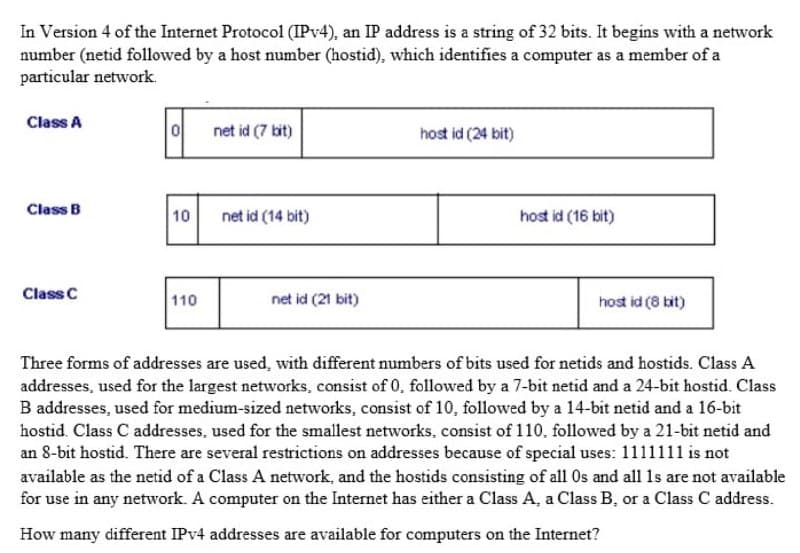
Transcribed Image Text:In Version 4 of the Internet Protocol (IPV4), an IP address is a string of 32 bits. It begins with a network
number (netid followed by a host number (hostid), which identifies a computer as a member of a
particular network.
Class A
|이
net id (7 bit)
host id (24 bit)
Class B
10
net id (14 bit)
host id (16 bit)
Class C
110
net id (21 bit)
host id (8 bit)
Three forms of addresses are used, with different numbers of bits used for netids and hostids. Class A
addresses, used for the largest networks, consist of 0, followed by a 7-bit netid and a 24-bit hostid. Class
B addresses, used for medium-sized networks, consist of 10, followed by a 14-bit netid and a 16-bit
hostid. Class C addresses, used for the smallest networks, consist of 110, followed by a 21-bit netid and
an 8-bit hostid. There are several restrictions on addresses because of special uses: 1111111 is not
available as the netid of a Class A network, and the hostids consisting of all 0s and all 1s are not available
for use in any network. A computer on the Internet has either a Class A, a Class B, or a Class C address.
How many different IPV4 addresses are available for computers on the Internet?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

LINUX+ AND LPIC-1 GDE.TO LINUX CERTIF.
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337569798
Author:
ECKERT
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

LINUX+ AND LPIC-1 GDE.TO LINUX CERTIF.
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337569798
Author:
ECKERT
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning