• Indicate whether there is a shortage (quantity demanded > quantity supplied) or a surplus (quantity supplied > quantity demanded) • Indicate the amount of the shortage or surplus. • Draw a graph and indicate the equilibrium on the graph. What is the EQ price?
• Indicate whether there is a shortage (quantity demanded > quantity supplied) or a surplus (quantity supplied > quantity demanded) • Indicate the amount of the shortage or surplus. • Draw a graph and indicate the equilibrium on the graph. What is the EQ price?
Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
14th Edition
ISBN:9781337794992
Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Chapter4: Supply And Demand: An Initial Look
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4TY: The following table summarizes information about the market for principles of economics textbooks:...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Imagine that you have opened a small business in your
school selling Italian ices. You make the ices from fresh
fruit – lemons, oranges, blueberries and cherries - using a
family recipe that your grandfather has passed along. You
are concerned about the price you pay for the fruit, as the
price you pay for the ingredients is reflected in the price
you charge your customers, and you are aware that there is
a limit to what your customers are willing to pay. Although
you would like to offer variety to your customers, if the
price of any of the fruits becomes too high, you will cut
back on your purchases, and offer less of that flavor to your
customers. The quantity of lemons you are willing to
purchase at various prices per bushel is presented in the
table below.
The lemon supplier obtains lemons directly from growers
in Al Ain and has a variety of customers that include
restaurants, supermarkets and fruit vendors.
The quantity of lemons you are willing to purchase and the
quantity of lemons the supplier is willing to offer at various
prices per bushel are presented in the table below:
Quantity supplied
(S)
Price per bushel
Quantity
demanded (D).
$40
20
60
$32
30
50
$24
40
40
$16
50
30
$8
60
20
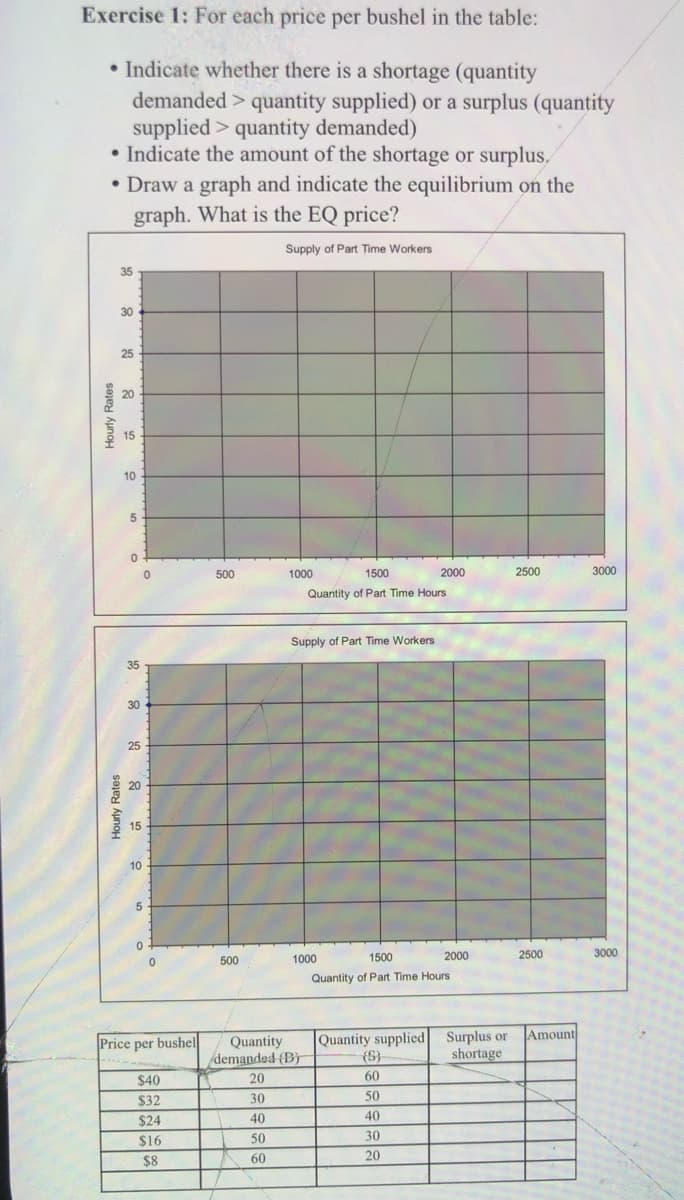
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise 1: For each price per bushel in the table:
• Indicate whether there is a shortage (quantity
demanded > quantity supplied) or a surplus (quantity
supplied > quantity demanded)
• Indicate the amount of the shortage or surplus,
• Draw a graph and indicate the equilibrium on the
graph. What is the EQ price?
Supply of Part Time Workers
35
30
25
20
15
10
5.
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
Quantity of Part Time Hours
Supply of Part Time Workers
35
30
25
20
15
10
1500
2000
2500
3000
500
1000
Quantity of Part Time Hours
Quantity supplied Surplus or
shortage
Amount
Quantity
demanded-(B)
Price per bushel
$40
20
60
$32
30
50
$24
40
40
$16
50
30
$8
60
20
Hourly Rates
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


