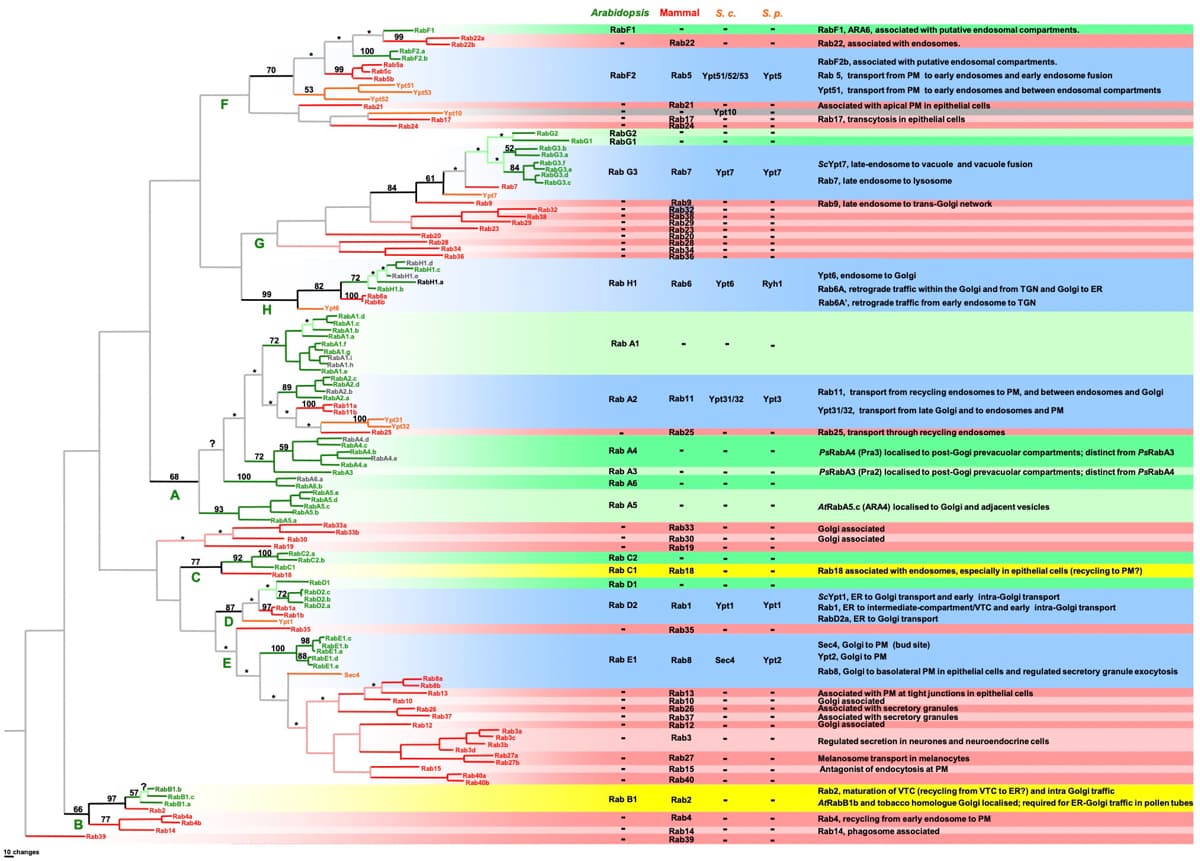
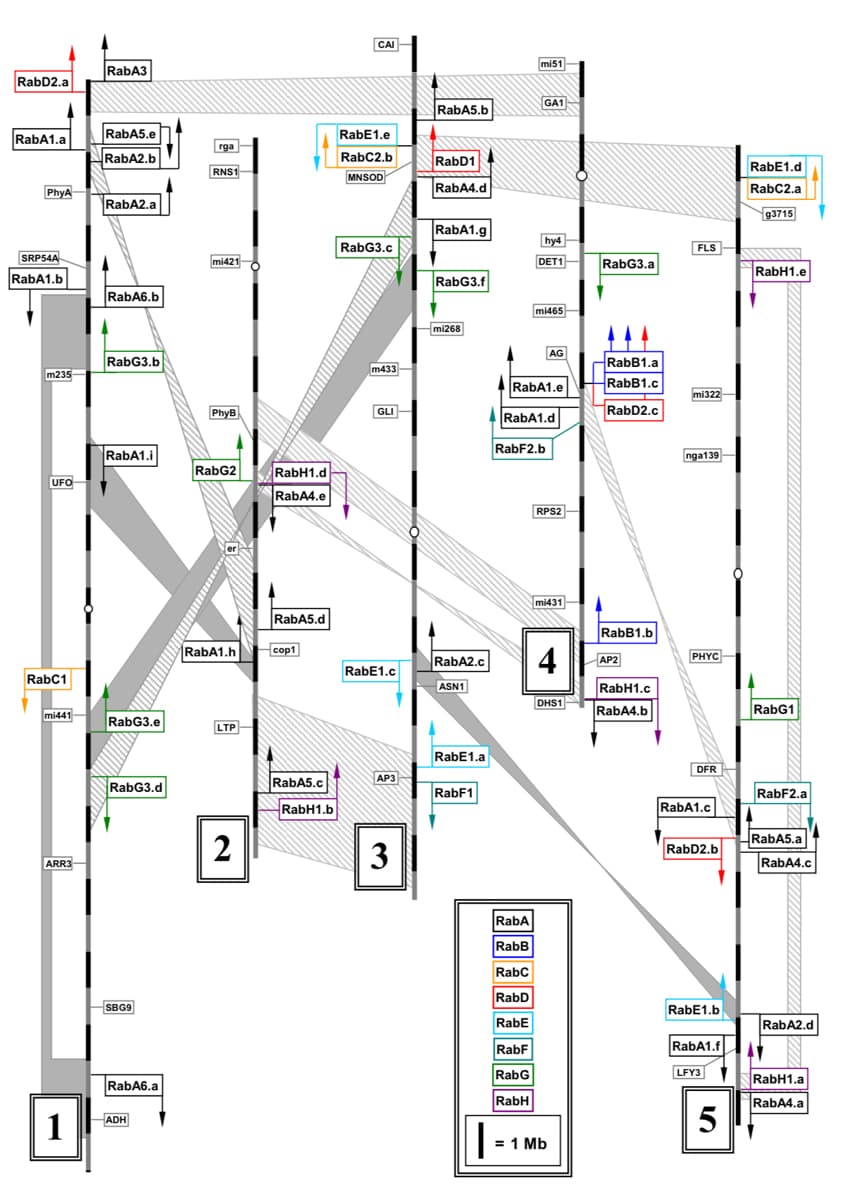
Instructions: have a look at “Figure 2.pdf”. This shows a diagram mapping the Arabidopsis Rab proteins onto regions of the Arabidopsis genome that appear to have been duplicated during the evolution of the genome. The vertical bars represent Arabidopsis chromosome 1-5, the broad shaded areas are regions that have high degrees of similarity between two chromosomes or regions of the same chromosome (and are therefore likely to have been duplication events of the chromosomes during evolution). The arrows show the direction (5’ to 3’) that the genes face on the chromosome. Compare the suggested evolutionary relationships of the green Rab proteins in “Figure 1.pdf” to their genomic location in “Figure 2.pdf”. Question: Briefly speculate about the implications of the results shown in “Figure 2.pdf” by thinking about how the diversity of Rab proteins might have arisen in this species. (Add at least 5 points)
Instructions: have a look at “Figure 2.pdf”. This shows a diagram mapping the Arabidopsis Rab proteins onto regions of the Arabidopsis genome that appear to have been duplicated during the evolution of the genome. The vertical bars represent Arabidopsis chromosome 1-5, the broad shaded areas are regions that have high degrees of similarity between two chromosomes or regions of the same chromosome (and are therefore likely to have been duplication events of the chromosomes during evolution). The arrows show the direction (5’ to 3’) that the genes face on the chromosome. Compare the suggested evolutionary relationships of the green Rab proteins in “Figure 1.pdf” to their genomic location in “Figure 2.pdf”. Question: Briefly speculate about the implications of the results shown in “Figure 2.pdf” by thinking about how the diversity of Rab proteins might have arisen in this species. (Add at least 5 points)
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter14: Biotechnology And Society
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4QP: Genetically Modified Foods The creation of transgenic crop plants using recombinant DNA methods...
Related questions
Question
Instructions:
have a look at “Figure 2.pdf”. This shows a diagram mapping the Arabidopsis Rab proteins onto regions of the Arabidopsis genome that appear to have been duplicated during the evolution of the genome. The vertical bars represent Arabidopsis chromosome 1-5, the broad shaded areas are regions that have high degrees of similarity between two chromosomes or regions of the same chromosome (and are therefore likely to have been duplication events of the chromosomes during evolution). The arrows show the direction (5’ to 3’) that the genes face on the chromosome.
Compare the suggested evolutionary relationships of the green Rab proteins in “Figure 1.pdf” to their genomic location in “Figure 2.pdf”.
Question: Briefly speculate about the implications of the results shown in “Figure 2.pdf” by thinking about how the diversity of Rab proteins might have arisen in this species.
(Add at least 5 points)
Transcribed Image Text:Arabidopsis Mammal
S.c.
S. p.
RabF1
RabF1, ARA6, associated with putative endosomal compartments.
-RabF1
99
-Rab22a
Raba2b
Rab22
Rab22, associated with endosomes.
100 Rab2a
RabF2.b
Raba
RabF2b, associated with putative endosomal compartments.
99 CRabsc
Rabsb
Ypts1
70
RabF2
Rab5 Ypt51/52/53
Ypt5
Rab 5, transport from PM to early endosomes and early endosome fusion
53
Ypt53
Ypt51, transport from PM to early endosomes and between endosomal compartments
F
-Ypt52
"Rah21
Associated with apical PM in epithelial cells
Rab17, transcytosis in epithelial cells
Rab21
Ypt10
Rabno
Rab24
Ypt10
Rab17
RabG2
RabG1
-
Rab02
RabG1
52-
RabG3.b
-Rab03a
Rab03
ScYpt7, late-endosome to vacuole and vacuole fusion
Rab3d
LRab03.c
Rab G3
Rab7
Ypt7
Ypt7
61
Rab7, late endosome to lysosome
84
Rab?
Ypt7
Rabe
Rabs
Rab32
Rab9, late endosome to trans-Golgi network
Rab32
-Rab
Rabas
Rab33
Rab38
Rab29
Rab23
Rab2
Kab28
Raht
Rab23
"Rab20
Rab28
Rab34
FRab36
G
RabH14
RabH1.e
E
72
-RabH1.e
RabH1a
Ypt6, endosome to Golgi
Rab H1
Rab6
Ypt6
Ryh1
-RabH1.b
100 rRaba
Rablo
Rab6A, retrograde traffic within the Golgi and from TGN and Golgi to ER
99
Rab6A', retrograde traffic from early endosome to TGN
H
Ypt6
C
-RabA1.d
RabA1.e
RabA1.b
RabA1a
72
FRabA1
RabA19
RabATI
RabA1.h
FRabA1e
Rab A1
RabA2e
RabAd
-RabA2.b
RabA2.a
100 CRabtta
Rab11, transport from recycling endosomes to PM, and between endosomes and Golgi
Rab A2
Rab11
Ypt31/32
Ypt3
Rab116
Ypt31/32, transport from late Golgi and to endosomes and PM
100Ypt31
CYpt32
Rab25
Rab25
Rab25, transport through recycling endosomes
F
RabAd
?
RabA4.e
59
72
Rab A4
PsRabA4 (Pra3) localised to post-Gogi prevacuolar compartments; distinct from PsRabA3
RabAde
RabA4.a
RabA3
Rab A3
PsRabA3 (Pra2) localised to post-Gogi prevacuolar compartments; distinct from PsRabA4
68
100
RabA6.a
Rab A6
RabA6.b
RabAS.e
A
FRabAS.d
-RabAS.
RabAS
93
Rab A5
AfRabA5.c (ARA4) localised to Golgi and adjacent vesicles
RabASa
Rab33a
Rab33b
Golgi associated
Golgi associated
Rab33
Rab30
Rab19
100CRac
RabC2.b
Rab30
Rab19
92
Rab C2
77
-RabC1
"Rab18
Rab18 associated with endosomes, especially in epithelial cells (recycling to PM?)
Rab C1
Rab18
Rab01
Rab D1
72HRaboze
Rab02.b
97cRabta RabD2a
Rabib
Ypt1
Rab3s
SeYpt1, ER to Golgi transport and early intra-Golgi transport
Rab1, ER to intermediate-compartment/VTC and early intra-Golgi transport
RabD2a, ER to Golgi transport
87
Rab D2
Rab1
Ypt1
Ypt1
Rab35
98CRabE1.e
RabE1.b
100 RASP
Sec4, Golgi to PM (bud site)
Ypt2, Golgi to PM
RabE1a
188-RabE1.d
Rabl1e
E
Rab E1
Rabs
Sec4
Ypt2
Rab8, Golgi to basolateral PM in epithelial cells and regulated secretory granule exocytosis
Secd
-Rabba
Rabb
Rabte Rab13
Rab26
Rab37
Rab13
Rab10
Rab26
Rab37
Rab12
Associated with PM at tight junctions in epithelial cells
Golgi associated
Associated with secretory granules
Associated with secretory granules
Golgi associated
Rab12
Rab3a
Rabe
Rab3
Regulated secretion in neurones and neuroendocrine cells
LM Rab
Rabad
-Rab27a
Rab27b
Rab27
Melanosome transport in melanocytes
Antagonist of endocytosis at PM
Rab15
Rab15
"Rab40a
Rab40b
Rab40
RabB1.b
57 h
97
RabB1.e
RabB1.a
Rab2, maturation of VTC (recycling from VTC to ER?) and intra Golgi traffic
AIRabB1b and tobacco homologue Golgi localised; required for ER-Golgi traffic in pollen tubes
Rab B1
Rab2
66
"Rab2
Rabla
Rab4b
Rab4
BL77
Rab4, recycling from early endosome to PM
Rab14, phagosome associated
Rab14
Rab14
Rab39
Rab39
10 changes
Transcribed Image Text:CAI-
mi51
RabA3
RabD2.a
GA1
RabA5.b
RabA1.a
RabA5.e
RabE1.e
rga
RabA2.b
RabC2.b
RabD1
RabE1.d
RNS1
MNSOD
PhyA
RabA4.d
RabC2.a
RabA2.a
93715
RabA1.g
hy4
RabG3.c
FLS
SRP54A
DET1
RabG3.a
mi421
RabH1.e
RabA1.b
RabG3.f
RabA6.b
mi465
mi268
AG
RabG3.b
RabB1.a
RabB1.c
m433
m235
RabA1.e
mi322
PhyB
GLIH
RabA1.d
RabD2.c
RabF2.b
RabA1.i
nga139
RabG2
RabH1.d
RabA4.e
UFO
RPS2
mi431
RabA5.d
RabB1.b
RabA1.h
cop1
4
RabA2.c
AP2
PHYC
RabE1.c
RabC1
ASN1
RabH1.c
DHS1
RabA4.b
RabG1
mi441
RabG3.e
LTP
RabE1.a
DFR
RabG3.d
RabA5.c
AP3
RabF1
RabF2.a
RabH1.b
RabA1.c
RabA5.a
2
3
RabD2.b
ARR3
RabA4.c
RabA
RabB
RabC
RabD
SBG9
RabE1.b
RabE
RabA2.d
RabF
RabA1.f
RabG
LFY3
RabH1.a
RabA6.a
RabH
RabA4.a
5
ADH
1
= 1 Mb
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning