Inventory Turnover and days' sales in inventory Kracker Corp., Foodstuff, Inc., and Winston Stores, Inc. are three grocery chains in the United States. Inventory management is an important aspect of the grocery retail business. Recent balance sheets for these three companies indicated the following merchandise inventory (in millions) information: Kracker Foodstuff Winston Corp. Inc. Stores Cost of merchandise sold $33,580.0 $34,675.0 $35,040.0 Inventory, beginning of 1,951.3 2,131.8 1,582.1 year Inventory, end of year 1,912.7 2,048.2 1,489.9 a. & b. Determine the inventory turnover and the number of days' sales in inventory (use 365 days and round to the nearest day) for the three companies. Round all interim calculations to one decimal place. For days' sales in inventory, round final answers to the nearest day, and for inventory turnover, round to one decimal place. Company names Inventory Turnover Days' Sales in Inventory Kracker days Foodstuff days Winston Stores days c. The inventory turnover ratios and days' sales in inventory are similar v for Kracker and Foodstuff. Winston Stores has a higher v inventory turnover and a lower days' sales in inventory than Kracker and Foodstuff. These results suggest that Kracker and Foodstuff are less v efficient than Winston Stores in managing inventory. d. If Kracker had Winston Stores' days' sales in inventory, how much additional cash flow would have been generated from the smaller inventory relative to its actual average inventory position? Round interim calculations to one decimal place and your final answer to the nearest million. $ million Feedback V Check My WWork a. 1. Determine the average daily cost of the merchandise sold by dividing the cost of goods sold by 365. 2. Divide the average inventory by the average daily cost of the merchandise sold. The average inventory is the total of the beginning and ending inventories divided by two. 3. Divide the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. b. Use the hypothetical numbers and refigure the average inventory using the number of days' sales in inventory calculation. Based on this, would Kracker have more or less cash tied up in inventory?
Inventory Turnover and days' sales in inventory Kracker Corp., Foodstuff, Inc., and Winston Stores, Inc. are three grocery chains in the United States. Inventory management is an important aspect of the grocery retail business. Recent balance sheets for these three companies indicated the following merchandise inventory (in millions) information: Kracker Foodstuff Winston Corp. Inc. Stores Cost of merchandise sold $33,580.0 $34,675.0 $35,040.0 Inventory, beginning of 1,951.3 2,131.8 1,582.1 year Inventory, end of year 1,912.7 2,048.2 1,489.9 a. & b. Determine the inventory turnover and the number of days' sales in inventory (use 365 days and round to the nearest day) for the three companies. Round all interim calculations to one decimal place. For days' sales in inventory, round final answers to the nearest day, and for inventory turnover, round to one decimal place. Company names Inventory Turnover Days' Sales in Inventory Kracker days Foodstuff days Winston Stores days c. The inventory turnover ratios and days' sales in inventory are similar v for Kracker and Foodstuff. Winston Stores has a higher v inventory turnover and a lower days' sales in inventory than Kracker and Foodstuff. These results suggest that Kracker and Foodstuff are less v efficient than Winston Stores in managing inventory. d. If Kracker had Winston Stores' days' sales in inventory, how much additional cash flow would have been generated from the smaller inventory relative to its actual average inventory position? Round interim calculations to one decimal place and your final answer to the nearest million. $ million Feedback V Check My WWork a. 1. Determine the average daily cost of the merchandise sold by dividing the cost of goods sold by 365. 2. Divide the average inventory by the average daily cost of the merchandise sold. The average inventory is the total of the beginning and ending inventories divided by two. 3. Divide the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. b. Use the hypothetical numbers and refigure the average inventory using the number of days' sales in inventory calculation. Based on this, would Kracker have more or less cash tied up in inventory?
Financial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337272124
Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Chapter7: Inventories
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7CP
Related questions
Question
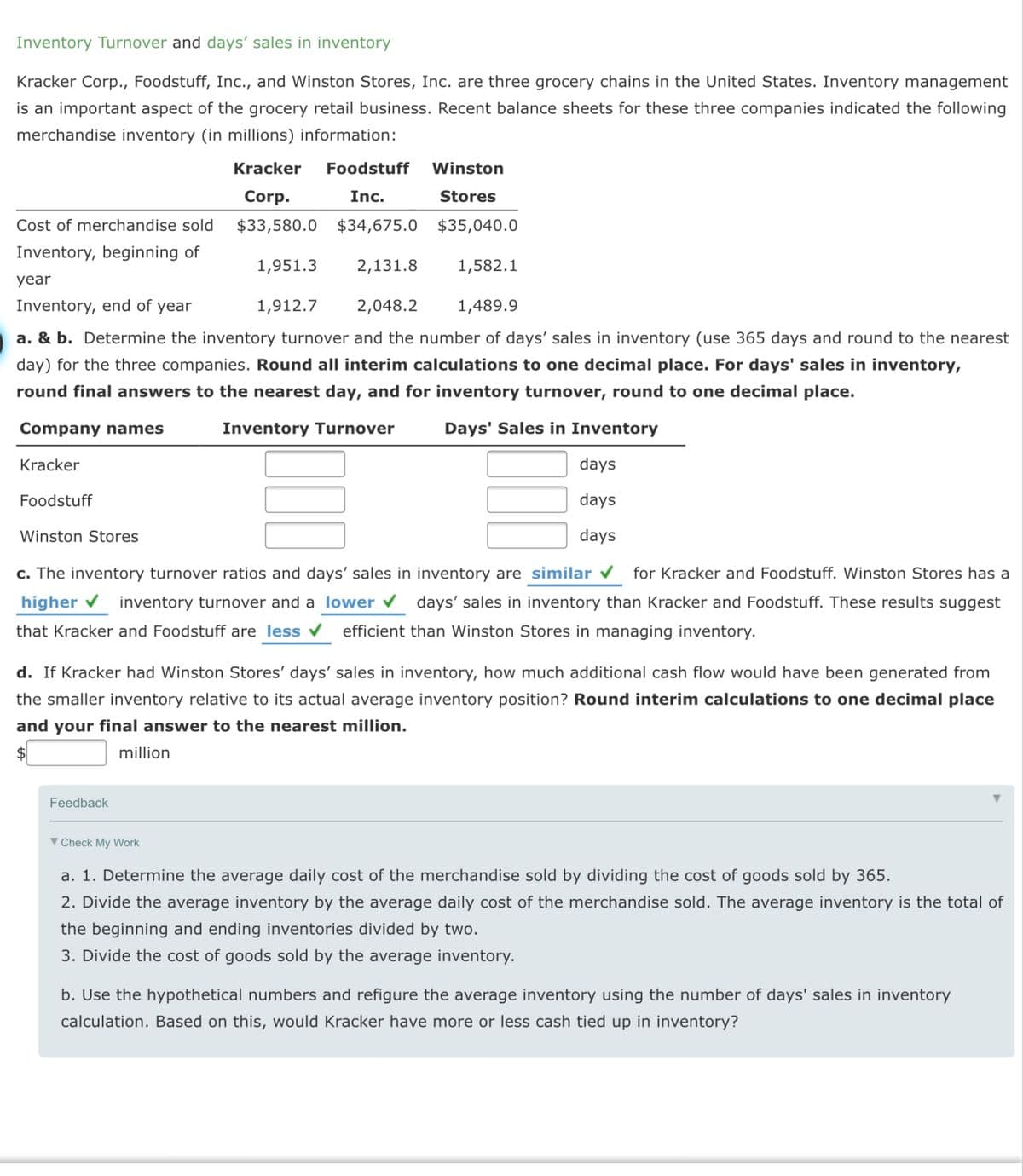
Transcribed Image Text:Inventory Turnover and days' sales in inventory
Kracker Corp., Foodstuff, Inc., and Winston Stores, Inc. are three grocery chains in the United States. Inventory management
is an important aspect of the grocery retail business. Recent balance sheets for these three companies indicated the following
merchandise inventory (in millions) information:
Kracker
Foodstuff
Winston
Corp.
Inc.
Stores
Cost of merchandise sold
$33,580.0 $34,675.0 $35,040.0
Inventory, beginning of
1,951.3
2,131.8
1,582.1
year
Inventory, end of year
1,912.7
2,048.2
1,489.9
a. & b. Determine the inventory turnover and the number of days' sales in inventory (use 365 days and round to the nearest
day) for the three companies. Round all interim calculations to one decimal place. For days' sales in inventory,
round final answers to the nearest day, and for inventory turnover, round to one decimal place.
Company names
Inventory Turnover
Days' Sales in Inventory
Kracker
days
Foodstuff
days
Winston Stores
days
c. The inventory turnover ratios and days' sales in inventory are similar
for Kracker and Foodstuff. Winston Stores has a
higher inventory turnover and a lower days' sales in inventory than Kracker and Foodstuff. These results suggest
that Kracker and Foodstuff are less
efficient than Winston Stores in managing inventory.
d. If Kracker had Winston Stores' days' sales in inventory, how much additional cash flow would have been generated from
the smaller inventory relative to its actual average inventory position? Round interim calculations to one decimal place
and your final answer to the nearest million.
$4
million
Feedback
▼ Check My Work
a. 1. Determine the average daily cost of the merchandise sold by dividing the cost of goods sold by 365.
2. Divide the average inventory by the average daily cost of the merchandise sold. The average inventory is the total of
the beginning and ending inventories divided by two.
3. Divide the cost of goods sold by the average inventory.
b. Use the hypothetical numbers and refigure the average inventory using the number of days' sales in inventory
calculation. Based on this, would Kracker have more or less cash tied up in inventory?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305088436
Author:
Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305088436
Author:
Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning