It is shown in Example 24.7 that the potential at a point P a distance a above one end of a uniformly charged rod of length e lying along the x axis is v = k,T le + V& + e² V= kIn a Use this result to derive an expression for the y component of the electric field at P. A rod of length € located along the xaxis has a total charge Q and a uniform linear charge density A. Find the electric potential at a point Plocated on the y axis a distance a from the origin (Fig. 24.16). P Figure 24.16 (Example 24.7) A uniform line charge of length e located along the xaxis. To calculate the electric potential at P, the line charge is divided into segments each of length dx and each carrying a charge dq = A dx. a dą
It is shown in Example 24.7 that the potential at a point P a distance a above one end of a uniformly charged rod of length e lying along the x axis is v = k,T le + V& + e² V= kIn a Use this result to derive an expression for the y component of the electric field at P. A rod of length € located along the xaxis has a total charge Q and a uniform linear charge density A. Find the electric potential at a point Plocated on the y axis a distance a from the origin (Fig. 24.16). P Figure 24.16 (Example 24.7) A uniform line charge of length e located along the xaxis. To calculate the electric potential at P, the line charge is divided into segments each of length dx and each carrying a charge dq = A dx. a dą
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter24: Electric Potential
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21P: It is shown in Example 24.7 that the potential at a point P a distance a above one end of a...
Related questions
Question
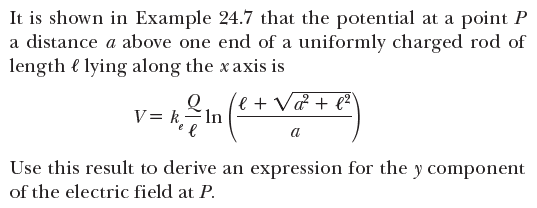
Transcribed Image Text:It is shown in Example 24.7 that the potential at a point P
a distance a above one end of a uniformly charged rod of
length e lying along the x axis is
v = k,T
le + V& + e²
V= kIn
a
Use this result to derive an expression for the y component
of the electric field at P.
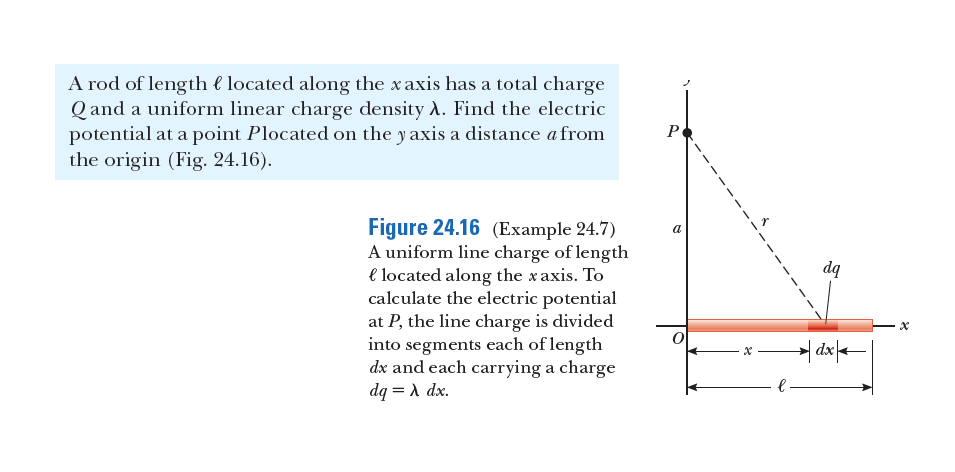
Transcribed Image Text:A rod of length € located along the xaxis has a total charge
Q and a uniform linear charge density A. Find the electric
potential at a point Plocated on the y axis a distance a from
the origin (Fig. 24.16).
P
Figure 24.16 (Example 24.7)
A uniform line charge of length
e located along the xaxis. To
calculate the electric potential
at P, the line charge is divided
into segments each of length
dx and each carrying a charge
dq = A dx.
a
dą
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning