Item 1 I Review | Constants | Periodic Table Elemental carbon usually exists in one of two forms: graphite or diamond. It is generally believed that diamonds last forever. The table shows the standard enthalpy of formation (AH:) and the standard molar entropy (S°) values for diamond and graphite. Substance AH: (kJ/mol) S° (J/mol K) Cgraphite 5.740 Caiamond 1.897 2.38 Part A What is the standard Gibbs free energy for the transformation of diamond to graphite at 298 K? Cdiamond→Cgraphite Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) ? AGm = Value Units
Item 1 I Review | Constants | Periodic Table Elemental carbon usually exists in one of two forms: graphite or diamond. It is generally believed that diamonds last forever. The table shows the standard enthalpy of formation (AH:) and the standard molar entropy (S°) values for diamond and graphite. Substance AH: (kJ/mol) S° (J/mol K) Cgraphite 5.740 Caiamond 1.897 2.38 Part A What is the standard Gibbs free energy for the transformation of diamond to graphite at 298 K? Cdiamond→Cgraphite Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) ? AGm = Value Units
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter16: Thermodynamics: Directionality Of Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 93QRT: The standard molar entropy of iodine vapor, I2(g), is 260.7 J Kl mol-1 and the standard molar...
Related questions
Question
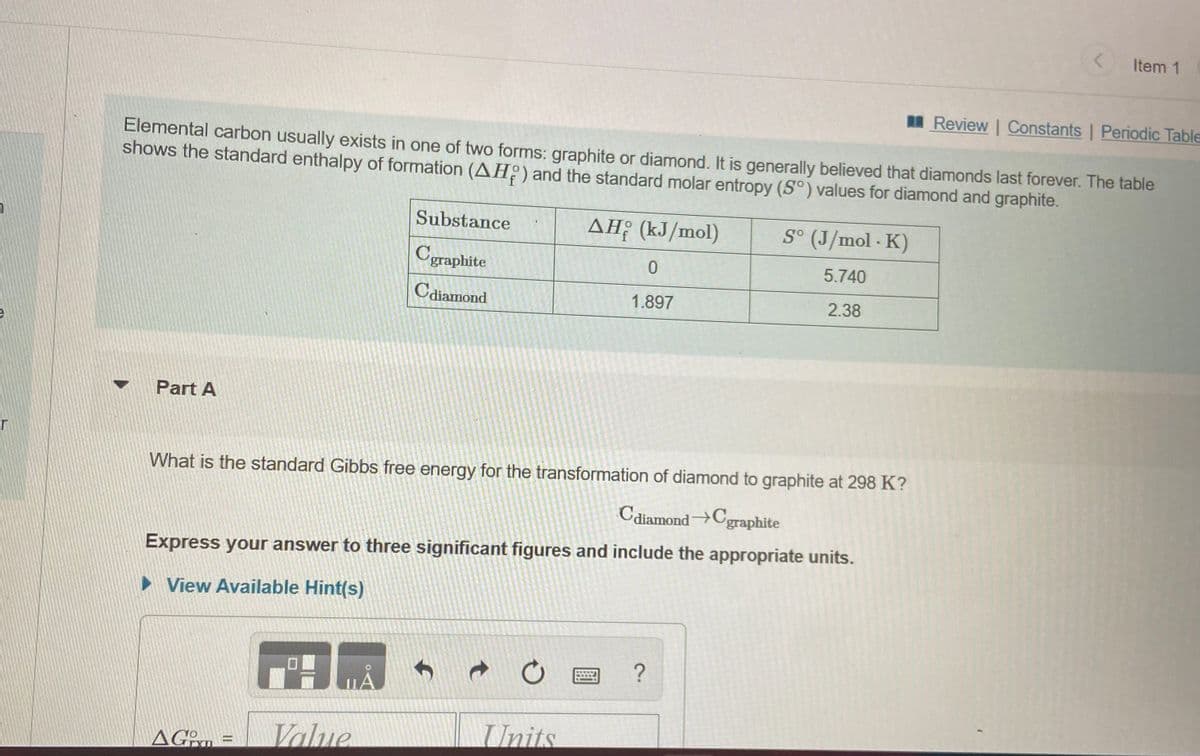
Transcribed Image Text:Item 1
I Review Constants | Periodic Table
Elemental carbon usually exists in one of two forms: graphite or diamond. It is generally believed that diamonds last forever. The table
shows the standard enthalpy of formation (AH:) and the standard molar entropy (S°) values for diamond and graphite.
Substance
ΔΗΡ (kJ/mol)
S° (J/mol - K)
Cgraphite
5.740
Cdiamond
1.897
2.38
Part A
What is the standard Gibbs free energy for the transformation of diamond to graphite at 298 K?
C
diamondCgraphite
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
> View Available Hint(s)
Value
Units
AGn
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax