Determine the Kb for a base by constructing an ICE table and using this information to construct and solve the equilibrium constant expression. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. NEXT > 1 2 The pH for a 0.0160 M solution of CH:C.H.NH: is 8.600. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine the unknown concentrations of all reactants and products. CH:C.H.NH:(aq)+ H:O(I) OH-(aq) +CH:CaH.NH:"(aq) Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) 5 RESET 0.0160 8.60 -8.60 0.93 -0.93 2.50 x 10* -2.50 x 109 3.98 х 10° -3.98 x 10 5.4 5.4
Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
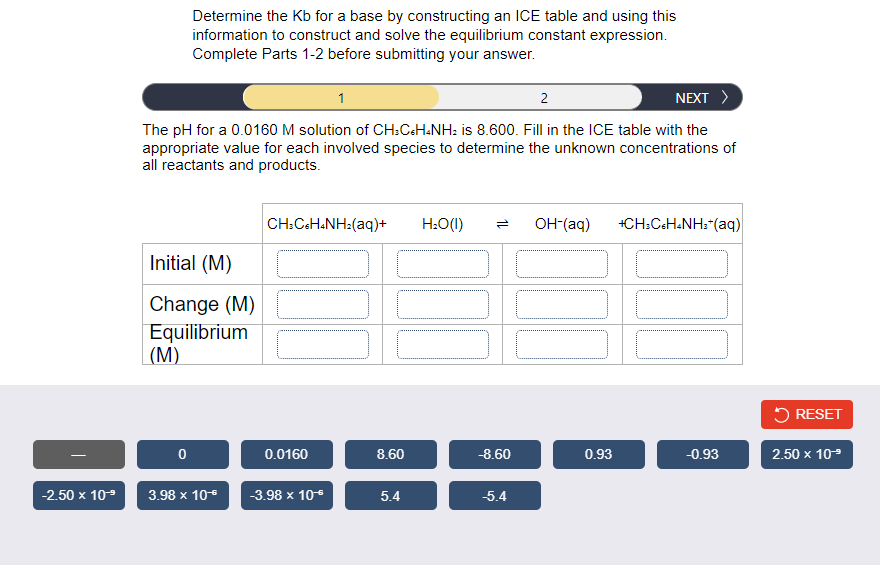
![Determine the Kb for a base by constructing an ICE table and using this
information to construct and solve the equilibrium constant expression.
Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer.
( PREV
1
2
Based on your ICE table (Part 1) and the definition of Kb, set up the expression for Kb.
Each reaction participant must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms.
Once the expression is constructed, solve for the Kb of this base.
K
5 RESET
[0]
[0.0160]
[8.60]
[0.93]
[2.5 x 10*)
[3.98 x 109
[5.4]
3.98 x 10-16
1.6 x 107
9.9 x 10-10
2.5 x 10*](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F84f39a0e-1c16-43ec-bcb3-7f889ca233a2%2Fe46d03d0-dc82-4ab8-ac89-7ced4d5ba785%2F17zmcd_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images


