Just as light waves have particle behavior, a moving particle has a wave nature. The faster the particle is moving, the higher its kinetic energy and the shorter its wavelength. The wavelength, A, of a particle of mass m, and moving at velocity v, is given by the de Broglie Part A relation The mass of an electron is 9.11 x 10 31 kg. If the de Broglie wavelength for an electron in a hydrogen atom is 3.31 x 10 10 m, how fast is the electron moving relative to the speed of light? The speed of light is 3.00 x 10 m/s where h = 6.626 x 10 34 J.s is Planck's constant. Express your answer numerically as a percent. > View Available Hint(s) This formula applies to all objects, regardless of size, but the de Broglie wavelength of macro objects is miniscule compared to their size, so we cannot observe their wave properties. In contrast, the wave properties of subatomic particles can be seen in such experiments as diffraction of electrons by a metal crystal. % Submit Part B The mass of a golf ball is 45.9 g. If it leaves the tee with a speed of 78.0 m/s, what is its corresponding wavelength? Express your answer with the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) HÀ ? Value Units Submit
Just as light waves have particle behavior, a moving particle has a wave nature. The faster the particle is moving, the higher its kinetic energy and the shorter its wavelength. The wavelength, A, of a particle of mass m, and moving at velocity v, is given by the de Broglie Part A relation The mass of an electron is 9.11 x 10 31 kg. If the de Broglie wavelength for an electron in a hydrogen atom is 3.31 x 10 10 m, how fast is the electron moving relative to the speed of light? The speed of light is 3.00 x 10 m/s where h = 6.626 x 10 34 J.s is Planck's constant. Express your answer numerically as a percent. > View Available Hint(s) This formula applies to all objects, regardless of size, but the de Broglie wavelength of macro objects is miniscule compared to their size, so we cannot observe their wave properties. In contrast, the wave properties of subatomic particles can be seen in such experiments as diffraction of electrons by a metal crystal. % Submit Part B The mass of a golf ball is 45.9 g. If it leaves the tee with a speed of 78.0 m/s, what is its corresponding wavelength? Express your answer with the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) HÀ ? Value Units Submit
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter5: Electron Configurations And The Periodic Table
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 133QRT
Related questions
Question
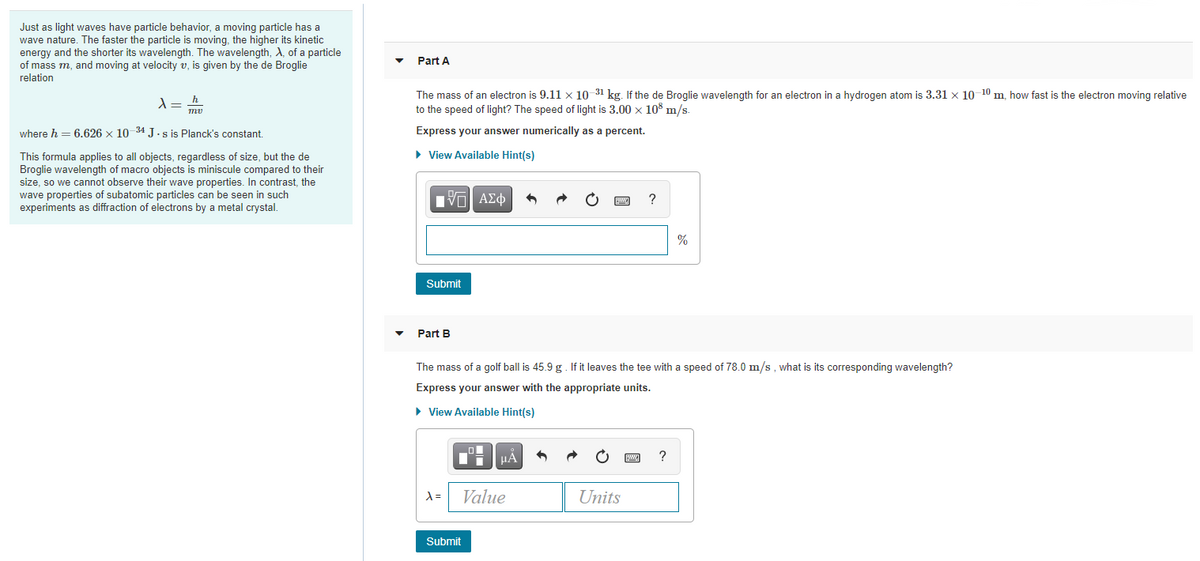
Transcribed Image Text:Just as light waves have particle behavior, a moving particle has a
wave nature. The faster the particle is moving, the higher its kinetic
energy and the shorter its wavelength. The wavelength, A, of a particle
of mass m, and moving at velocity v, is given by the de Broglie
relation
Part A
The mass of an electron is 9.11 x 10 31 kg. If the de Broglie wavelength for an electron in a hydrogen atom is 3.31 x 10 10 m, how fast is the electron moving relative
to the speed of light? The speed of light is 3.00 x 10³ m/s.
where h = 6.626 x 10 34 J.s is Planck's constant.
Express your answer numerically as a percent.
• View Available Hint(s)
This formula applies to all objects, regardless of size, but the de
Broglie wavelength of macro objects is miniscule compared to their
size, so we cannot observe their wave properties. In contrast, the
wave properties of subatomic particles can be seen in such
experiments as diffraction of electrons by a metal crystal.
Hνα ΑΣφ
?
Submit
Part B
The mass of a golf ball is 45.9 g. If it leaves the tee with a speed of 78.0 m/s, what is its corresponding wavelength?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
• View Available Hint(s)
?
=
Value
Units
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning