Kimberley-Clark makes luxury hampers for sale in a chain of high-class department stores. The following financial information is available in Table Q2. Current output and sales are set at 30,000 hampers per year, though the firm has the capacity to produce 50,000 hampers per year. Table Q2 COST ELEMENT PRICE (RM) 80 1. Wholesale price 2. Labor and material costs 15 3. Bought-in components 4. Overheads 25 800,000 (i) Identify and calculate the fixed cost. (ii) Identify and calculate the variable cost. (iii) Calculate the break-even quantity for the firm. (iv) Calculate the level of profit the firm is making.
Kimberley-Clark makes luxury hampers for sale in a chain of high-class department stores. The following financial information is available in Table Q2. Current output and sales are set at 30,000 hampers per year, though the firm has the capacity to produce 50,000 hampers per year. Table Q2 COST ELEMENT PRICE (RM) 80 1. Wholesale price 2. Labor and material costs 15 3. Bought-in components 4. Overheads 25 800,000 (i) Identify and calculate the fixed cost. (ii) Identify and calculate the variable cost. (iii) Calculate the break-even quantity for the firm. (iv) Calculate the level of profit the firm is making.
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Chapter10: Cost Analysis For Management Decision Making
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13P: Deuce Sporting Goods manufactures a high-end model tennis racket. The company’s forecasted income...
Related questions
Question
Please answer please arjent help
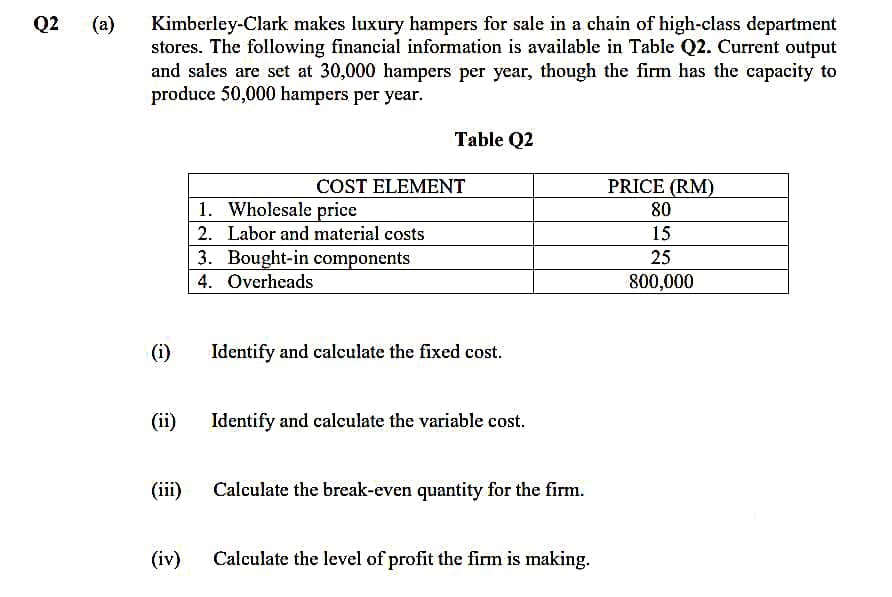
Transcribed Image Text:Q2
(a)
Kimberley-Clark makes luxury hampers for sale in a chain of high-class department
stores. The following financial information is available in Table Q2. Current output
and sales are set at 30,000 hampers per year, though the firm has the capacity to
produce 50,000 hampers per year.
Table Q2
COST ELEMENT
PRICE (RM)
1. Wholesale price
80
2. Labor and material costs
15
3. Bought-in components
4. Overheads
25
800,000
(i)
Identify and calculate the fixed cost.
(ii)
Identify and calculate the variable cost.
(ii)
Calculate the break-even quantity for the firm.
(iv)
Calculate the level of profit the firm is making.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning