Koontz Company manufactures two models of industrial components-a Basic model and an Advanced Model. The company considers all of its manufacturing overhead costs to be fixed and it uses plantwide manufacturing overhead cost allocation based on direct labor-hours. Koontz's controller prepared the segmented income statement that is shown below for the most recent year (he allocated selling and administrative expenses to products based on sales dollars): Basic Advanced Total 30, e00 Number of units produced and sold 20,000 10,e0e Sales Cost of goods sold Gross nargin Selling and administrative expenses $3,e00,e00 2,300, e00 700,000 720,e00 $2,e00,000 1,350,000 650,000 480,000 $ 170,000 $ 150,000 $ 5,000,009 3,650,000 1,350,e00 1,200,000 Net operating incone (loss) $ (20,000) Direct laborers are paid $20 per hour. Direct materials cost $40 per unit for the Basic model and $60 per unit for the Advanced model. Koontz is considering a change from plantwide overhead allocation to a departmental approach. The overhead costs in the company's Molding Department would be allocated based on machine-hours and the overhead costs in its Assemble and Pack Department would be allocated based on direct labor-hours. To enable further analysis, the controller gathered the following information: Molding $ 787,5e0 Assenble and Pack $ 562,500 $1358,000 Total Manufacturing overhead costs Direct labor hours: Basic 10,e00 5,e00 20,000 10,e00 30,000 15,000 Advanced Machine hours: Basic Advanced 12,e00 10, e00 12,000 10,000 Required: 1. Using the plantwide approach: a. Calculate the plantwide overhead rate. b. Calculate the amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. 2. Using a departmental approach: a. Calculate the departmental overhead rates. b. Calculate the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. c. Using your departmental overhead cost allocations, redo the controller's segmented income statement (continue to allocate selling and administrative expenses based on sales dollars). 3. Koontz's production manager has suggested using activity-based costing instead of either the plantwide or departmental approaches. To facilitate the necessary calculations, she assigned the company's total manufacturing overhead cost to five activity cost pools as follows: Activity Cost Pool Machining Assenble and pack Order processing Setups Other (unused capacíty) Activity Measure Machine-hours in Molding Direct labor-hours in Assenble and Pack Number of customer orders Setup hours Manufacturing Overhead $ 417,500 282,se0 230,000 340,000 $1,350,000 She also determined that the average order size for the Basic and Advanced models is 400 units and 50 units, respectively. The molding machines require a setup for each order. One setup hour is required for each customer order of the Basic model and three hours are required to setup for an order of the Advanced model. The company pays a sales commissions of 5% for the Basic model and 10% for the Advanced model. Its traceable fixed advertising costs include $150,000 for the Basic model and $200,000 for the Advanced model. The remainder of the company's selling and administrative costs are organization-sustaining in nature. Using the additional information provided by the production manager, calculate: a. An activity rate for each activity cost pool. b. The total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach. c. The total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach. 4. Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented income statement that is adapted from Exhibit 6-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable fixed expenses, and common fixed expenses.) 5. Using your contribution format segmented income statement from requirement 4, calculate the break-even point in dollar sales for the Advanced model.
Koontz Company manufactures two models of industrial components-a Basic model and an Advanced Model. The company considers all of its manufacturing overhead costs to be fixed and it uses plantwide manufacturing overhead cost allocation based on direct labor-hours. Koontz's controller prepared the segmented income statement that is shown below for the most recent year (he allocated selling and administrative expenses to products based on sales dollars): Basic Advanced Total 30, e00 Number of units produced and sold 20,000 10,e0e Sales Cost of goods sold Gross nargin Selling and administrative expenses $3,e00,e00 2,300, e00 700,000 720,e00 $2,e00,000 1,350,000 650,000 480,000 $ 170,000 $ 150,000 $ 5,000,009 3,650,000 1,350,e00 1,200,000 Net operating incone (loss) $ (20,000) Direct laborers are paid $20 per hour. Direct materials cost $40 per unit for the Basic model and $60 per unit for the Advanced model. Koontz is considering a change from plantwide overhead allocation to a departmental approach. The overhead costs in the company's Molding Department would be allocated based on machine-hours and the overhead costs in its Assemble and Pack Department would be allocated based on direct labor-hours. To enable further analysis, the controller gathered the following information: Molding $ 787,5e0 Assenble and Pack $ 562,500 $1358,000 Total Manufacturing overhead costs Direct labor hours: Basic 10,e00 5,e00 20,000 10,e00 30,000 15,000 Advanced Machine hours: Basic Advanced 12,e00 10, e00 12,000 10,000 Required: 1. Using the plantwide approach: a. Calculate the plantwide overhead rate. b. Calculate the amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. 2. Using a departmental approach: a. Calculate the departmental overhead rates. b. Calculate the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product. c. Using your departmental overhead cost allocations, redo the controller's segmented income statement (continue to allocate selling and administrative expenses based on sales dollars). 3. Koontz's production manager has suggested using activity-based costing instead of either the plantwide or departmental approaches. To facilitate the necessary calculations, she assigned the company's total manufacturing overhead cost to five activity cost pools as follows: Activity Cost Pool Machining Assenble and pack Order processing Setups Other (unused capacíty) Activity Measure Machine-hours in Molding Direct labor-hours in Assenble and Pack Number of customer orders Setup hours Manufacturing Overhead $ 417,500 282,se0 230,000 340,000 $1,350,000 She also determined that the average order size for the Basic and Advanced models is 400 units and 50 units, respectively. The molding machines require a setup for each order. One setup hour is required for each customer order of the Basic model and three hours are required to setup for an order of the Advanced model. The company pays a sales commissions of 5% for the Basic model and 10% for the Advanced model. Its traceable fixed advertising costs include $150,000 for the Basic model and $200,000 for the Advanced model. The remainder of the company's selling and administrative costs are organization-sustaining in nature. Using the additional information provided by the production manager, calculate: a. An activity rate for each activity cost pool. b. The total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach. c. The total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach. 4. Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented income statement that is adapted from Exhibit 6-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable fixed expenses, and common fixed expenses.) 5. Using your contribution format segmented income statement from requirement 4, calculate the break-even point in dollar sales for the Advanced model.
Chapter5: Process Costing
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2PB: The following product costs are available for Kellee Company on the production of eyeglass frames:...
Related questions
Question
100%
Please help me fix what "Assemble and Pack" should be that was marked incorrect. I think it may be "Sales Comissions" but I am unsure. I know it is not "Selling and Administrative." Thanks!
Transcribed Image Text:Reg 1A
Req 18
Req 2A
Req 28
Req 20
Req 3A
Req 38
Reg 30
Req 4
Req 5
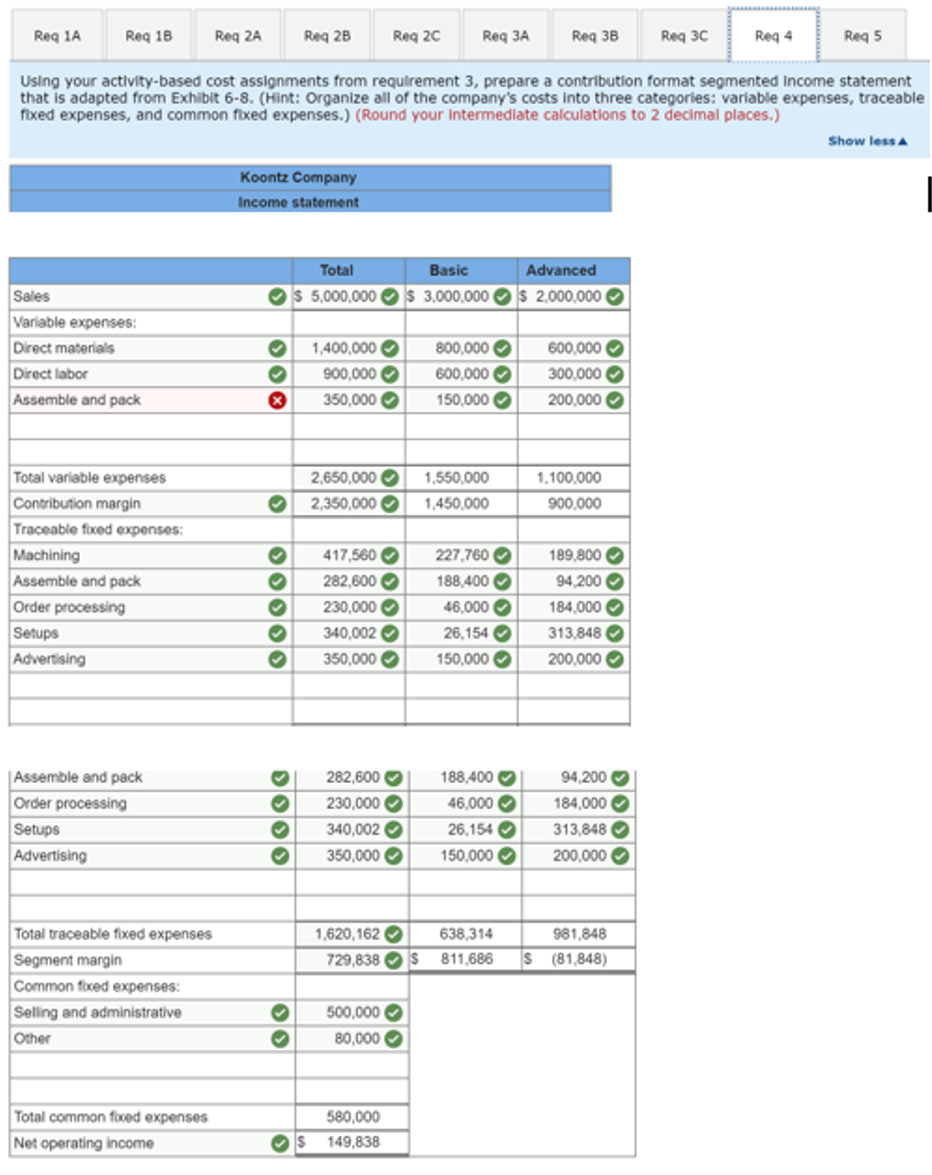
Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented Income statement
that is adapted from Exhibit 6-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable
fixed expenses, and common fixed expenses.) (Round your Intermedlate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
Show less A
Koontz Company
Income statement
Total
Basic
Advanced
Sales
Os 5,000,000 Os 3,000,000 Os 2,000,000
Variable expenses:
1,400,000 O
900,000 O
800,000 O
600,000 O
600,000 O
300,000 O
200,000 O
Direct materials
Direct labor
Assemble and pack
350,000 O
150,000 O
Total variable expenses
2,650,000 O
1,550,000
1,100,000
Contribution margin
2,350,000 O
1,450,000
900,000
Traceable foxed expenses:
Machining
417,560 O
282,600 O
227,760 O
189,800 O
188,400 O
46,000 O
Assemble and pack
94,200 O
Order processing
230,000 O
184,000 O
Setups
Advertising
340,002 O
26,154 O
313,848 O
350,000 O
150,000 O
200,000
Assemble and pack
282,600 O
188,400 O
94,200 O
Order processing
230,000 O
340,002 O
46,000 O
26,154 O
184,000 O
Setups
313,848 O
Advertising
350,000 O
150,000 O
200,000 O
Total traceable fixed expenses
1,620,162 O
638,314
981,848
Segment margin
729,838 Os
811,686
(81,848)
Common foxed expenses:
500,000 O
80,000 O
Selling and administrative
Other
Total common foxed expenses
580,000
Net operating income
149,838
O 000
O 0000O
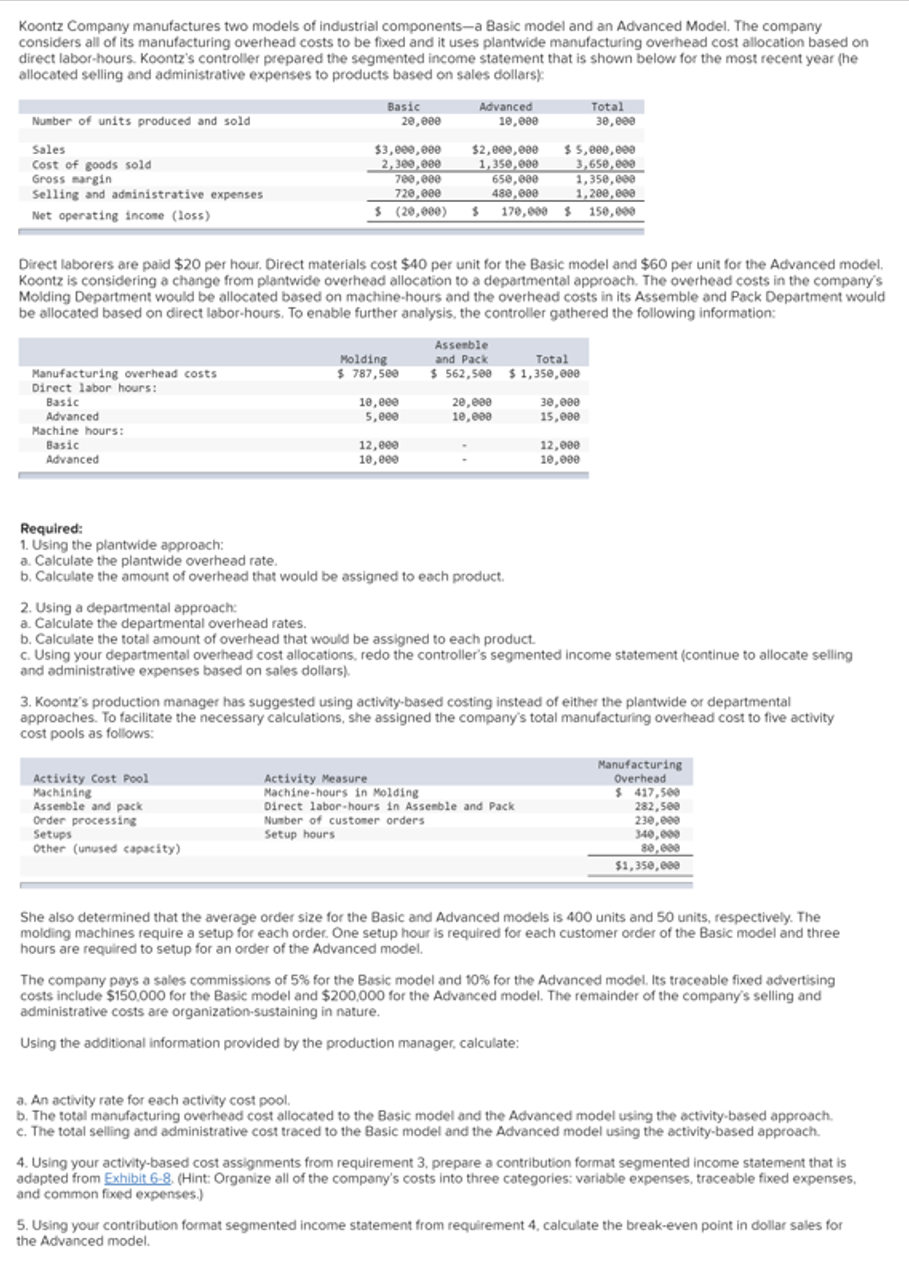
Transcribed Image Text:Koontz Company manufactures two models of industrial components-a Basic model and an Advanced Model. The company
considers all of its manufacturing overhead costs to be fixed and it uses plantwide manufacturing overhead cost allocation based on
direct labor-hours. Koontz's controller prepared the segmented income statement that is shown below for the most recent year (he
allocated selling and administrative expenses to products based on sales dollars):
Basic
20,000
Total
30,eee
Advanced
Number of units produced and sold
10,000
$3,e00,000
2,300, 000
700,000
720,000
$2,e00,000
1,350,000
65e,000
480,000
170,000 $ 150,000
$ 5,000, e0e
3,650,000
1,350,e00
1,200, eee
Sales
Cost of goods sold
Gross nargin
Selling and administrative expenses
Net operating income (loss)
$ (20,000)
Direct laborers are paid $20 per hour. Direct materials cost $40 per unit for the Basic model and $60 per unit for the Advanced model.
Koontz is considering a change from plantwide overhead allocation to a departmental approach. The overhead costs in the company's
Molding Department would be allocated based on machine-hours and the overhead costs in its Assemble and Pack Department would
be allocated based on direct labor-hours. To enable further analysis, the controller gathered the following information:
Assenble
Molding
$ 787,5ee
and Pack
Total
$ 562,508 $ 1,350,000
Manufacturing overhead costs
Direct labor hours:
Basic
18,ee0
5,ee0
20,e00
10,e00
30,000
15,000
Advanced
Machine hours:
Basic
12,eee
10,eee
12,000
10,000
Advanced
Required:
1. Using the plantwide approach:
a. Calculate the plantwide overhead rate.
b. Calculate the amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product.
2. Using a departmental approach:
a. Calculate the departmental overhead rates.
b. Calculate the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each product.
c. Using your departmental overhead cost allocations, redo the controller's segmented income statement (continue to allocate selling
and administrative expenses based on sales dollars).
3. Koontz's production manager has suggested using activity-based costing instead of either the plantwide or departmental
approaches. To facilitate the necessary calculations, she assigned the company's total manufacturing overhead cost to five activity
cost pools as follows:
Activity Cost Pool
Machining
Assemble and pack
Order processing
Setups
Other (unused capacity)
Activity Measure
Machine-hours in Molding
Direct labor-hours in Assemble and Pack
Number of customer orders
Setup hours
Manufacturing
Overhead
$ 417,500
282,500
230,000
340,000
80,000
$1,350,e00
She also determined that the average order size for the Basic and Advanced models is 400 units and 50 units, respectively. The
molding machines require a setup for each order. One setup hour is required for each customer order of the Basic model and three
hours are required to setup for an order of the Advanced model.
The company pays a sales commissions of 5% for the Basic model and 10% for the Advanced model. Its traceable fixed advertising
costs include $150,000 for the Basic model and $200,000 for the Advanced model. The remainder of the company's selling and
administrative costs are organization-sustaining in nature.
Using the additional information provided by the production manager, calculate:
a. An activity rate for each activity cost pool.
b. The total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach.
c. The total selling and administrative cost traced to the Basic model and the Advanced model using the activity-based approach.
4. Using your activity-based cost assignments from requirement 3, prepare a contribution format segmented income statement that is
adapted from Exhibit 6-8. (Hint: Organize all of the company's costs into three categories: variable expenses, traceable fixed expenses,
and common fixed expenses.)
5. Using your contribution format segmented income statement from requirement 4, calcculate the break-even point in dollar sales for
the Advanced model.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning