Learning Goal: Review | Constants To understand that adding vectors by using geometry and by using components gives the same result, and that manipulating vectors with components is much easier. The vectors A and B have lengths A and B, respectively, and B makes an angle 0 from the direction of A. Vectors may be manipulated either geometrically or using components. In this problem we consider the addition of two vectors using both of these two methods Vector addition using geometry Vector addition using geometry is accomplished by putting the tail of one vector (in this case B) on the tip of the other (A) (Figure 1) and using the laws of plane geometry to find the length C, and angle , of Figure 1 of 2 the resultant (or sum) vector, C A + B A2B2-2AB cos(c), 1. C (ga) B sin(c) 2. sin Vector addition using components B Vector addition using components requires the choice of a coordinate system. In this problem, the x axis is chosen along the direction of A (Figure 2). Then the x and y components of B are B cos (0) and B sin(0) respectively. This means that the x and y components of C are given by A 3. Ca AB cos (0) 4. Cy Bsin(0) Part A Which of the following sets of conditions, if true, would show that the expressions 1 and 2 above define the same vector C as expressions 3 and 4? Check all that apply The two pairs of expressions give the same length and direction for C. C. The two pairs of expressions give the same length and x component for The two pairs of expressions give the same direction and x component for C. The two pairs of expressions give the same length and y component for C The two pairs of expressions give the same direction and y component for C. The two pairs of expressions give the same x and y components for C Submit Request Answer
Learning Goal: Review | Constants To understand that adding vectors by using geometry and by using components gives the same result, and that manipulating vectors with components is much easier. The vectors A and B have lengths A and B, respectively, and B makes an angle 0 from the direction of A. Vectors may be manipulated either geometrically or using components. In this problem we consider the addition of two vectors using both of these two methods Vector addition using geometry Vector addition using geometry is accomplished by putting the tail of one vector (in this case B) on the tip of the other (A) (Figure 1) and using the laws of plane geometry to find the length C, and angle , of Figure 1 of 2 the resultant (or sum) vector, C A + B A2B2-2AB cos(c), 1. C (ga) B sin(c) 2. sin Vector addition using components B Vector addition using components requires the choice of a coordinate system. In this problem, the x axis is chosen along the direction of A (Figure 2). Then the x and y components of B are B cos (0) and B sin(0) respectively. This means that the x and y components of C are given by A 3. Ca AB cos (0) 4. Cy Bsin(0) Part A Which of the following sets of conditions, if true, would show that the expressions 1 and 2 above define the same vector C as expressions 3 and 4? Check all that apply The two pairs of expressions give the same length and direction for C. C. The two pairs of expressions give the same length and x component for The two pairs of expressions give the same direction and x component for C. The two pairs of expressions give the same length and y component for C The two pairs of expressions give the same direction and y component for C. The two pairs of expressions give the same x and y components for C Submit Request Answer
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Vectors In Two And Three Dimensions
Section9.4: Vectors In Three Dimensions
Problem 49E
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
Review | Constants
To understand that adding vectors by using geometry
and by using components gives the same result, and
that manipulating vectors with components is much
easier.
The vectors A and B have lengths A and B, respectively, and B makes an angle 0 from the direction of
A.
Vectors may be manipulated either geometrically or
using components. In this problem we consider the
addition of two vectors using both of these two
methods
Vector addition using geometry
Vector addition using geometry is accomplished by putting the tail of one vector (in this case B) on the
tip of the other (A) (Figure 1) and using the laws of plane geometry to find the length C, and angle , of
Figure
1 of 2
the resultant (or sum) vector, C
A + B
A2B2-2AB cos(c),
1. C
(ga)
B sin(c)
2. sin
Vector addition using components
B
Vector addition using components requires the choice of a coordinate system. In this problem, the x axis
is chosen along the direction of A (Figure 2). Then the x and y components of B are B cos (0) and
B sin(0) respectively. This means that the x and y components of C are given by
A
3. Ca AB cos (0)
4. Cy Bsin(0)
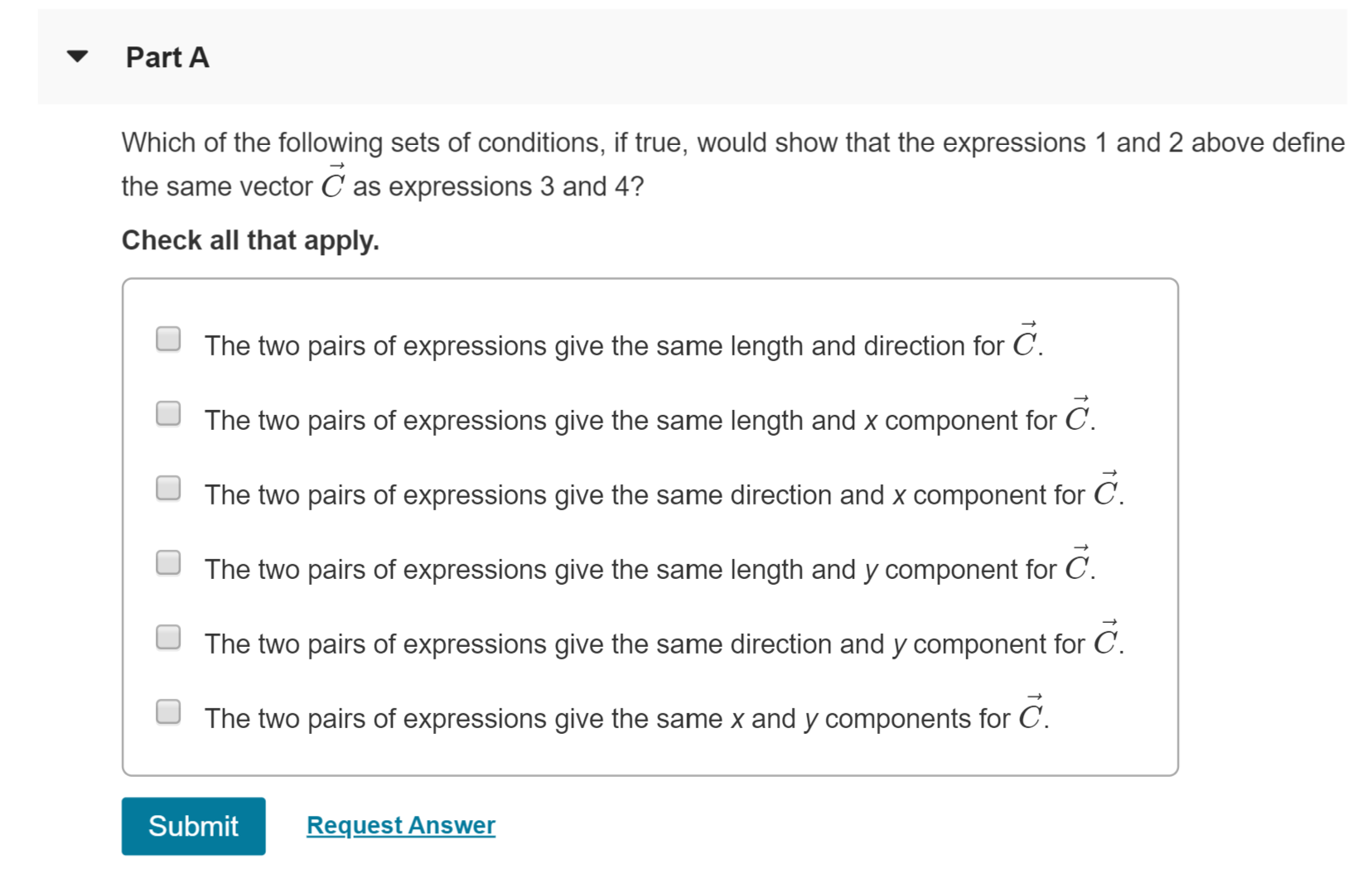
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Which of the following sets of conditions, if true, would show that the expressions 1 and 2 above define
the same vector C as expressions 3 and 4?
Check all that apply
The two pairs of expressions give the same length and direction for C.
C.
The two pairs of expressions give the same length and x component for
The two pairs of expressions give the same direction and x component for C.
The two pairs of expressions give the same length and y component for C
The two pairs of expressions give the same direction and y component for C.
The two pairs of expressions give the same x and y components for C
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Step 1
VIEWTrending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 1 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning