Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter23: The Chemistry Of Life
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 43A
Related questions
Question
Question #26 needed
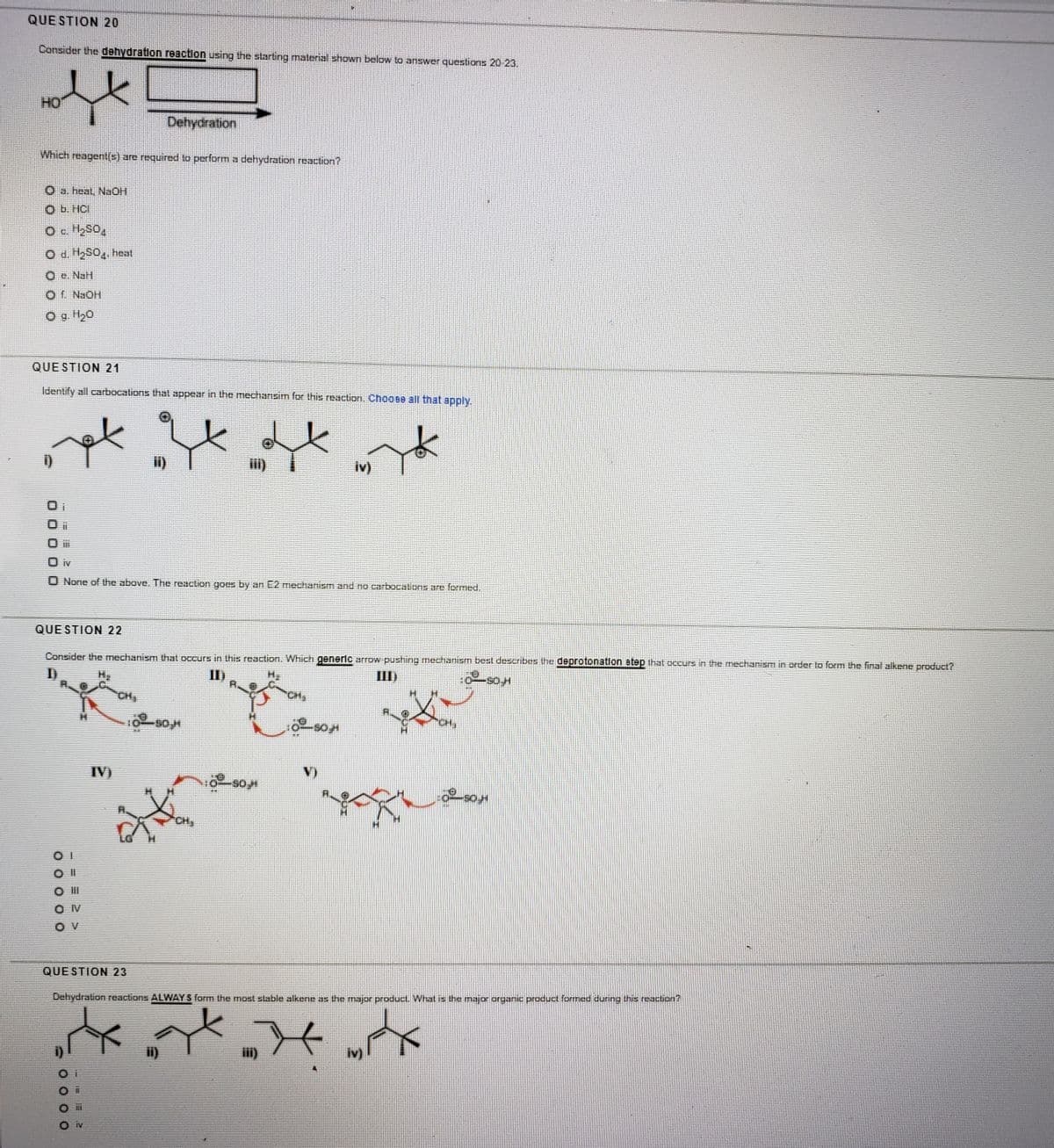
Transcribed Image Text:QUE STION 20
Consider the dehydration reaction using the starting material shown below to answer questions 20 23.
HO
Dehydration
Which reagent(s) are required lo perform a dehydration reaction?
O a. heal, NaOH
Ob. HCI
O c H2SO4
O e. NaH
Of NaOH
O 9 H20
QUE STION 21
Identify all carbocations thal appear in the mechansim for this reaction. Choose all that apply.
i)
i)
iv)
IV
None of the above. The reaction goes by an E2 mechanism and no carbocalions are formed.
QUE STION 22
Consider the mechanism that occurs in this reaction. Which generlc arrow pushing mectianism best describes the deprotonation step that occurs in the mechanism in order to form the final alkene product?
I)
I)
III)
CH,
CH,
IV)
CH
O II
O V
QUE STION 23
Dehydration reaclions ALWAY S form the most stable alkene as the major product. What is the major organic product formed during this reaction?
ii)
iii)
iv)
IV
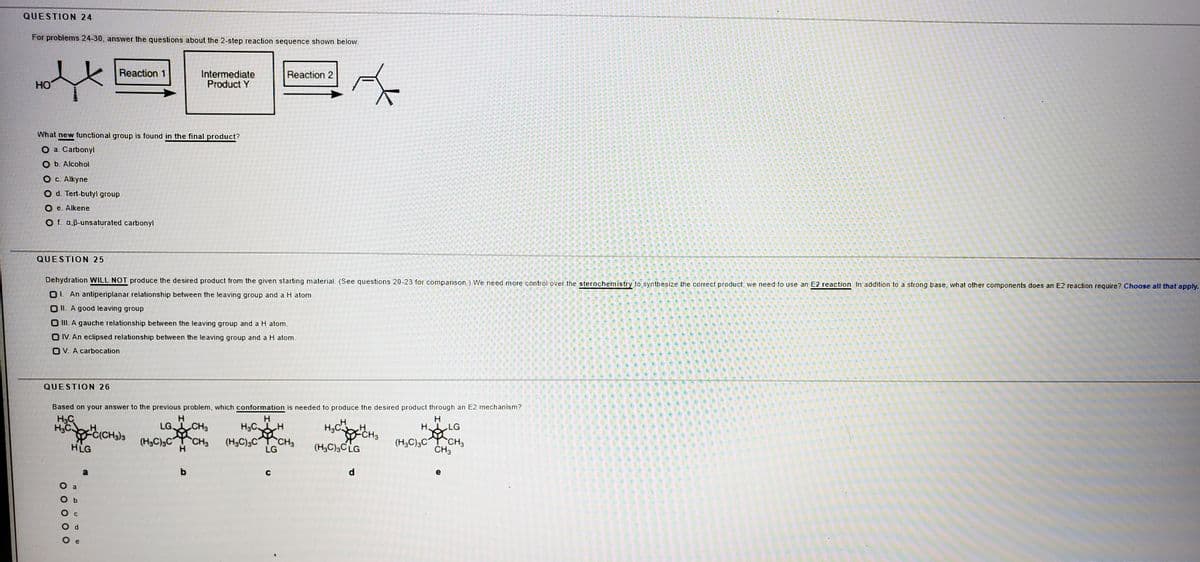
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 24
For problems 24-30, answer the questions about the 2-step reaction sequence shown below.
Reaction 1
Intermediate
Product Y
Reaction 2
HO
What new functional group is found in the final product?
О а. Carbonyl
O b. Alcohol
Ос. Alkyne
O d. Tert-butyl group
O e. Alkene
O f. a,B-unsaturated carbonyl
QUESTION 25
Dehydration WILL NOT produce the desired product from the given starting material. (See questions 20-23 for comparison.) We need more control over the sterochemistry to synthesize the correct product; we need to use an E2 reaction. In addition to a strong base, what other components does an E2 reaction require? Choose all that apply.
O1. An antiperiplanar relationship between the leaving group and a H atom.
O II. A good leaving group
O II. A gauche relationship between the leaving group and a H atom.
O IV. An eclipsed relationship between the leaving group and a H atom.
OV. A carbocation
QUESTION 26
Based on your answer to the previous problem, which conformation is needed to produce the desired product through an E2 mechanism?
H3C
HCH
Č(CH3)3
HLG
H
LG CH3
H3C H
by
(H3C)3C CH3
LG
H LG
FCH3
(H3C)3C LG
(H,C),CYCH,
(H3C)3C CH3
C
d
e
O O O 0O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning