Links Pin K12 mm 2.5 mm T - Sprocket R -L Chain
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Chapter46: Suspension Systems
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2RQ: Explain the difference between sprung and unsprung weight.
Related questions
Question
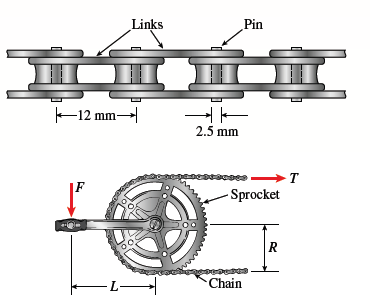
A bicycle chain consists of a series of small
links, where each are 12 mm long between the centers
of the pins (see figure). You might wish to examine
a bicycle chain and observe its construction.
Note particularly the pins, which have a diameter
of 2.5 mm.
To solve this problem, make two measurements
on a bicycle (see figure): (1) the length L of the crank
arm from main axle to pedal axle and (2) the radius R
of the sprocket (the toothed wheel, sometimes called
the chainring).
(a) Using your measured dimensions, calculate
the tensile force T in the chain due to a force
F = 800 N applied to one of the pedals.
(b) Calculate the average shear stress τaver in the pins.
Transcribed Image Text:Links
Pin
K12 mm
2.5 mm
T
- Sprocket
R
-L
Chain
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781133612315
Author:
Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781133612315
Author:
Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning