Liza owns a small bakery company catering for gourmet cakes and pastries. Her fixed cost is the cost of the mixer and baking tools, while variable costs include flour, sugar, eggs, and edible decorations. Contemplating business expansion, she is trying to decide how many commercial mixers to purchase and came out with the following projections: Variable Cost (RM) 30 orders 45 orders Quantity of Mixers Fixed Cost (RM) 15 orders 2 6,000 2,000 5,000 12,000 3 7,000 1,800 3,800 10,800 4 8,000 1,200 3,600 8,400 b) What is Liza's long-run average total cost for 15 orders per week? Please explain why this short-run average total cost of producing 15 orders per week when the number of mixers is fixed at 3 is greater than her long-run total average cost of producing 15 orders per week.
Liza owns a small bakery company catering for gourmet cakes and pastries. Her fixed cost is the cost of the mixer and baking tools, while variable costs include flour, sugar, eggs, and edible decorations. Contemplating business expansion, she is trying to decide how many commercial mixers to purchase and came out with the following projections: Variable Cost (RM) 30 orders 45 orders Quantity of Mixers Fixed Cost (RM) 15 orders 2 6,000 2,000 5,000 12,000 3 7,000 1,800 3,800 10,800 4 8,000 1,200 3,600 8,400 b) What is Liza's long-run average total cost for 15 orders per week? Please explain why this short-run average total cost of producing 15 orders per week when the number of mixers is fixed at 3 is greater than her long-run total average cost of producing 15 orders per week.
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter4: Extent (how Much) Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3MC
Related questions
Question
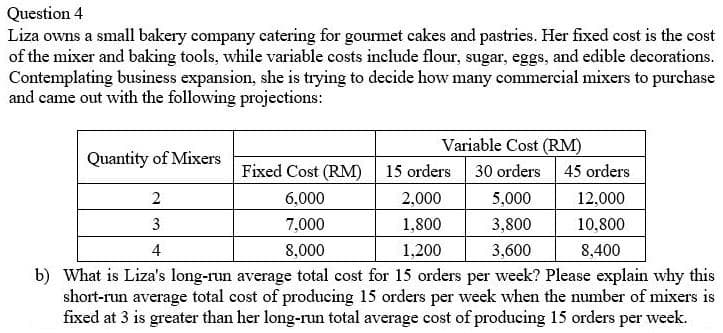
Transcribed Image Text:Question 4
Liza owns a small bakery company catering for gourmet cakes and pastries. Her fixed cost is the cost
of the mixer and baking tools, while variable costs include flour, sugar, eggs, and edible decorations.
Contemplating business expansion, she is trying to decide how many commercial mixers to purchase
and came out with the following projections:
Variable Cost (RM)
Quantity of Mixers
Fixed Cost (RM)
15 orders
30 orders
45 orders
6,000
2,000
5,000
12,000
3
7,000
1,800
3,800
10,800
4
8,000
1,200
3,600
8,400
b) What is Liza's long-run average total cost for 15 orders per week? Please explain why this
short-run average total cost of producing 15 orders per week when the number of mixers is
fixed at 3 is greater than her long-run total average cost of producing 15 orders per week.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax
