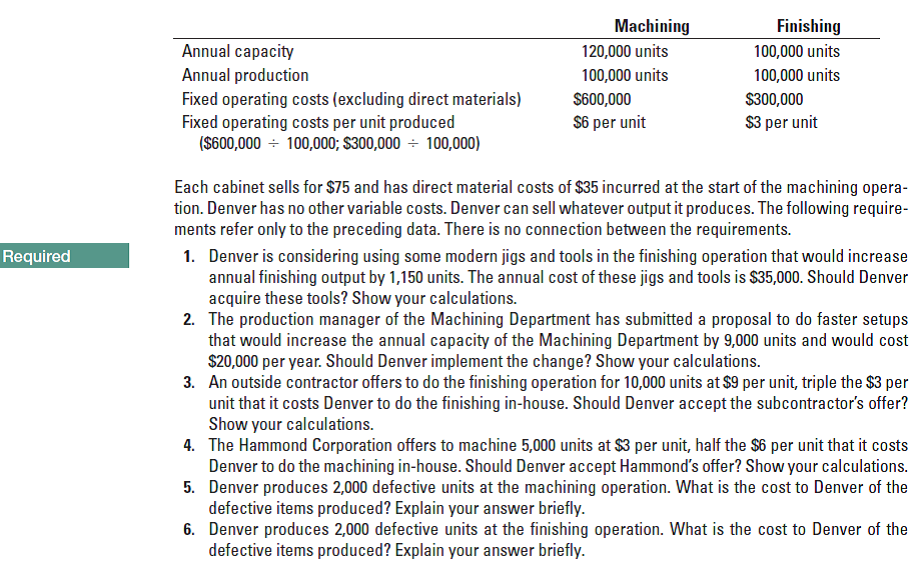
Machining Finishing Annual capacity 120,000 units 100,000 units Annual production Fixed operating costs (excluding direct materials) Fixed operating costs per unit produced ($600,000 - 100,000; $300,000 ÷ 100,000) 100,000 units 100,000 units S600,000 $300,000 S6 per unit S3 per unit Each cabinet sells for $75 and has direct material costs of $35 incurred at the start of the machining opera- tion. Denver has no other variable costs. Denver can sell whatever output it produces. The following require- ments refer only to the preceding data. There is no connection between the requirements. Required 1. Denver is considering using some modern jigs and tools in the finishing operation that would increase annual finishing output by 1,150 units. The annual cost of these jigs and tools is $35,000. Should Denver acquire these tools? Show your calculations. 2. The production manager of the Machining Department has submitted a proposal to do faster setups that would increase the annual capacity of the Machining Department by 9,000 units and would cost $20,000 per year. Should Denver implement the change? Show your calculations. 3. An outside contractor offers to do the finishing operation for 10,000 units at $9 per unit, triple the $3 per unit that it costs Denver to do the finishing in-house. Should Denver accept the subcontractor's offer? Show your calculations. 4. The Hammond Corporation offers to machine 5,000 units at $3 per unit, half the $6 per unit that it costs Denver to do the machining in-house. Should Denver accept Hammond's offer? Show your calculations. 5. Denver produces 2,000 defective units at the machining operation. What is the cost to Denver of the defective items produced? Explain your answer briefly. 6. Denver produces 2,000 defective units at the finishing operation. What is the cost to Denver of the defective items produced? Explain your answer briefly.
Variance Analysis
In layman's terms, variance analysis is an analysis of a difference between planned and actual behavior. Variance analysis is mainly used by the companies to maintain a control over a business. After analyzing differences, companies find the reasons for the variance so that the necessary steps should be taken to correct that variance.
Standard Costing
The standard cost system is the expected cost per unit product manufactured and it helps in estimating the deviations and controlling them as well as fixing the selling price of the product. For example, it helps to plan the cost for the coming year on the various expenses.
Theory of constraints, throughput margin, relevant costs. The Denver Corporation manufactures ling cabinets in two operations: machining and nishing. It provides the following information:
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 14 images








