Mark's Meals produces frozen meals, which it sells for $9 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs and production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business (Click the icon to view the data) Read the requirements Requirement 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this first for January and then for February January February Variable Absorption costing costing 1 Total product cost ■ 70 Requirement 2a. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February, using absorption costing T Less: Less: Less: Mark's Meals Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Month Ended Less Absorption costing January 31 Requirement 2b. Prepare Mark's Meals' January and February income statements using variable costing Mark's Meals Contribution Margin Income Statement (Variable Costing) Month Ended Variable costing February 28 January 31 February 28 Data table Sales... Production... January 1,600 meals 2,000 meals $3 Variable manufacturing expense per meal $1 Sales commission expense per meal. Total fixed manufacturing overhead........... $800 Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses.. $600 Print Done February 1,800 meals 1.600 meals $3 $1 $800 $600
Mark's Meals produces frozen meals, which it sells for $9 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs and production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business (Click the icon to view the data) Read the requirements Requirement 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this first for January and then for February January February Variable Absorption costing costing 1 Total product cost ■ 70 Requirement 2a. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February, using absorption costing T Less: Less: Less: Mark's Meals Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Month Ended Less Absorption costing January 31 Requirement 2b. Prepare Mark's Meals' January and February income statements using variable costing Mark's Meals Contribution Margin Income Statement (Variable Costing) Month Ended Variable costing February 28 January 31 February 28 Data table Sales... Production... January 1,600 meals 2,000 meals $3 Variable manufacturing expense per meal $1 Sales commission expense per meal. Total fixed manufacturing overhead........... $800 Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses.. $600 Print Done February 1,800 meals 1.600 meals $3 $1 $800 $600
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Chapter18: Pricing And Profitability Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3CE: Pattison Products, Inc., began operations in October and manufactured 40,000 units during the month...
Related questions
Question
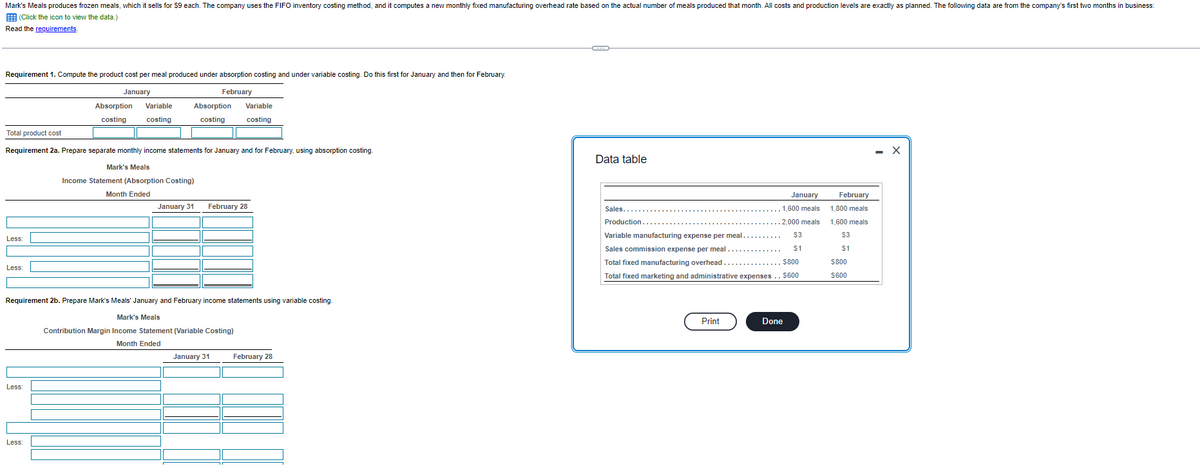
Transcribed Image Text:Mark's Meals produces frozen meals, which it sells for $9 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs and production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business:
(Click the icon to view the data.)
Read the requirements.
Requirement 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this first for January and then for February.
February
January
Less
Less:
Absorption
costing
Total product cost
Requirement 2a. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February, using absorption costing.
Less:
Variable
costing
Less:
Absorption
costing
Mark's Meals
Income Statement (Absorption Costing)
Month Ended
Variable
costing
Requirement 2b. Prepare Mark's Meals' January and February income statements using variable costing.
Mark's Meals
Contribution Margin Income Statement (Variable Costing)
Month Ended
January 31 February 28
January 31
February 28
Data table
Sales....
Production..
January
1,600 meals
2.000 meals
$3
$1
Variable manufacturing expense per meal.
Sales commission expense per meal..
Total fixed manufacturing overhead
$800
Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses .. $600
Print
Done
February
1,800 meals
1,600 meals
$3
$1
$800
$600
- X
Transcribed Image Text:Mark's Meals produces frozen meals, which it sells for $9 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs and production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business:
(Click the icon to view the data.)
Read the requirements.
Less
Less:
Less:
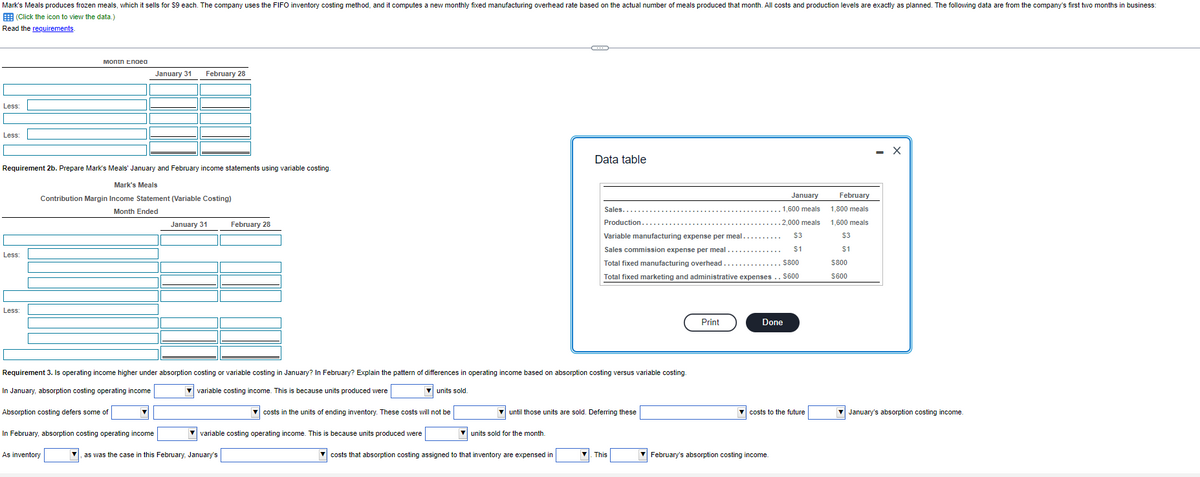
Requirement 2b. Prepare Mark's Meals' January and February income statements using variable costing.
Less:
Montn Endea
Mark's Meals
Contribution Margin Income Statement (Variable Costing)
Month Ended
January 31 February 28
As inventory
▼
In February, absorption costing operating income
January 31
February 28
Requirement 3. Is operating income higher under absorption costing or variable costing in January? In February? Explain the pattern of differences in operating income based on absorption costing versus variable costing.
In January, absorption costing operating income
▼variable costing income. This is because units produced were
▼ units sold.
Absorption costing defers some of
▼costs in the units of ending inventory. These costs will not be
variable costing operating income. This is because units produced were
as was the case in this February, January's
G
Data table
costs that absorption costing assigned to that inventory are expensed in
Sales...
Production..
Variable manufacturing expense per meal..
Sales commission expense per meal
until those units are sold. Deferring these
units sold for the month.
Total fixed manufacturing overhead
$800
Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses.. $600
This
Print
January
1.600 meals
2.000 meals
Done
$3
$1
▼ February's absorption costing income.
costs to the future
February
1,800 meals
1,600 meals
$3
$1
$800
$600
January's absorption costing income.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College


Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:
9781111581565
Author:
Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,