masses at A, B, and C, the center of mass of that system is given by the intersections of the medians of the triangle. 9. (a) Let u, v e R2. Describe the vectors x su + tv, where s +t = 1. Pay particular attention to the location of x when s > 0 and whent > 0. (b) Let u, v, w e Ri. Describe the vectors x ru +sV + tw, wherer+s +t = 1. Pay particular attention to the location of x when each of r, s, and t is positive. 10. Suppose x, y e R" are nonparallel vectors. (Recall the definition on p. 3.)
masses at A, B, and C, the center of mass of that system is given by the intersections of the medians of the triangle. 9. (a) Let u, v e R2. Describe the vectors x su + tv, where s +t = 1. Pay particular attention to the location of x when s > 0 and whent > 0. (b) Let u, v, w e Ri. Describe the vectors x ru +sV + tw, wherer+s +t = 1. Pay particular attention to the location of x when each of r, s, and t is positive. 10. Suppose x, y e R" are nonparallel vectors. (Recall the definition on p. 3.)
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.2: Determinants
Problem 10AEXP
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
I need help for problem 9. Thanks!

Transcribed Image Text:masses at A, B, and C, the center of mass of that system is given by the intersections of the medians
of the triangle.
9. (a) Let u, v e R2. Describe the vectors x su + tv, where s +t = 1. Pay particular attention
to the location of x when s > 0 and whent > 0.
(b) Let u, v, w e Ri. Describe the vectors x ru +sV + tw, wherer+s +t = 1. Pay particular
attention to the location of x when each of r, s, and t is positive.
10. Suppose x, y e R" are nonparallel vectors. (Recall the definition on p. 3.)
Expert Solution
Step 1
For (a)

Step 2
Now we will check the behaviour of x for values of s and t.

Step 3
If both s ≥ 0, t ≥ 0 and satisfying s + t = 1, then the position of x will lie on the u-v vector as shown in fig.
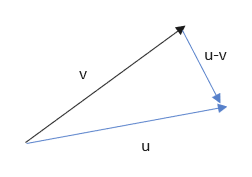
Step 4
Now for (b),

Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning