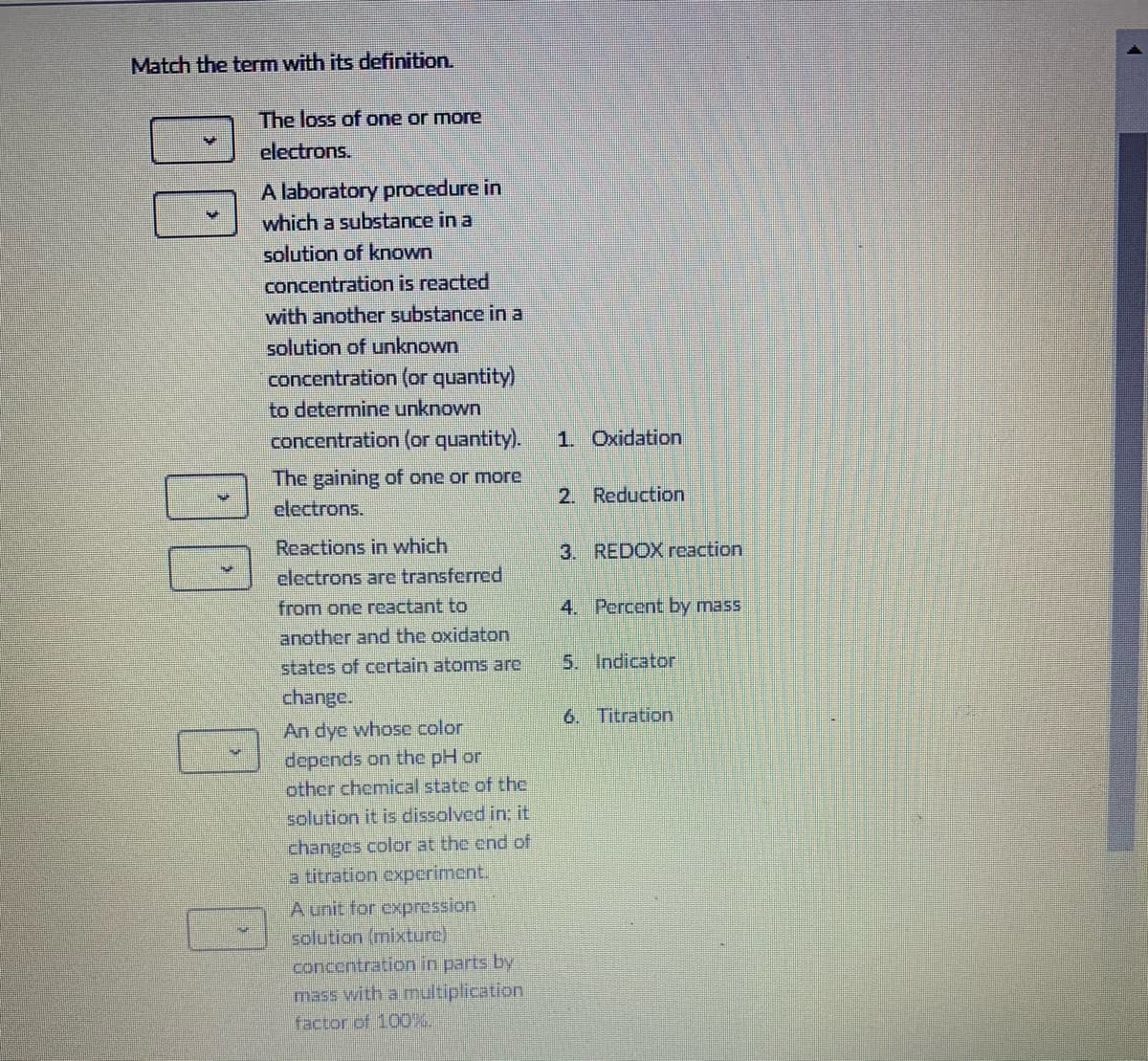
Match the term with its definition. The loss of one or more electrons. A laboratory procedure in which a substance in a solution of known concentration is reacted with another substance in a solution of unknown concentration (or quantity) to determine unknown concentration (or quantity). 1. Oxidation The gaining of one or more 2. Reduction electrons. Reactions in which 3. REDOX reaction electrons are transferred from one reactant to 4. Percent by mass another and the oxidaton states of certain atoms are 5. Indicator change. 6. Titration An dye whose color depends on the pH or other chemical state of the solution it is dissolved in: it changes color at the end of a titration experiment. A unit for expression solution (mixture) concentration in parts by mass with a multiplication factor of 100%. 00 00
Science behind corrosion-test
Corrosion is defined as an activity that transforms refined metals into more chemically stable forms such as oxide, hydroxide, carbonate, or sulfide. It refers to the slow decomposition of things (typically metals); thanks to chemical and/or electrochemical reactions with their surroundings. Corrosion engineering is the science of preventing and controlling corrosion.
Corrosion
Corrosion is defined as an activity that transforms refined metals into more chemically stable forms such as oxide, hydroxide, carbonate, or sulfide. It refers to the slow decomposition of things (typically metals); thanks to chemical and/or electrochemical reactions with their surroundings. Corrosion engineering is the science of preventing and controlling corrosion.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps









