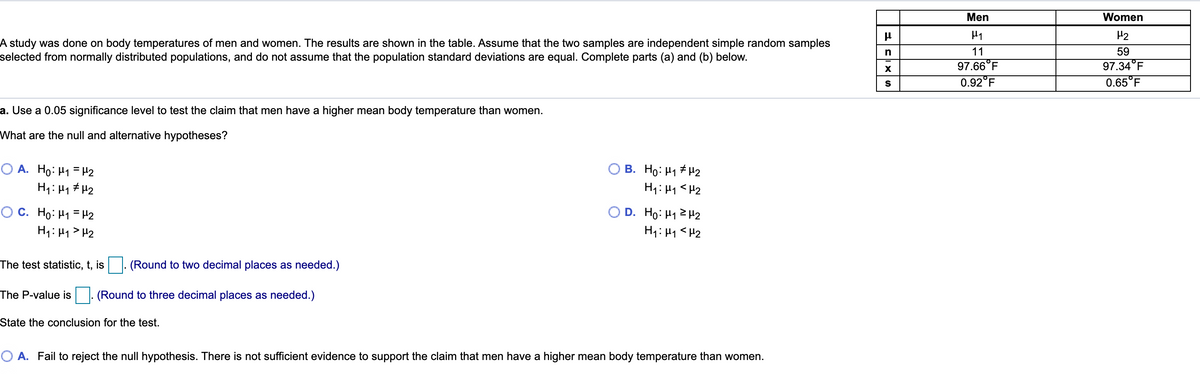
Men Women H2 59 97.34 F 0.65 F A study was done on body temperatures of men and women. The results are shown in the table. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. 11 97.66"F 0.92"F n a. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that men have a higher mean body temperature than women. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: H1 =H2 O B. Ho: H1 H2 Hy: H1

a)
Denote μ1, μ2 as the population mean body temperatures for men and women, respectively.
It is needed to check whether men have a higher mean body temperature than women.
The null and alternative hypotheses are as follows:
H0: μ1 = μ2, Vs. H1: μ1 > μ2.
Correct option is C.
Consider that n1 = 11, x̅1 = 97.66 and s1 = 0.92, are the sample size, sample mean and sample standard deviation of body temperatures for men, respectively.
Consider that n2 = 59, x̅2 = 97.34 and s2 = 0.65 are the sample size, sample mean and sample standard deviation of body temperatures for women, respectively.
The two-sample t test with unequal variance (Welch’s t-test) is to be conducted, at level of significance α = 0.05.
The degrees of freedom for the test is,
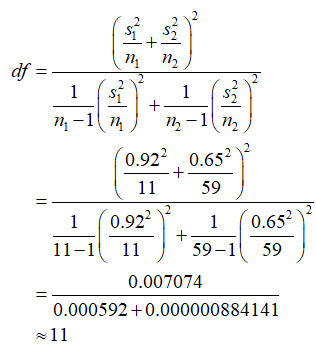
The test statistic is found as follows:
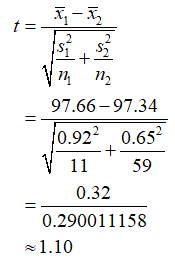
The test statistic is 1.10.
Using Excel formulae: =T.DIST.RT(1.10,11), the P-value is 0.147.
Decision rule:
If the P-value is less than or equal to the level of significance, then reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Since the P-value (0.147) is greater than the level of significance (0.05), fail to reject H0.
Hence, there is not enough evidence to claim that, the men have a higher mean body temperature than women, at 5% level of significance.
Correct option is A.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









