Mercury Company has only one inventory pool. On December 31, 2021, Mercury adopted the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. The inventory on that date using the dollar-value LIFO method was $208,000. Inventory data are as follows: Ending Inventory at Year-End Costs Ending Inventory at Base Year Costs Year 2022 $247,800 326, 600 328, 800 $236,000 284,000 274,000 2023 2024 Required: Compute the inventory at December 31, 2022, 2023, and 2024, using the dollar-value LIFO method. (Round "Year end cost index" to
Mercury Company has only one inventory pool. On December 31, 2021, Mercury adopted the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. The inventory on that date using the dollar-value LIFO method was $208,000. Inventory data are as follows: Ending Inventory at Year-End Costs Ending Inventory at Base Year Costs Year 2022 $247,800 326, 600 328, 800 $236,000 284,000 274,000 2023 2024 Required: Compute the inventory at December 31, 2022, 2023, and 2024, using the dollar-value LIFO method. (Round "Year end cost index" to
Chapter18: Accounting Periods And Methods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 67P
Related questions
Question
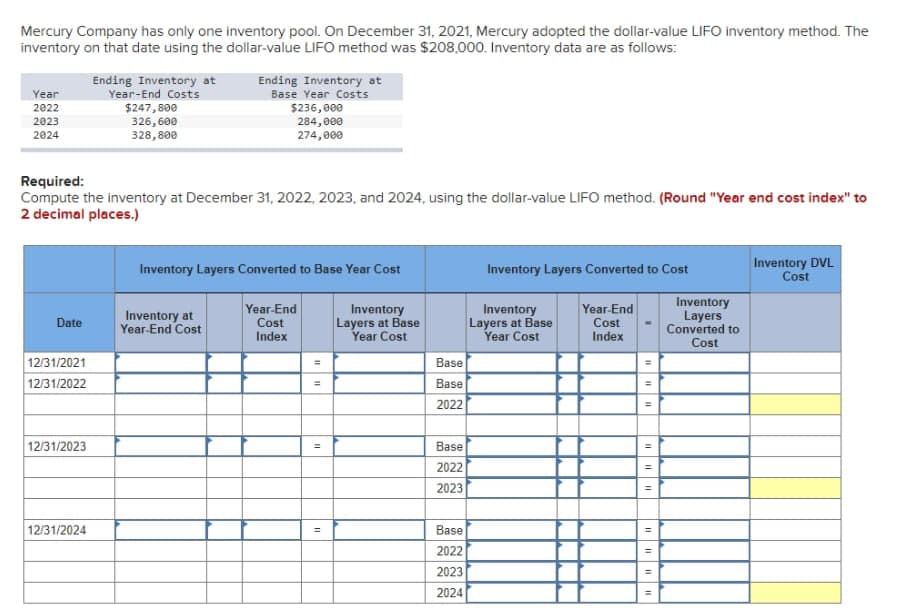
Transcribed Image Text:Mercury Company has only one inventory pool. On December 31, 2021, Mercury adopted the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. The
inventory on that date using the dollar-value LIFO method was $208,000. Inventory data are as follows:
Ending Inventory at
Year-End Costs
Ending Inventory at
Base Year Costs
Year
$247,800
326,600
328,800
$236, 000
284,000
274, 000
2022
2023
2024
Required:
Compute the inventory at December 31, 2022, 2023, and 2024, using the dollar-value LIFO method. (Round "Year end cost index" to
2 decimal places.)
Inventory Layers Converted to Cost
Inventory DVL
Cost
Inventory Layers Converted to Base Year Cost
Inventory
Layers
Converted to
Year-End
Inventory
Inventory
Layers at Base
Year Cost
Year-End
Inventory at
Year-End Cost
Date
Cost
Index
Cost
Layers at Base
Year Cost
Index
Cost
12/31/2021
Base
12/31/2022
Base
%3D
2022
12/31/2023
Base
2022
%3D
2023
12/31/2024
Base
2022
2023
2024
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:
9780357109731
Author:
Hoffman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:
9780357109731
Author:
Hoffman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College