Methane and water react to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen, like this: CH4(g)+H,0(g) → CO(g)+3H,(g) Imagine 140. mmol of CHA and 140. mmol of H,0 are added to an empty flask, and then answer the following questions. O Zero. What is the rate of the forward reaction before any CH4 or H20 has been added to the flask? O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Zero. What is the rate of the forward reaction just after the CH4 and H20 has been added to the flask? O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Zero. O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction. What is the rate of the forward reaction at equilibrium? O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. O None. O Some, but less than 140. mmol. How much CH4 is in the flask at equilibrium? O 140. mmol. O More than 140. mmol.
Methane and water react to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen, like this: CH4(g)+H,0(g) → CO(g)+3H,(g) Imagine 140. mmol of CHA and 140. mmol of H,0 are added to an empty flask, and then answer the following questions. O Zero. What is the rate of the forward reaction before any CH4 or H20 has been added to the flask? O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Zero. What is the rate of the forward reaction just after the CH4 and H20 has been added to the flask? O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. O Zero. O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction. What is the rate of the forward reaction at equilibrium? O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. O None. O Some, but less than 140. mmol. How much CH4 is in the flask at equilibrium? O 140. mmol. O More than 140. mmol.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter12: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 96AE: Iodomethane (CH3I) is a commonly used reagent in organic chemistry. When used properly, this reagent...
Related questions
Question
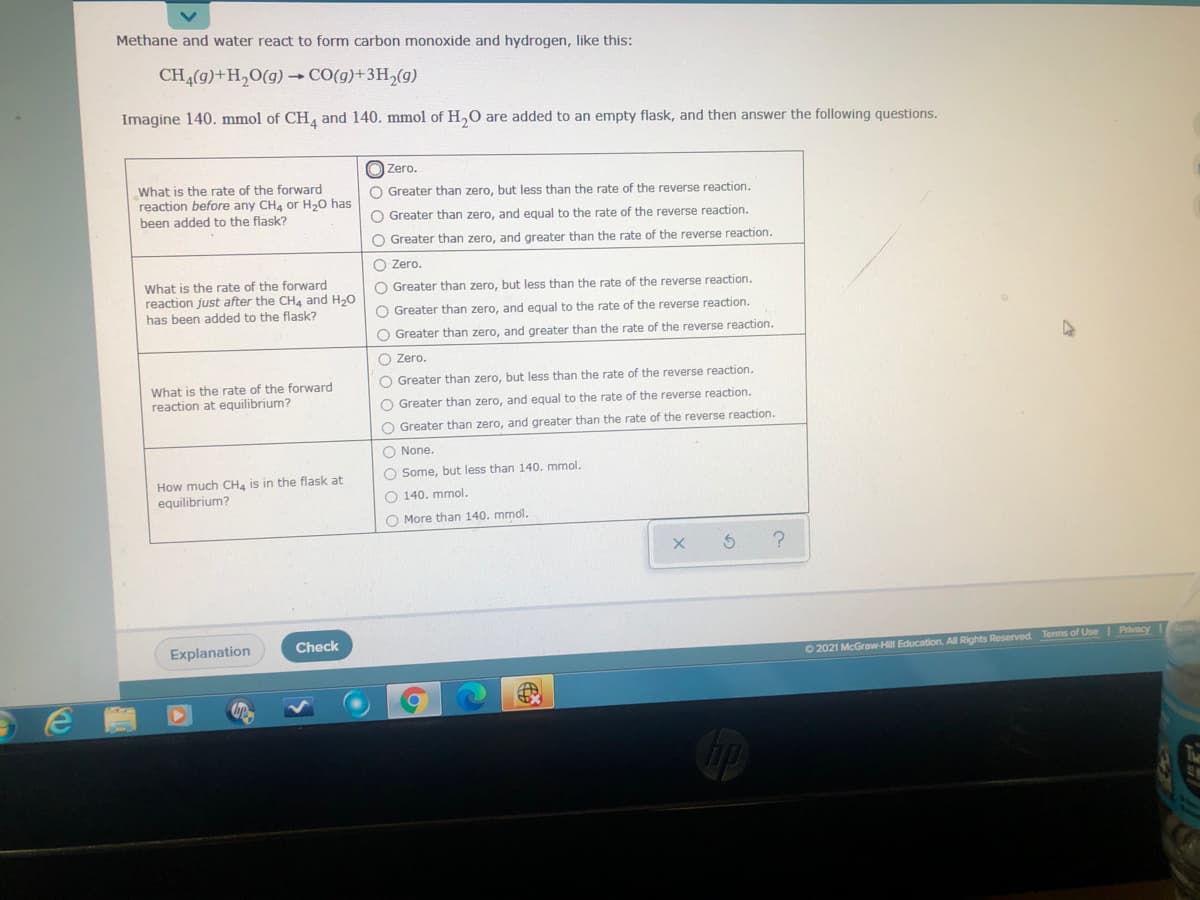
Transcribed Image Text:Methane and water react to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen, like this:
CH4(g)+H,0(g) CO(g)+3H2(g)
Imagine 140. mmol of CH and 140. mmol of H,0 are added to an empty flask, and then answer the following questions.
O Zero.
What is the rate of the forward
reaction before any CH4 or H20 has
been added to the flask?
Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Zero.
What is the rate of the forward
reaction just after the CH4 and H20
has been added to the flask?
O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Zero.
O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the reverse reaction.
What is the rate of the forward
reaction at equilibrium?
O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
O None.
O Some, but less than 140, mmol.
How much CH, is in the flask at
equilibrium?
O 140. mmol.
O More than 140. mmol.
Explanation
Check
Privacy
O 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax