Modify the RedBrand example so that all flows must be from plants to warehouses and from warehouses to customers. Disallow all other arcs. How much does this restriction cost RedBrand, relative to the original optimal shipping cost?
Modify the RedBrand example so that all flows must be from plants to warehouses and from warehouses to customers. Disallow all other arcs. How much does this restriction cost RedBrand, relative to the original optimal shipping cost?
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
Modify the RedBrand example so that all flows must be from plants to warehouses and from warehouses to customers. Disallow all other arcs. How much does this restriction cost RedBrand, relative to the original optimal shipping cost?
Transcribed Image Text:Inputs
Common arc capacity
200
Shrinkage factor
90%
Network formulation
Node balance constraints
%3D
Origin
Destination
Unit Cost
Flow
Arc Capacity
Plant constraints
1
2
200
Node
Plant net outflow
Plant capacity
1
180
<=
200
1
180
<=
200
1
4
200
300
<=
300
1
<=
200
3
100
<=
100
1
6
20
<=
200
1
7
20
200
Warehouse constraints
2
1
200
Node
Warehouse net outflow
Required
2
200
4
10
%3D
2
4
1
100
200
28
%3D
2
1
<=
200
8.
200
200
Customer constraints
2
7
15
<=
200
Node
Customer net inflow
Customer demand
1
0.4
<=
200
400
>=
400
3
2
8
<=
200
7
180
180
4
1
<=
200
0.5
280
200
10
200
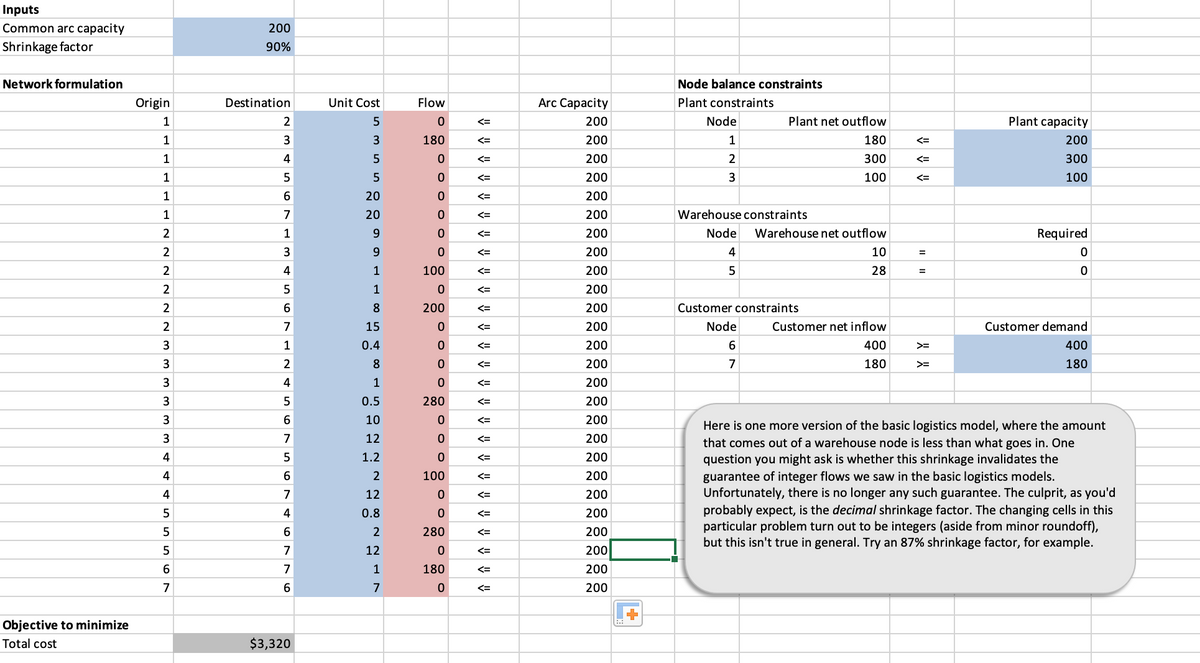
Here is one more version of the basic logistics model, where the amount
7
12
200
that comes out of a warehouse node is less than what goes in. One
question you might ask is whether this shrinkage invalidates the
guarantee of integer flows we saw in the basic logistics models.
Unfortunately, there is no longer any such guarantee. The culprit, as you'd
probably expect, is the decimal shrinkage factor. The changing cells in this
particular problem turn out to be integers (aside from minor roundoff),
but this isn't true in general. Try an 87% shrinkage factor, for example.
4
5
1.2
200
4
2
100
<=
200
7
12
<=
200
5
4
0.8
200
5
6
2
280
<=
200
5
7
12
<=
200
7
1
180
<=
200
7
6
7
200
Objective to minimize
Total cost
$3,320
O o O O o O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.